For forensic toxicology use only.
In this application note we describe the development of a rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of 10 benzodiazepines. Limits of detection of 0.2 μg/L or better were achieved when just 25 μL plasma was used.
Benzodiazepines are the most widely prescribed psychoactive drugs in the world for the symptomatic treatment of anxiety and sleep disorders. However, misuse of these compounds has been reported and they are frequently encountered in postmortem blood analysis (suicide or accidental death).
Here we describe the development of a rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of 10 benzodiazepines. Limits of detection of 0.2 μg/L or better were achieved when just 25 μL plasma was used.
In addition, we present the application of this method to the analysis of benzodiazepines in Calliphora vicina larvae. Insects and their larvae are commonly used in the estimation of postmortem interval. Furthermore, they may serve as a reliable alternate source for toxicological analysis in the absence of suitable tissues and fluids that are normally taken for this purpose.
|
LC system: |
Waters Alliance 2690 |
|
|
Column: |
Conventional Phenyl Column (2.1 x 150 mm, 5 μm) |
|
|
Mobile phase: |
A = 10:10:80 acetonitrile:80 acetonitrile: methanol:20 mM ammonium acetate B = 95:5 acetonitrile:20 mM ammonium acetate |
|
|
Flow rate: |
0.25 mL/min |
|
|
Injection volume: |
10 μL |
|
Mass spectrometer: |
Quattro Ultima |
|
Ionisation Mode: |
ES positive ion |
|
Capillary voltage: |
3 kV |
|
MS/MS: |
MRM analysis (Table 1). Collision gas Argon at 2.5 x 10-3 mbar |
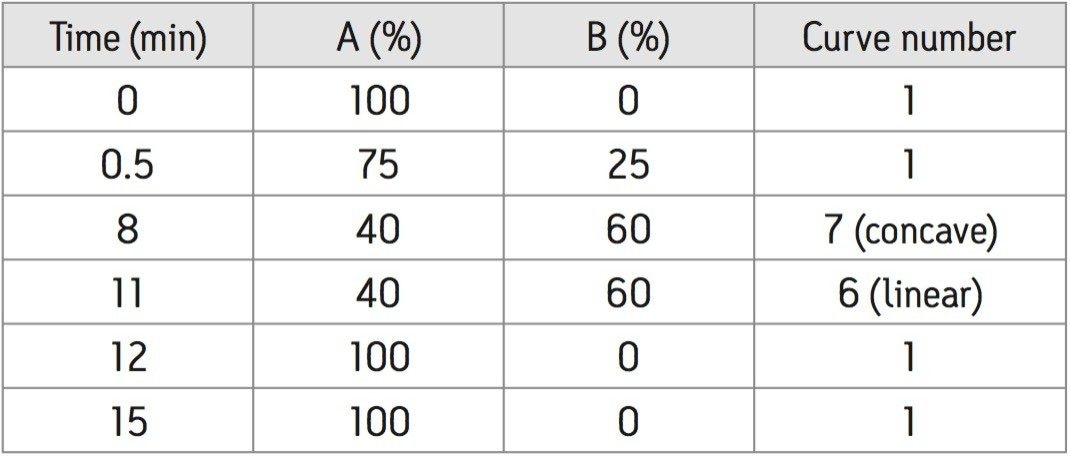
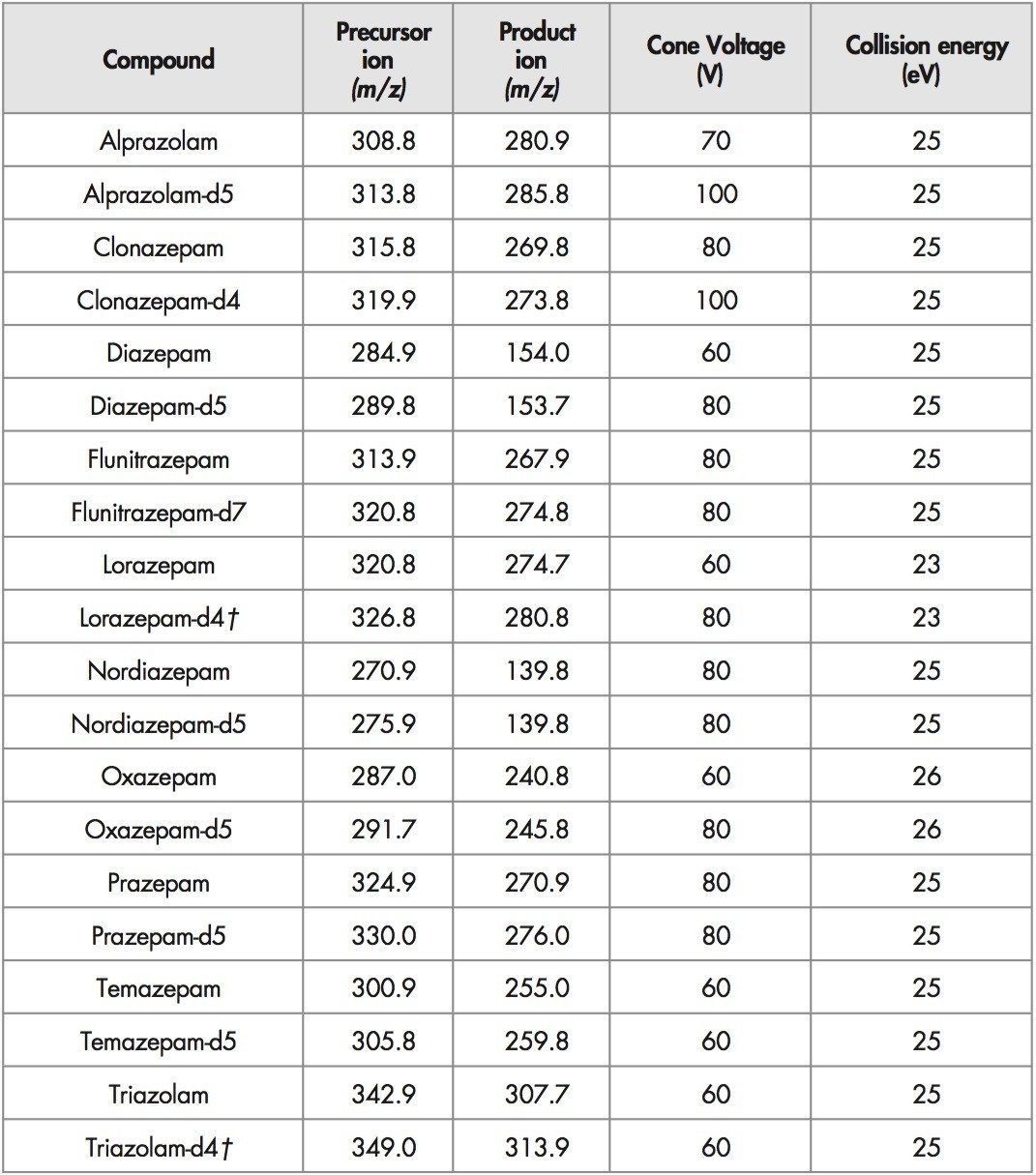
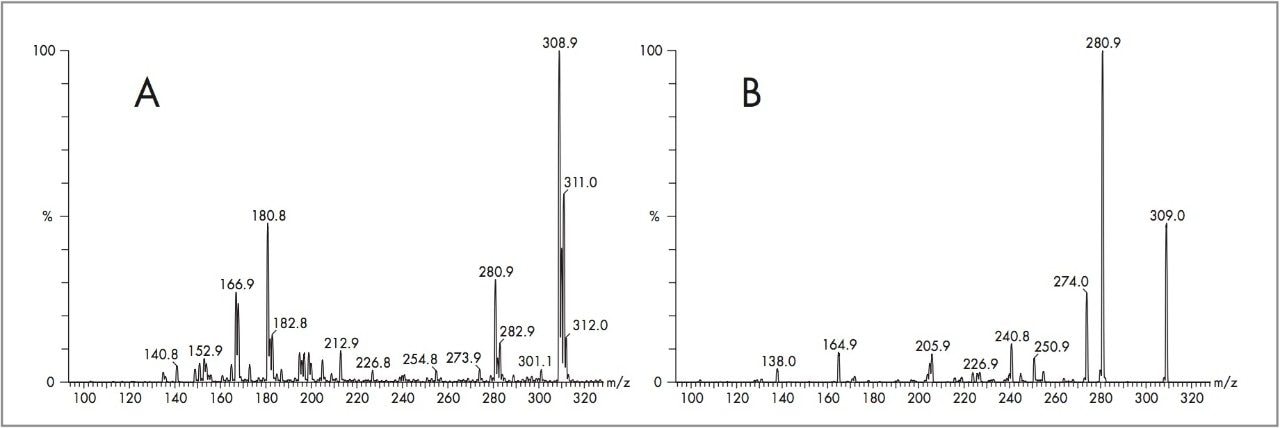
Figure 1 shows the MS and MS/MS spectra for alprazolam. Table 1 summarizes the MRM transitions and conditions used for this and several other benzodiazepines (and their respective deuterated analogues). The latter were used as internal standards for quantification purposes.
