
Major oil spills in the world's oceans have brought attention to the problem of PAH contamination, and to the challenges related to PAH analysis in food and environmental samples. QuEChERS sample preparation, followed by LC with fluorescence detection, provides fast screening analysis of PAHs.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are toxic compounds commonly found in nature, and are constituents of coal and petroleum. The US EPA has classified seven PAHs as probable human carcinogens. The US FDA has set the limit of concern (LOC) for benzo[a]pyrene, one of the most widely occurring and potent PAHs, at 35 ppb in shellfish. Major oil spills in the world’s oceans have brought attention to the problem of PAH contamination, and to the challenges related to PAH analysis in food and environmental samples. This application describes a QuEChERS-based sample preparation protocol for the determination of PAH in shrimp. QuEChERS methodology is quicker, easier, cheaper, safer than, and as rugged as prior methods of sample preparation. The methodology is now commonly used worldwide for sample preparation of fruits and vegetables prior to GC-MS or LC-MS for the determination of pesticide residues. This application note demonstrates that the QuEChERS extraction and cleanup technology can be applied to other types of analytes, and other types of sample matrices as an alternative to more cumbersome methods of sample preparation.
Place 15 g homogenized shrimp into a 50-mL centrifuge tube (p/n 186006814). Add 15 mL acetonitrile (ACN), and shake the tube vigorously for 1 min. Add contents of DisQuE pouch salts for AOAC QuEChERS (p/n 186006812), and shake vigorously for 1 min. Centrifuge for 3 min at 4000 rpm, and take a suitable portion for LC-FLR analysis.
|
System: |
ACQUITY UPLC H-Class with Large Volume Flow Cell (LVFC) |
|
Column: |
PAH 4.6 x 50 mm, 3 μm |
|
Column temp.: |
35.0 °C |
|
