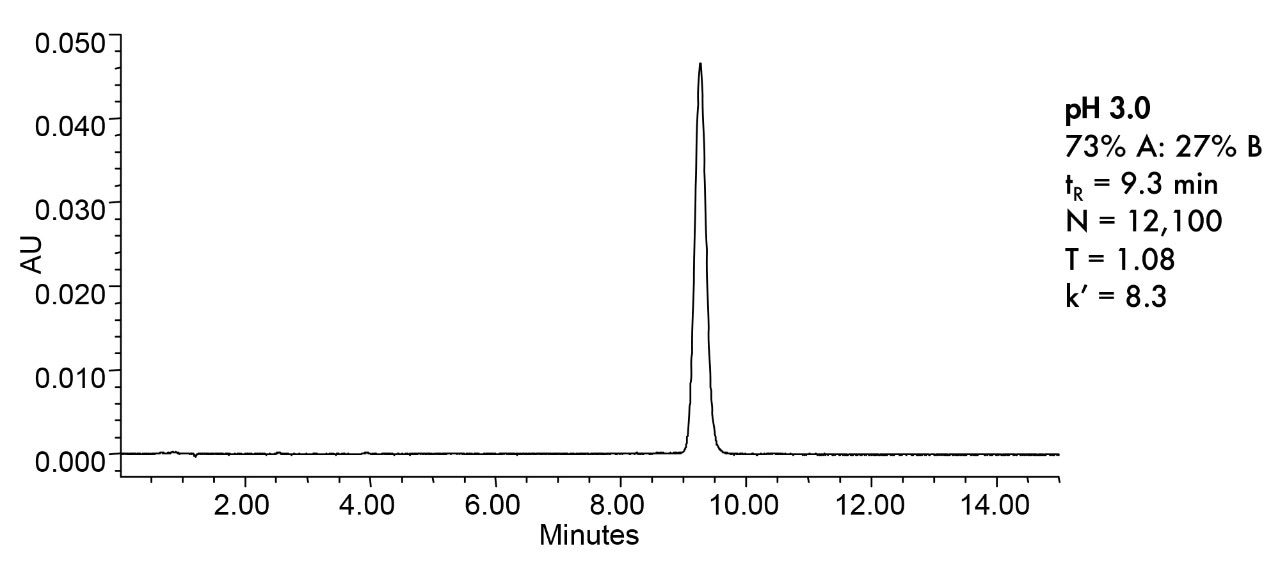
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
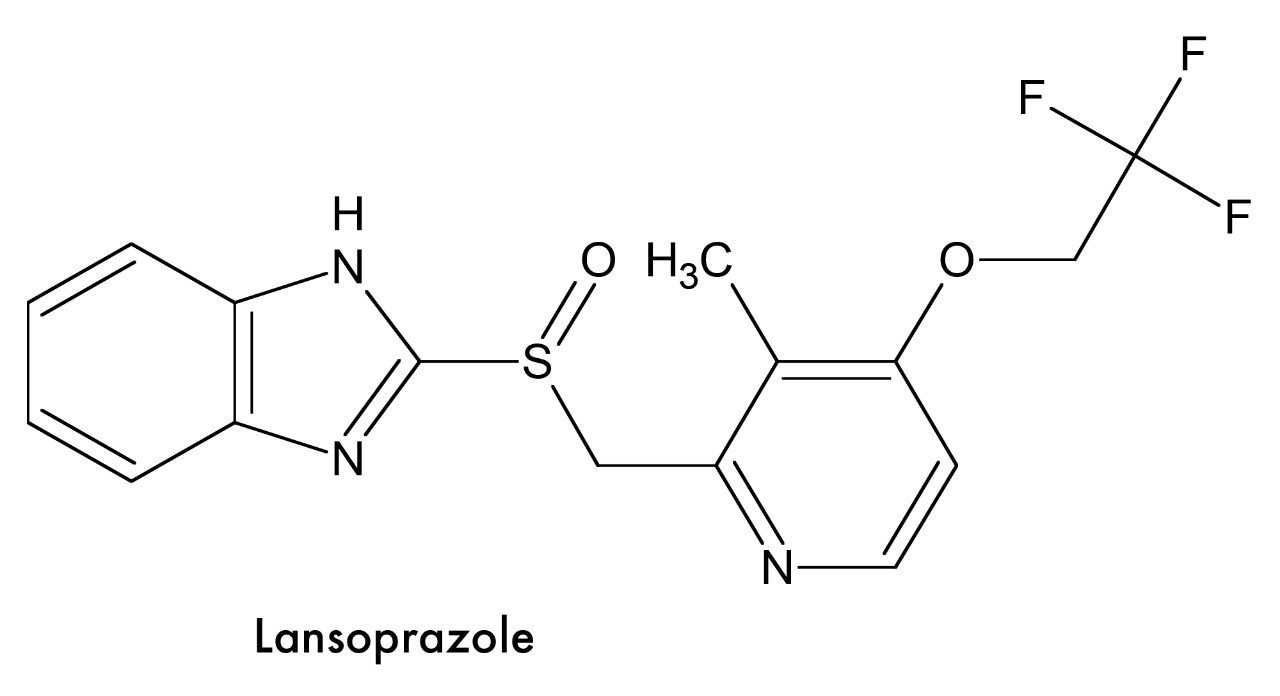
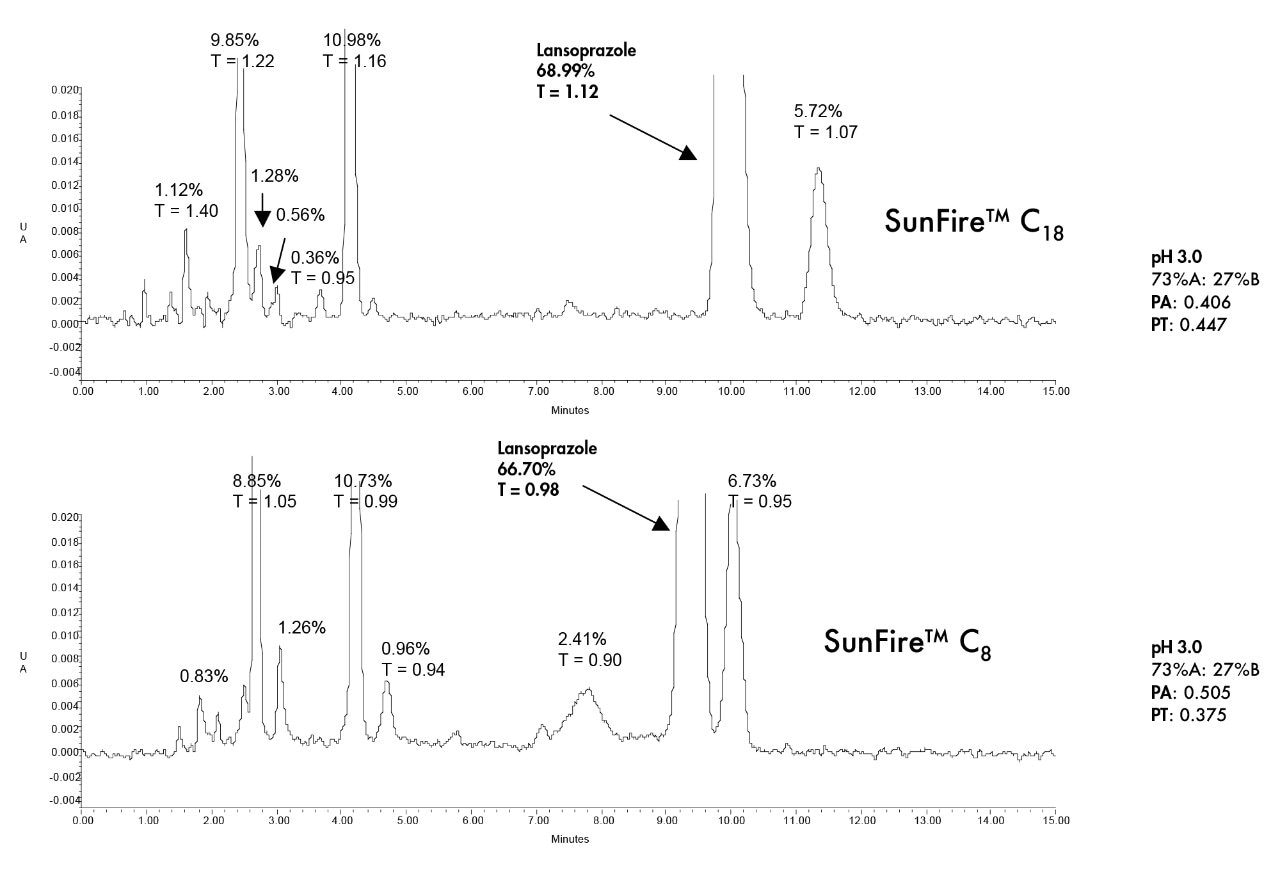
This application brief highlights the isocratic separation and degradation of lansoprazole.
Lansoprazole is used to treat ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and conditions where the stomach produces too much acid.