A series of calibrators (1, 10, 40, 100, 200, 400 and 800 μg/L) were prepared by adding the benzodiazepines to drug-free plasma. Plasma samples were isolated from the matrix using a simple acetonitrile clean-up procedure (which also incorporates the addition of the internal standards).
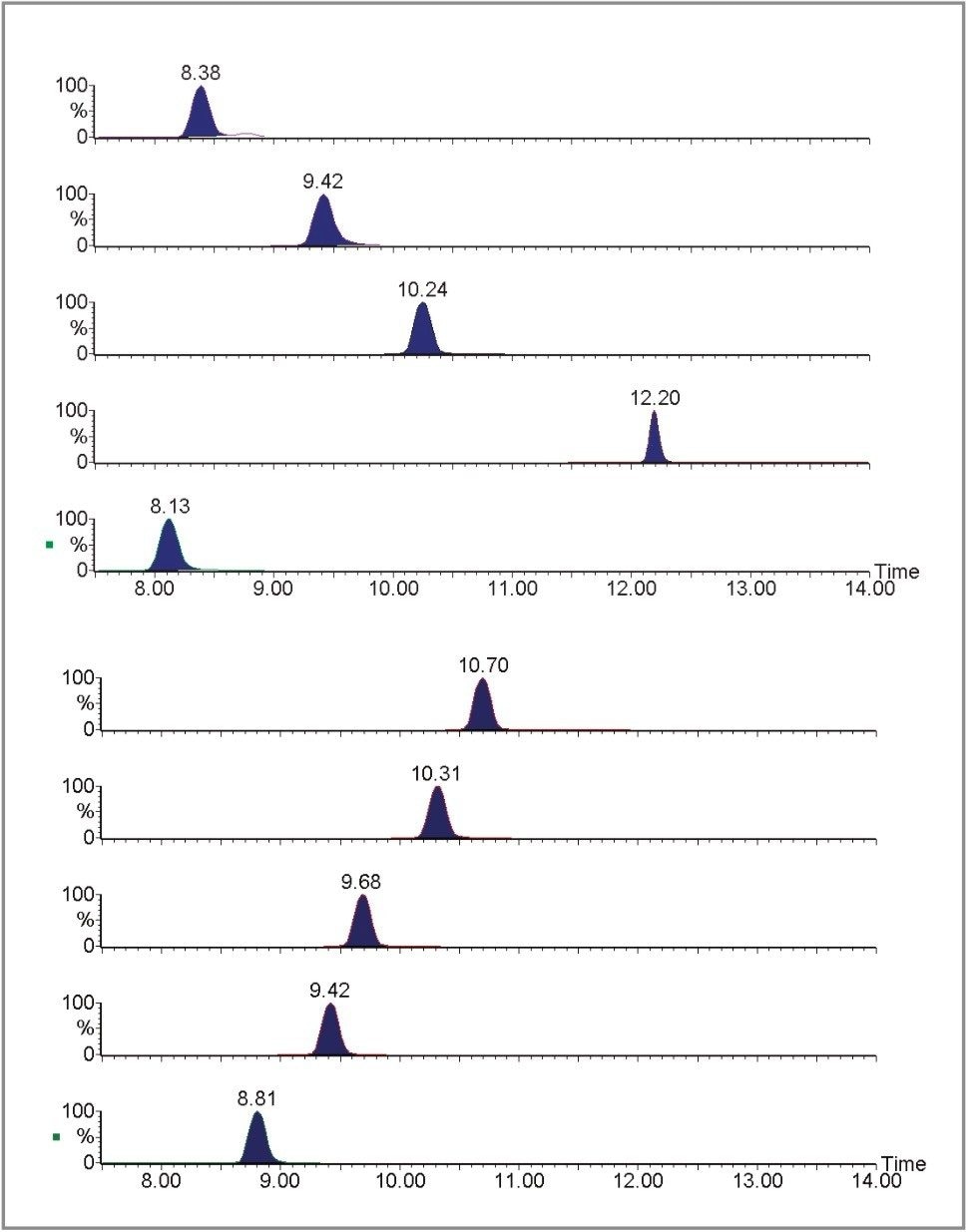
Figure 2 shows the MRM chromatograms of the benzodiazepines obtained with a 10 μL injection of the 10 μg/L plasma calibrator. Quantification was performed by integration of the area under the specific MRM chromatograms. Figure 3 shows a typical standard curve for diazepam in plasma.
