
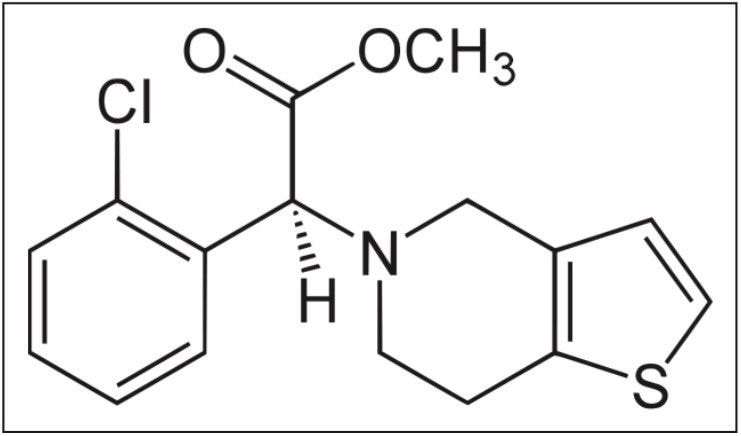
Clopidogrel is a thienopyridine derivative antiplatelet pro-drug used in the prevention of artherosclerotic events. This application note describes the development of a highly sensitive solid phase extraction and LC-MS/MS assay for the analysis of the pro-drug clopidogrel in human plasma with an assay sensitivity of 2.5 pg/mL.
The analysis of clopidogrel in human plasma was successfully completed using a high sensitivity method.
Clopidogrel is a thienopyridine derivative antiplatelet pro-drug used in the prevention of artherosclerotic events. Following oral administration, the dosed compound undergoes hepatic metabolism giving rise to the active thiol-metabolite and the inactive carboxylic acid metabolite. The inactive metabolite accounts for the majority of circulating clopidogrel-related material in humans, while the active metabolite and unchanged pro-drug are present at very low levels. The mechanism of action is derived from the binding of the active thiol-metabolite to cell receptor P2Y12, irreversibly inhibiting the platelet activation process.1
Due to the reactivity of the active thiol-metabolite coupled with the low levels of the unchanged pro-drug, most quantitative studies are based on the circulating levels of the inactive metabolite. This application note describes the development of a highly sensitive solid phase extraction and LC-MS/MS assay for the analysis of the pro-drug clopidogrel in human plasma with an assay sensitivity of 2.5 pg/mL.
Samples were prepared using an Oasis MCX μElution Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) Plate. 350 μL of plasma sample was mixed with 20 μL of internal standard (deuterated clopidogrel) solution and 350 uL of aqueous buffer. The samples were applied to the solid phase extraction plate that was previously conditioned with methanol and aqueous buffer. The sample was washed with an aqueous – methanol solution and eluted with 2 x 25 μL of 5% NH4OH in 60:40 IPA/ACN, then further diluted with 25 μL of water prior to injection. The analysis was performed on an ACQUITY UPLC H-Class chromatography system. A 10-μL aliquot of the sample was injected onto an ACQUITY UPLC C18 2.1 x 50 mm, 1.7 μm Column. The column was eluted under gradient conditions over 3 min at a flow rate of 600 μL/min. The column effluent was monitored using a Xevo TQD Mass Spectrometer operated in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) positive ion electrospray mode. The transition 322 → 212 was employed for the clopidogrel and the transition 326 → 216 was employed for the d4 internal standard.
