Robustness in Regulated Bioanalysis: A 30,000 Injection Study of Naltrexone in Human Plasma using the Xevo™ TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer
Henry Foddy1, David Farrell2, Sally Hannam2, Peter Hancock1, Nikunj Tanna3, Robert S. Plumb3
1Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, United Kingdom
2Alderley Analytical, Macclesfield, United Kingdom
3Waters Corporation, Milford, United States
Published on November 24, 2025
Abstract
The study presents a 30,000-injection sequence for the quantification of Naltrexone and its primary active metabolite, 6β-Naltrexol, in a human plasma matrix. Throughout the analytical workflow, representative of a routine, high-throughput bioanalytical operation - key performance indicators were monitored to assess system performance over time. These included signal stability, accuracy, precision, chromatographic integrity, and carryover. The Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer, equipped with the new StepWave™ XR Ion Guide, maintained consistent sensitivity and quantitative integrity over more than 30,000 injections, even at sub-ng/mL concentrations, demonstrating the capability to deliver precise, reliable measurements under demanding analytical conditions. The stable, downtime-free performance of the instrument across the full injection sequence presents the Xevo TQ Absolute XR as a robust solution for high-throughput bioanalysis, supporting greater productivity, sample throughput, and cost efficiency for bioanalytical laboratories.
Benefits
- Robust analytical performance across more than 30,000 matrix injections and over 21 mL of human plasma are injected into the system, with no instrument downtime, demonstrating suitability for high-throughput discovery and regulated bioanalysis applications
- Reliable quantification at sub-ng/mL levels in complex human plasma matrix, with calculated bias and precision fully compliant with FDA M10 criteria across the entire study
- Streamlined data review in waters_connect™ for Quantitation Software, enhancing analyst efficiency and overall workflow productivity
Introduction
Quantitative bioanalysis is a cornerstone in the understanding of drug exposure, efficacy, and safety, throughout both drug development and post-market monitoring. Central to these studies is the need for analytical platforms capable of accurately quantifying low-level analyte concentrations, often at sub-ng/mL, in complex biological matrices such as plasma or serum.
Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) has become the established benchmark for such analyses, providing high selectivity, sensitivity, and throughput for targeted quantification. As bioanalytical laboratories manage both an increasing volume and a broader spectrum of sample assays, instrumentation must be capable of withstanding diverse workflows while maintaining reliable analytical performance.
For such laboratories, operating under high-throughput conditions with long-term assay stability and uptime is essential for sustained productivity. However, these workflows often involve the quantification of trace-level analytes in complex biological matrices where matrix effects, ion suppression, and signal variability present significant analytical challenges. Achieving reliable performance under these conditions, therefore, requires instrumentation that maintains performance for a given method, over prolonged and demanding analytical workflows.

In practice, large-scale analytical batches comprising thousands of injections further amplify these demands, as gradual contamination of the MS ion path can compromise reproducibility and increase maintenance frequency. Such interruptions can slow the generation of critical data, delaying scientific insight, decision-making, and overall project advancement across bioanalytical workflows. Whether in discovery, development, or regulated studies, increased downtime and maintenance reduce efficiency, elevate operational costs, and limit the throughput of essential analyses.
Maintaining instrument robustness is therefore essential to sustaining productivity, accelerating data delivery, and supporting cost-effective, confident decision-making while maintaining trace-level analytical performance.
The StepWave XR Ion Guide, a novel slotted bandpass ion guide within the Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer, effectively mitigates MS1 quadrupole contamination by preventing unwanted high mass ion transmission. Filtering out high m/z ions from biological matrices prevents quadrupole charging and associated losses in sensitivity, which are observed when these ions accumulate on the MS1 quadrupole rods.