Mobile phase A: |
Water |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Methanol |
|
Mobile phase C: |
Acetonitrile |
|
Flow rate: |
2.0 mL/minute |
|
Gradient: |
30% A, 70% B initial, linear gradient to 70% B, 30% C at 2.25 min, to 100% C at 3.5 min, back to 30% A, 70% B at 3.6 min, and re-equilibrate. |
|
Injection volume: |
10 μL |
|
Detection: |
Fluorescence (FLR) using programmed wavelength changes |
|
Vials: |
LCGC Certified Vials (p/n 186000307C) |
|
Time |
Excitation (nm) |
Emission (nm) |
|---|---|---|
|
0.00 |
276 |
331 |
|
1.00 |
295 |
315 |
|
1.33 |
248 |
380 |
|
1.62 |
246 |
488 |
|
1.97 |
275 |
380 |
|
2.40 |
300 |
422 |
|
2.70 |
364 |
408 |
|
2.89 |
298 |
410 |
|
3.17 |
305 |
500 |
Figure 1 shows a LC-FLR chromatogram obtained from the analysis of a shrimp sample spiked at 20 ng/g (ppb) of PAH compounds. PAH recovery was measured at 20 and 200 ppb (n = 5 for each level). Recovery data, shown in Table 1, generally ranged from 83% to 99%. Recovery was calculated by comparing the peak area for samples spiked prior to QuEChERS extraction (pre-spiked samples) with the peak area for samples spiked after QuEChERS extraction (post-spiked samples).
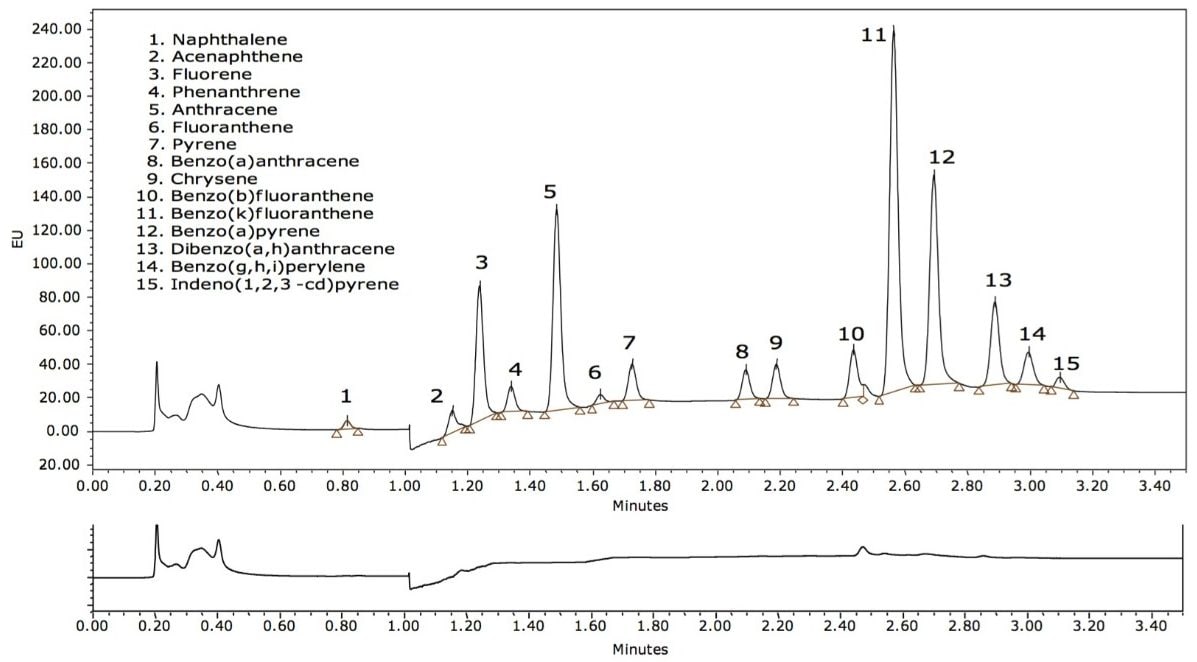
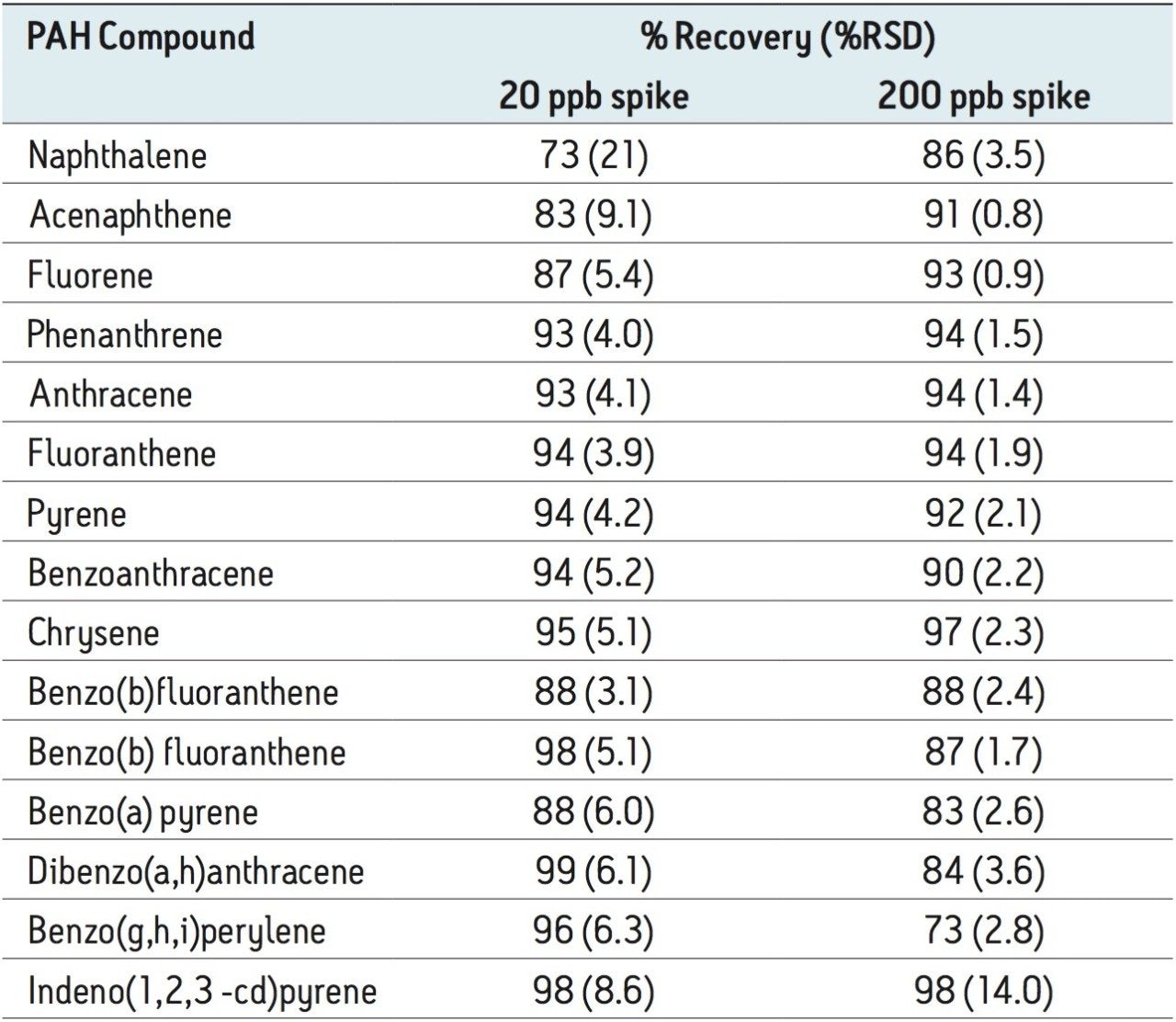
Recently, two application notes were published that demonstrated the utility of QuEChERS sample preparation applied to the determination of PAH residues in seafood, using LC with FLR detection (LC-FLR),1 and tandem GC-MS after a further sample cleanup of the QuEChERS extract.2 The results showed very good accuracy and precision. In this follow-up application, the DisQuE pouch format was used to prepare the homogenized shrimp samples to simplify the addition of the QuEChERS salts. Results were equivalent to those results reported in reference 1.
If GC-MS analysis is preferred, the cleanup procedure presented in reference 2 is recommended.
720004454, September 2012