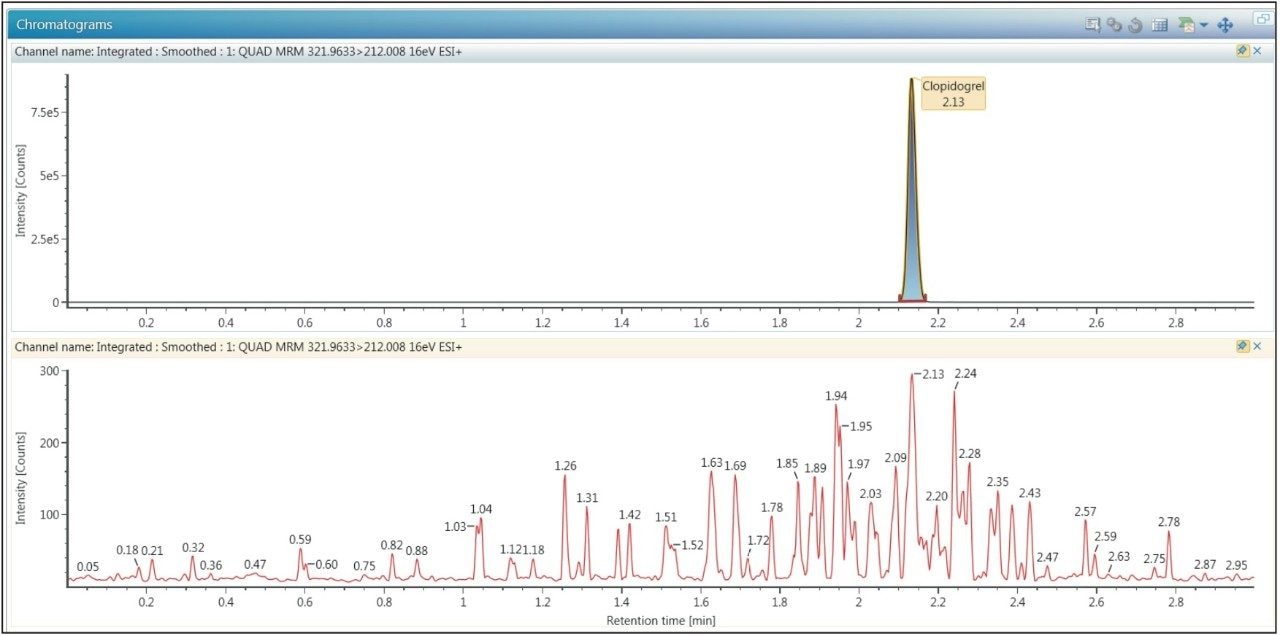
Clopidogrel eluted at a retention time of 2.10 min, as shown in Figure 2. The peak produced by the chromatography system was very symmetrical with a width at the base of 3 seconds. The sharpness of the peak and the symmetrical nature enabled efficient processing and peak integration. The three-minute analysis time allows for a total analysis time of five hours for a 96-well SPE plate, providing at least two plates to be processed per day. The data displayed in Figure 2 illustrates the injection of an extracted plasma blank injection immediately following analysis of the 500 pg/mL standard. This data revealed that there was no discernible carryover in the blank chromatogram. The extremely low carryover exhibited by the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System allowed the full sensitivity of the Xevo TQD Mass Spectrometer to be exploited.