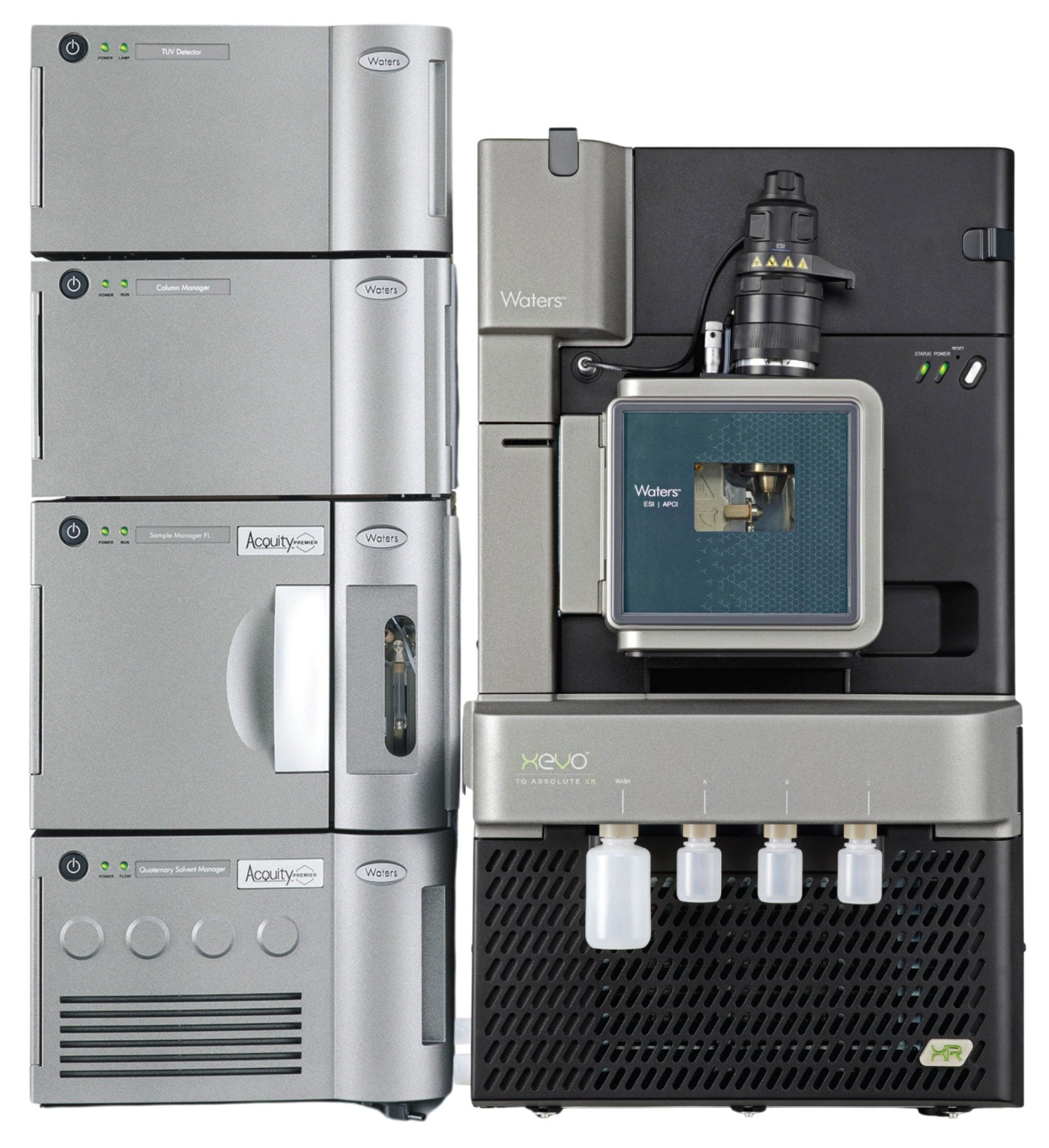
In this study, the long-term robustness and quantitative analytical performance of the Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer (Figure 1) was evaluated through the determination of Naltrexone and its primary active metabolite, 6β-Naltrexol, in human plasma. Naltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist widely used in the management of alcohol and opioid dependence, and its analysis typically requires highly sensitive and selective analytical methods due to low systemic concentrations.1
Experimental
Sample Preparation
Standards of Naltrexone and 6β-Naltrexol were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Gillingham, UK), supplied as 1.0 mg/mL certified solutions in methanol. Internal standards of Naltrexone-d3 and 6β-Naltrexol-d3 were also purchased from Sigma Aldrich, as was the formic acid used throughout the analysis. An in-house supply of 18.2Ω ultrapure water was used as the mobile phase, while methanol was purchased from Fisher Scientific. A calibration line was constructed for Naltrexone and 6β-Naltrexol in human plasma over the range of 0.2–100 ng/mL, quality control (QC) samples were also constructed in human plasma at concentrations of 0.2, 0.6, 40.0, 80.0, and 100.0 ng/mL.