|
Column: |
SunFire C18 4.6 x 150 mm, 5.0 μm (p/n: 186002559) |
|
Mobile phase A: |
20 mM HCOO-NH4 +, pH 3.0 |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Acetonitrile |
|
Isocratic: |
as indicated |
|
Flow rate: |
1.4 mL/min |
|
Injection volume: |
2 μL |
|
Sample Diluent: |
75:25 H2O:ACN |
|
Sample concentration: |
350 μg/mL |
|
Temperature: |
30 °C |
|
Detection: |
UV @ 254 nm |
|
Sampling rate: |
10 pts/sec |
|
Time Constant: |
0.1 |
|
Instrument: |
Waters Alliance HT 2795, with 2996 |
|
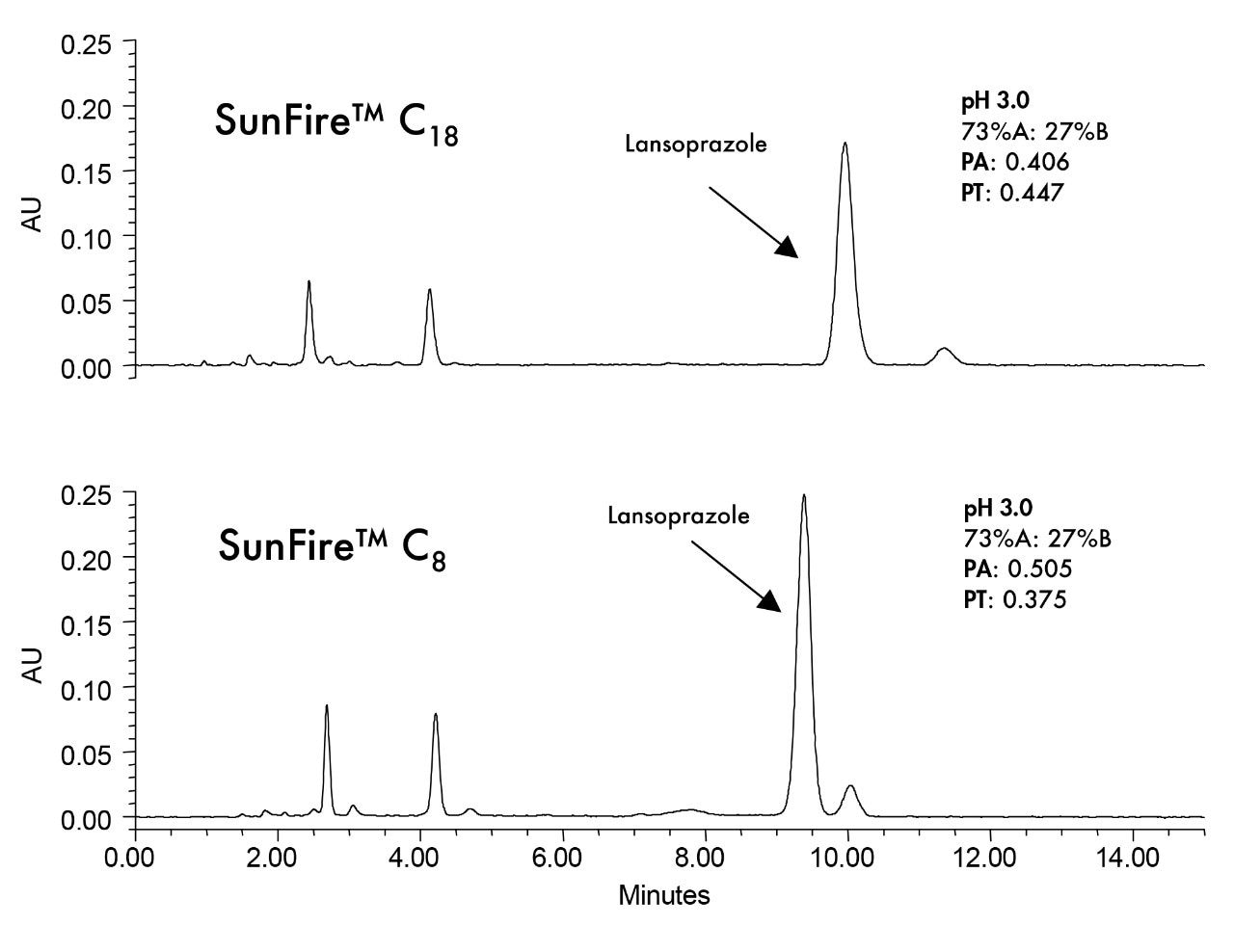
Column: |
SunFire C18 4.6 x 150 mm, 5.0 μm (p/n: 186002559) SunFire C8 4.6 x 150 mm, 5.0 μm (p/n: 186002737) |
|
Mobile phase A: |
20 mM HCOO-NH4 +, pH 3.0 |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Acetonitrile |
|
Isocratic: |
as indicated |
|
Flow rate: |
1.4 mL/min |
|
Injection volume: |
5 μL |
|
Sample Diluent: |
50:50 H2O:ACN |
|
Sample concentration: |
2.63 mg/mL |
|
Temperature: |
30 °C |
|
Detection: |
UV @ 254 nm |
|
Sampling rate: |
5 pts/sec |
|
Time Constant: |
1 |
|
Instrument: |
Waters Alliance HT 2795, with 2996 |
Temperature: ambient
50 mg of Lansoprazole + 5 mL of 0.4N HCl stirred for ~ 30 seconds
Stop reaction by add 0.9 mL of 0.4N NaOH, then dilute with 1.9 mL ACN
Lansoprazole degraded ~ 32%
WA41893, March 2005