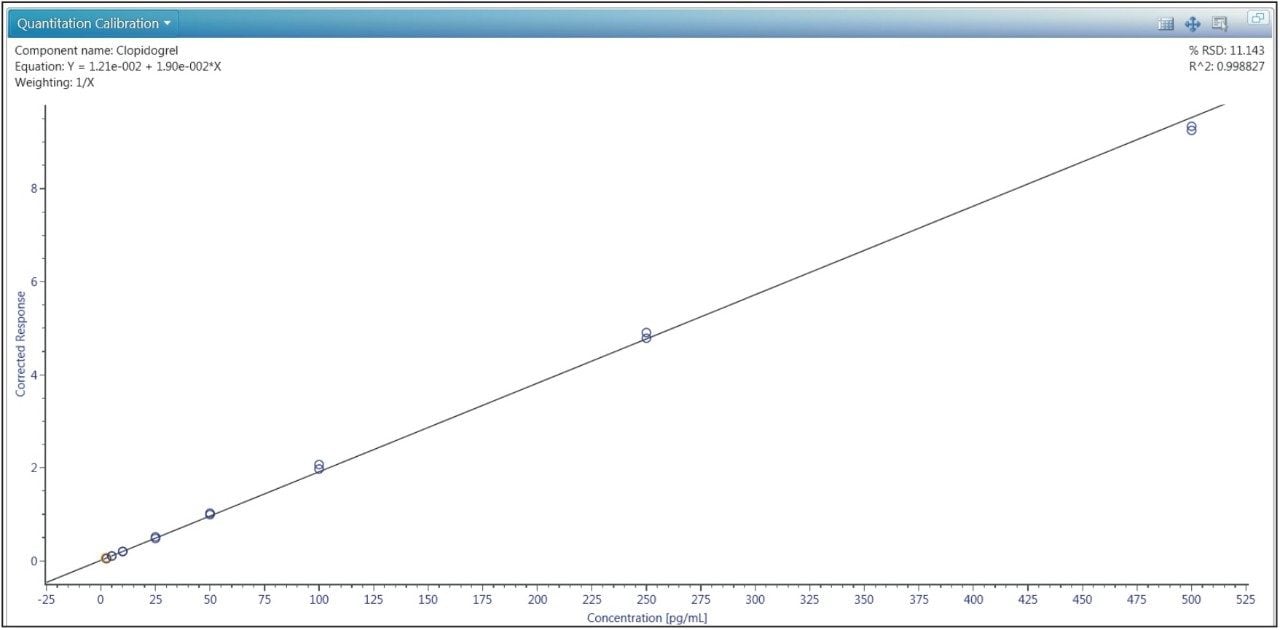
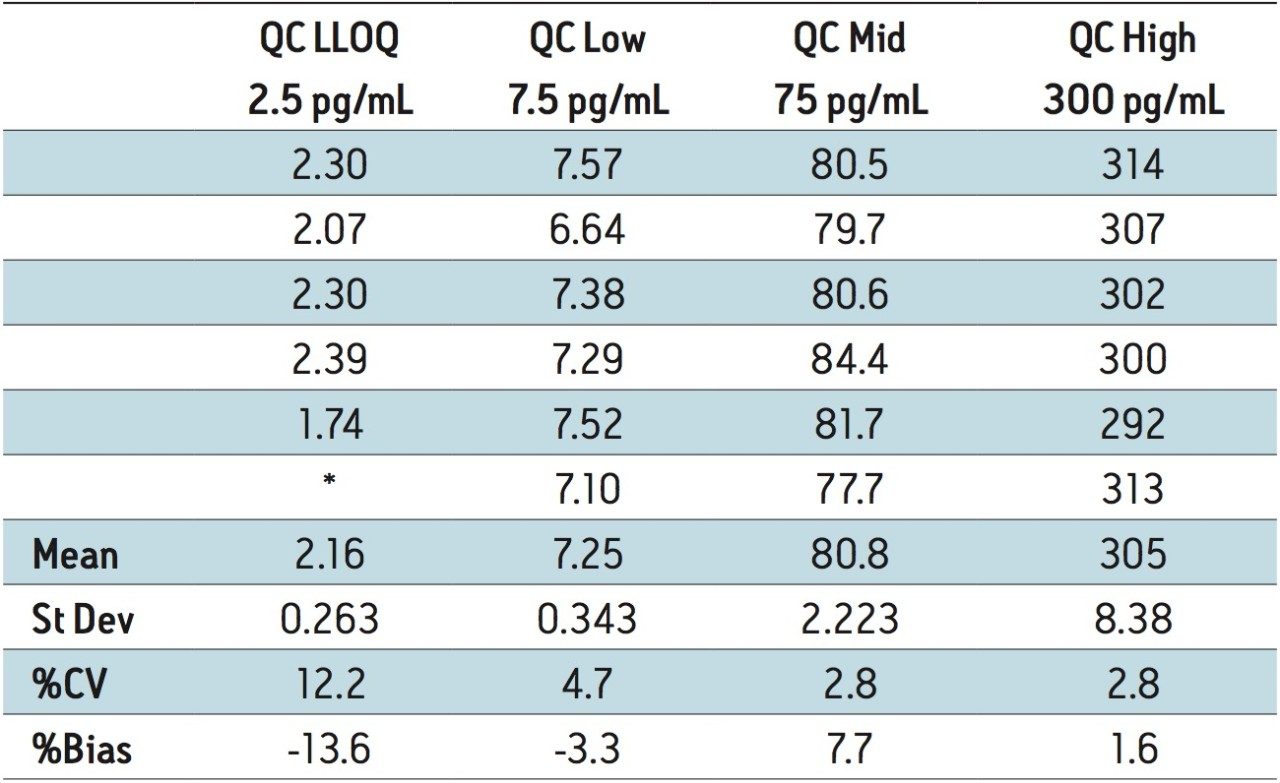
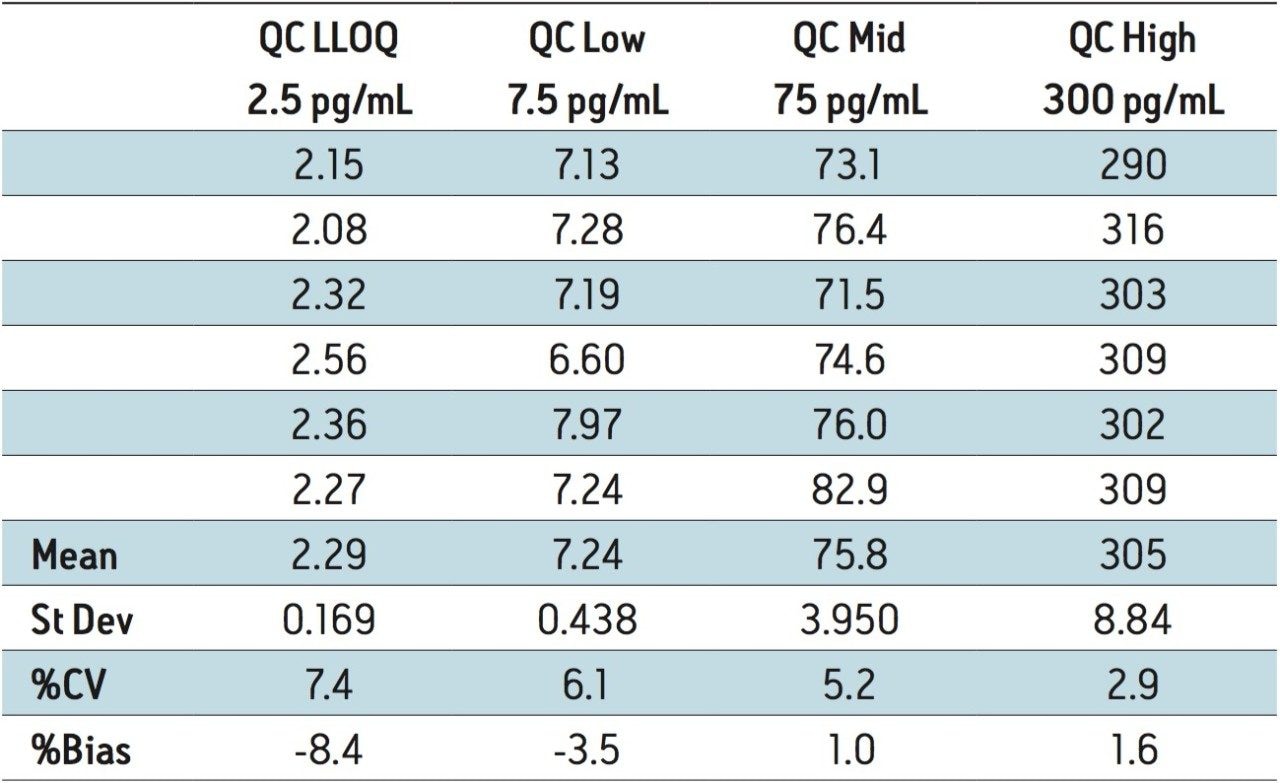
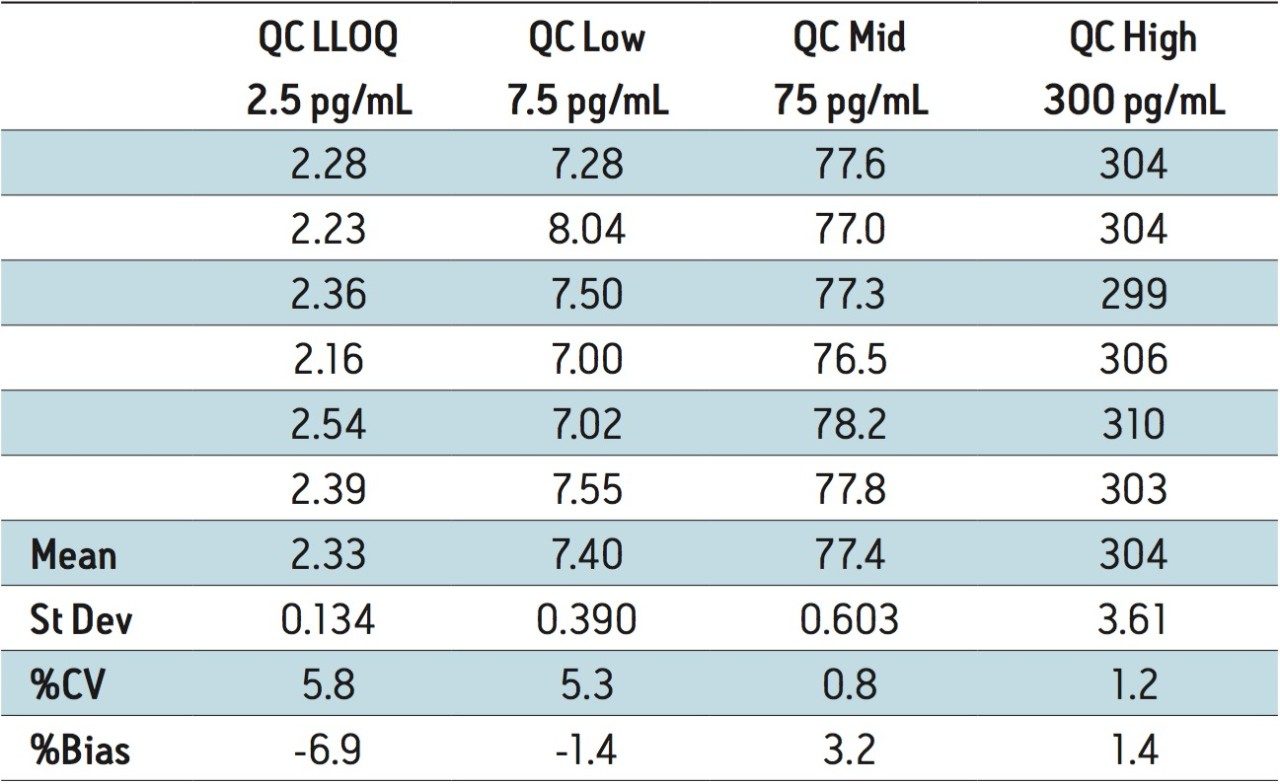
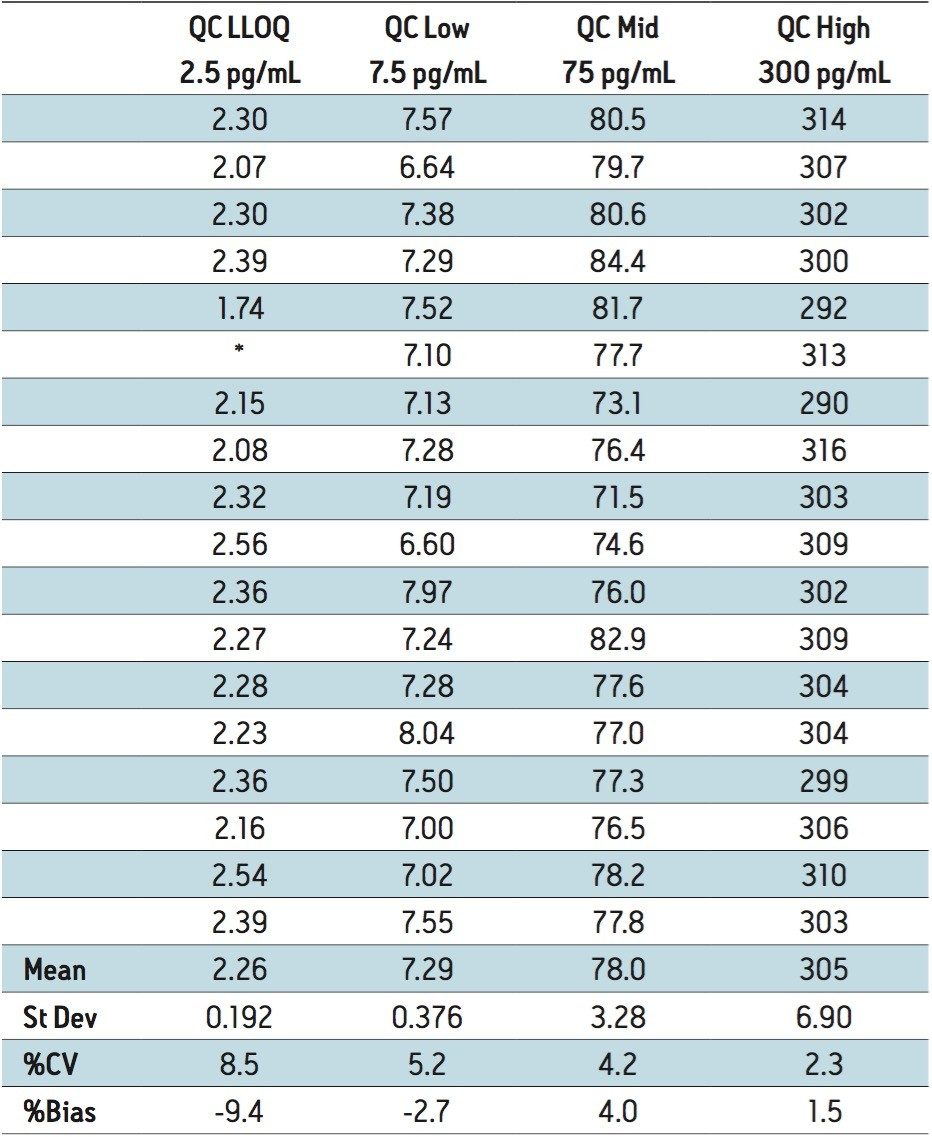
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for the assay was determined to be 2.5 pg/mL. The assay was validated with separate 96 well batches on three consecutive days over the range of 2.5 to 500.0 pg/mL. A typical calibration obtained for the assay is shown in Figure 3. The correlation coefficient ranged between 0.9988 and 0.9995 using a 1/x weighted linear regression. The intra-day precision and accuracy validation data is shown in Tables 1, 2, and 3. The validation data shows that the coefficient of variation ranged from 5.8% to 12.2% for the 2.5 pg/mL LLOQ with a bias between -6.9% and -13.6%. For the high QC (300 pg/mL), the coefficient of variation ranged from 1.2% to 2.9% with a bias between 1.4% and 1.6%. The inter-day precision and accuracy data is displayed in Table 4. The coefficient of variation was determined to be 8.5% for the 2.5 pg/mL LLOQ with a bias of -9.4. For the high QC (300 pg/mL), the coefficient of variation was determined to be 2.3% with a bias of 1.5%.
720004566, January 2013