A high-throughput protein precipitation procedure - adapted for robustness evaluation rather than routine analysis - was used to prepare samples in 96-well plates (Figure 2).
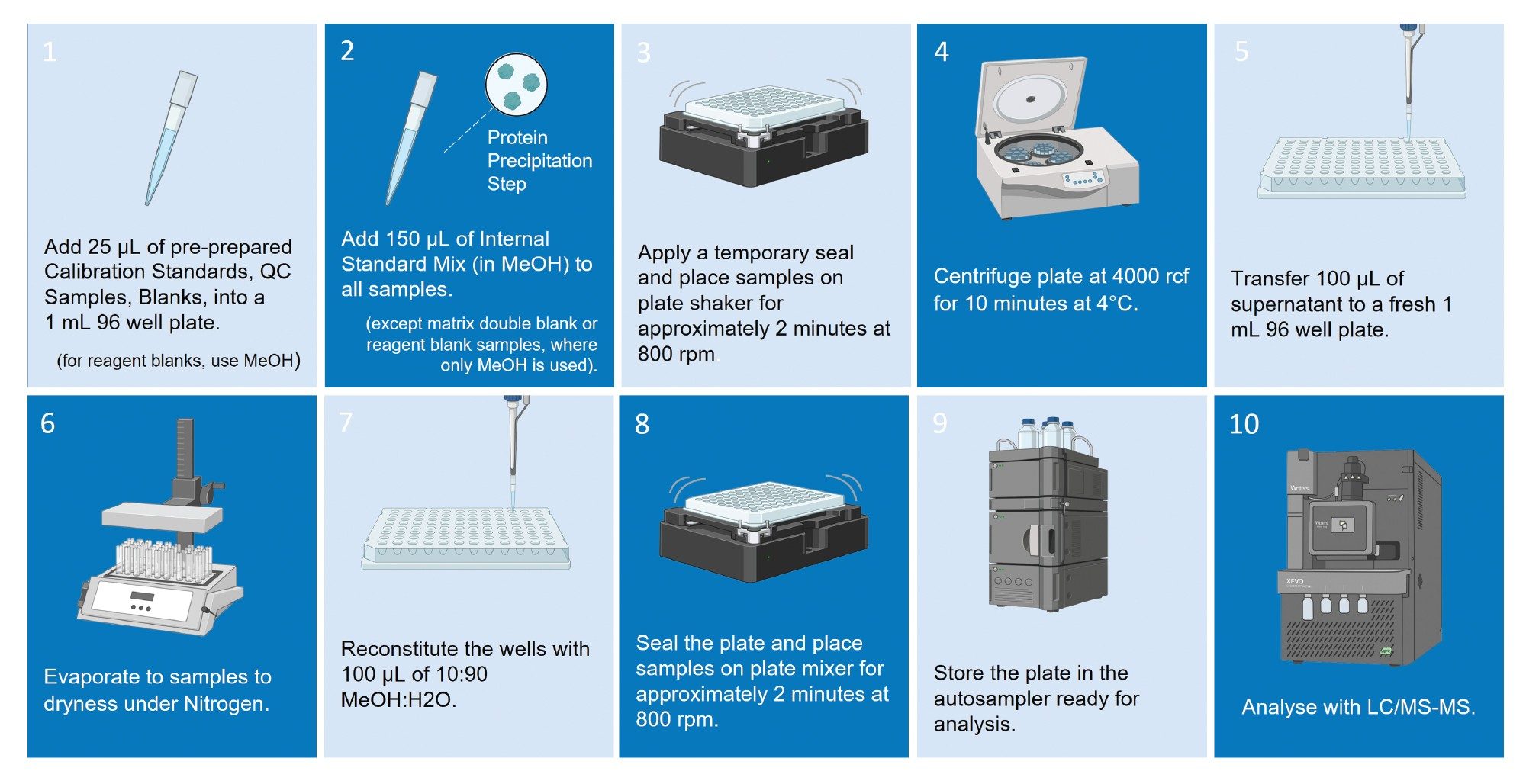
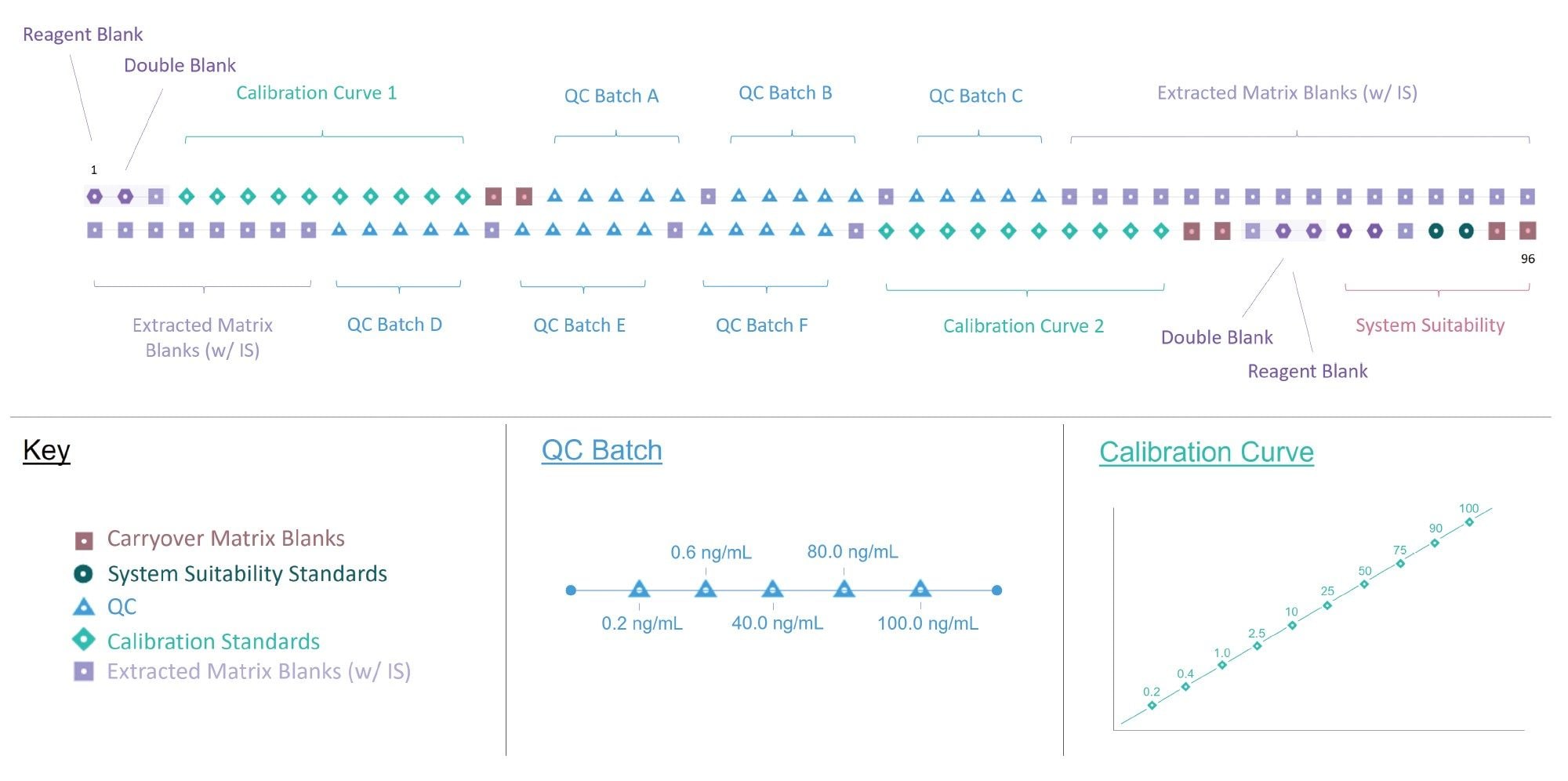
A 96-well plate was prepared as shown in Figure 3, consisting of a bracketed calibration sequence from 0.2–100 ng/mL, QC batch replicates (0.2, 0.6, 40.0, 80.0, and 100.0 ng/mL), matrix extracted blanks, system suitability injections, reagent blanks, double blanks, and carryover matrix blanks. Methanol was used to prepare the two reagent blanks, with the other 94 samples in the plate prepared using matrix.
Throughout the study, a total of 64 sample plates were prepared, with each sample-well injected sequentially, and each plate analyzed five consecutive times before being replaced by a freshly prepared plate, giving a total of 30,720 injections over the duration of the study.