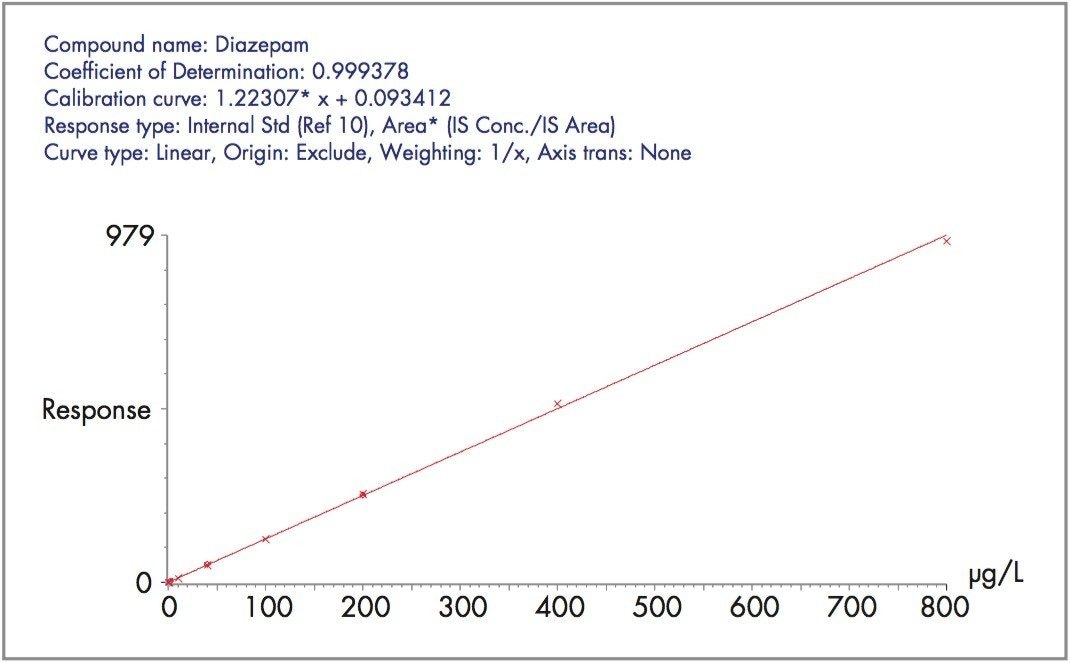
Responses were linear, in all cases, over the range investigated (Coefficient of Determination >0.99).
For all compounds, LOD’s of 0.2 μg/L (or better) and LOQ’s of 1 μg/L (or better) were achieved. The precision of the assay was assessed by performing replicate (n=5) extractions of plasma samples containing low, medium and high concentrations of the benzodiazepines (i.e. 2, 40, and 200 μg/L respectively). Coefficients of variation (%CV’s) were found to be highly satisfactory (<15%).
The developed LC-MS/MS was subsequently applied to the analysis of Calliphora vicina larvae in a study to assess the feasibility of using insects and their larvae as alternate specimens in the absence of any suitable human specimens for toxicological analysis.
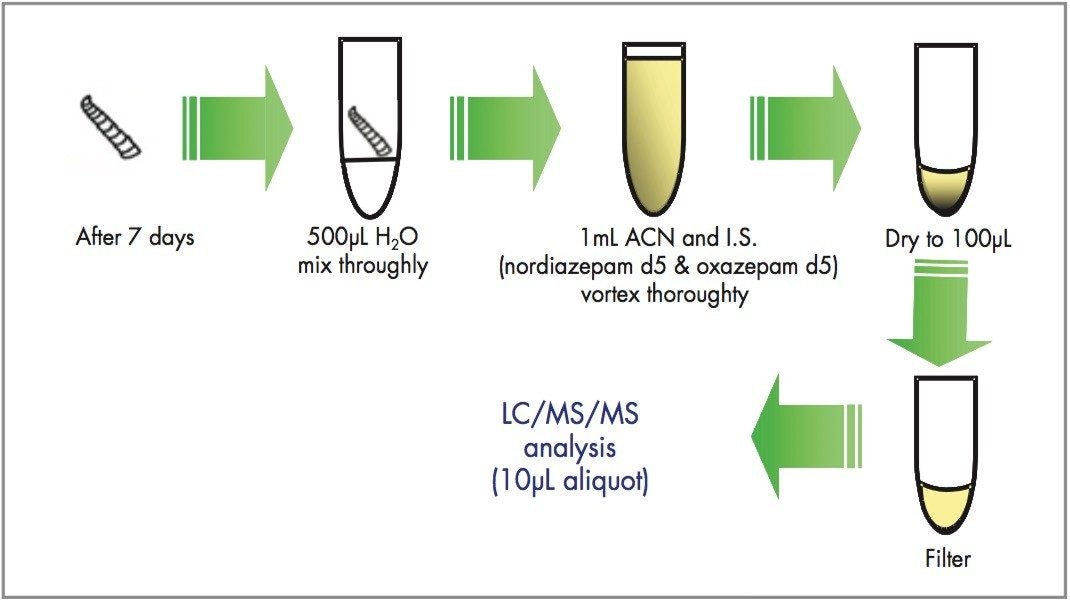
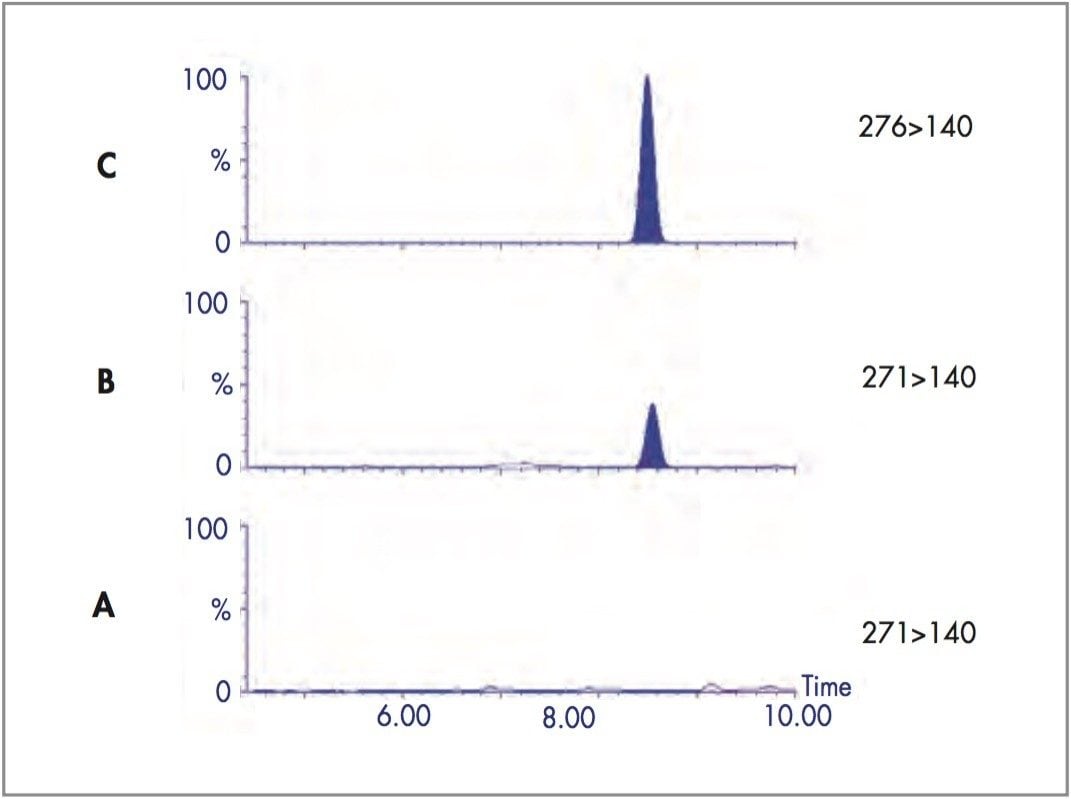
Larvae were reared on artificial foodstuff (beefheart) spiked with a range of concentrations of nordiazepam (0, 0.5, 1 and 2 μg/g). Post-feeding larvae were harvested (after 7 days) for analysis of drug content by LC-MS/MS. Figure 4 outlines the initial sample preparation method used for these specimens. All control larvae reared on spiked foodstuff were positive for nordiazepam and the metabolite oxazepam. All control samples were negative. Figure 5 shows the MRM chromatograms obtained following LC-MS/MS analysis of a control larva and a larva positive for nordiazepam. The method was sufficiently sensitive to measure benzodiazepines in single larvae whereas previous analytical techniques e.g. GC-MS, RIA, TLC have required pools i.e. typically 20 larvae.
We have developed a simple, rapid method that allows the simultaneous quantification of 10 benzodiazepines in plasma a single chromatographic run. LOD’s were better than 0.2 μg/L when only 25 μL plasma was used. The method involves a simple protein precipitation step with acetonitrile followed by LC-MS/MS analysis.
The method was subsequently applied to the analysis of Calliphora vicina larvae in a study designed to assess the feasibility of using insects as alternate specimens in the absence of any suitable human tissues.
The sensitivity was such that it was possible to detect benzodiazepines in single larvae whereas previous methods have required pools.
720001542, March 2007