To simulate the typical protocol of a bioanalytical lab, the cone assembly of the sample cone and cone gas nozzle were cleaned at the start of each week of analysis, which was performed without breaking the instrument vacuum. A reversed-phase column was used for this analysis, using a column temperature of 60 °C. This limited the column lifetime, and therefore the column was replaced when appropriate.
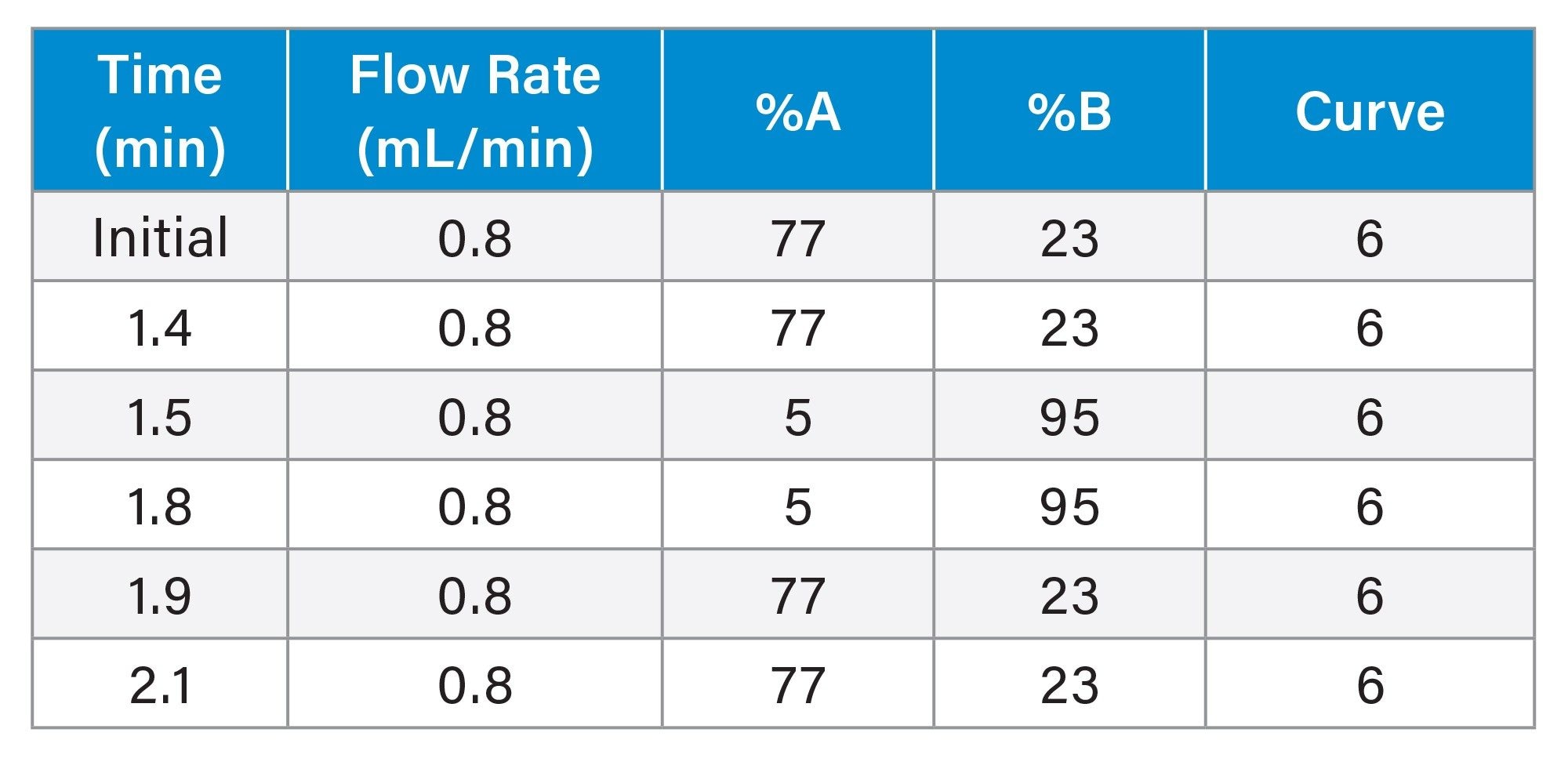
LC Conditions
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY Premier System with Binary Solvent Manager and Flow-Through Needle |
|
Sample temperature: |
10 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
5 μL |
|
Flow rate: |
0.8 mL/min |
|
Run time: |
2.1 min |
|
Mobile phase A: |
0.1% Formic acid in Water |
|
Mobile phase B: |
0.1% Formic acid in Methanol |
Gradient Table
MS Conditions
|
MS system: |
Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer |
|
Ionization: |
Positive Electrospray (ESI+) |
|
Capillary voltage: |
0.6 kV |
|
Desolvation temperature: |
600 °C |
|
Desolvation gas flow: |
800 L/Hr |
|
Cone gas flow: |
150 L/Hr |
|
Source temperature: |
150 °C |
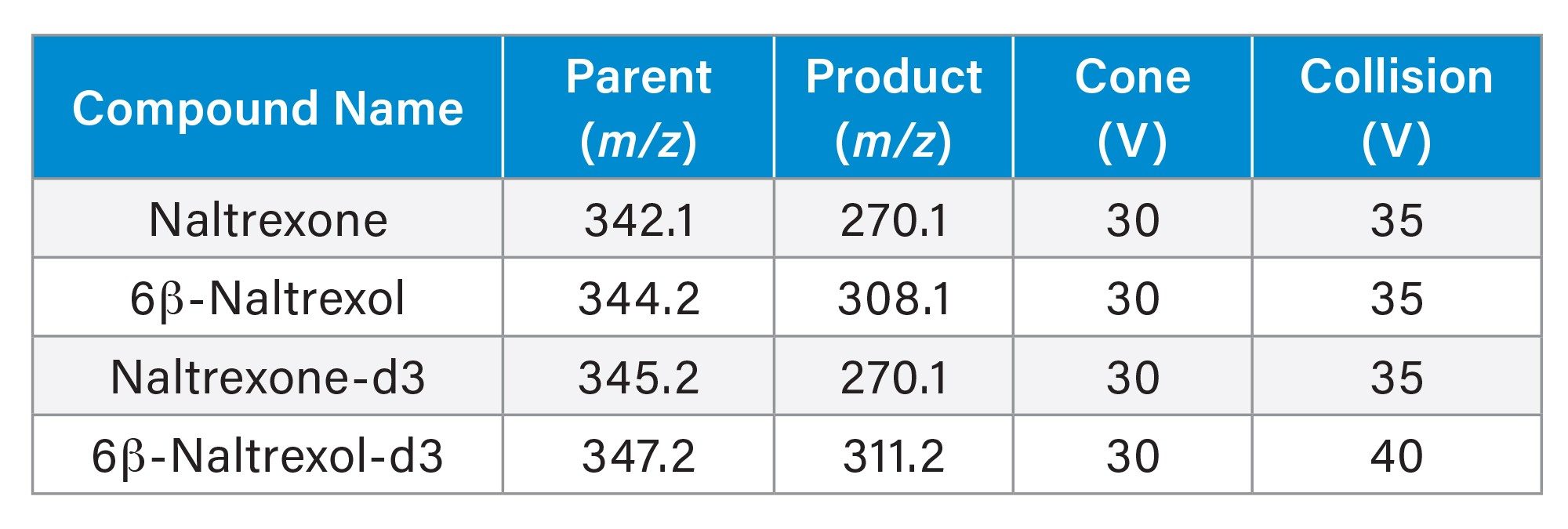
MRM Conditions
Data Management
|
Software: |
waters_connect for Quantitation Software |
Results and Discussion
The Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer demonstrated consistent performance throughout the entire analytical workflow, with no measurable decline in sensitivity, precision, or accuracy over the study period. More than 30,000 injections were successfully analyzed in this study, over more than 55 days of continuous acquisition. Over 21 mL of human plasma was injected into the system throughout the duration of the study.
QC samples within each 96-well plate replicate were quantified using bracketed calibration curves - generated using a 1/x² weighting - which met the FDA M10 Bioanalytical Method Validation (BMV) and study sample analysis acceptance criteria2, confirming the robustness and reliability of the method. Each of the 320 individual sample plate runs successfully met these regulatory standards for calibration linearity, QC accuracy and precision, as well as the absence of carryover in subsequent blank samples.
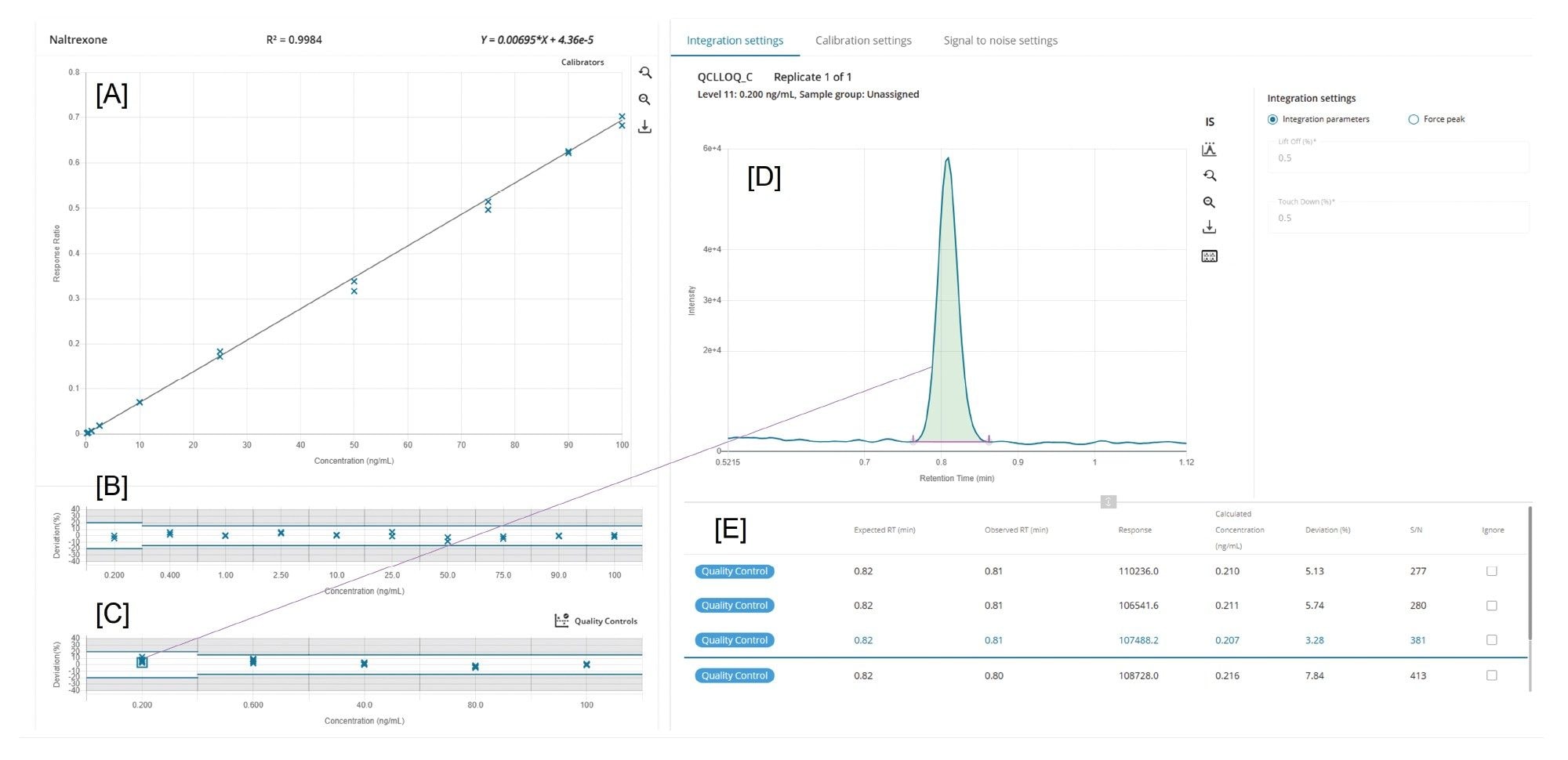
Implementation of the review-by-exception workflow within MS Quan in waters_connect for Quantitation Software substantially streamlined data processing, flagging any outliers or exceptions in the dataset for manual review. This functionality enabled efficient oversight of parameters such as linearity, QC accuracy, and blank carryover assessment, acceptance criteria for which can be set using a predefined ruleset within the software. This significantly reduced analyst workload in manual processing and data review for high-throughput datasets. Figure 4 shows how calibration and QC samples can be reviewed within MS Quan Application.
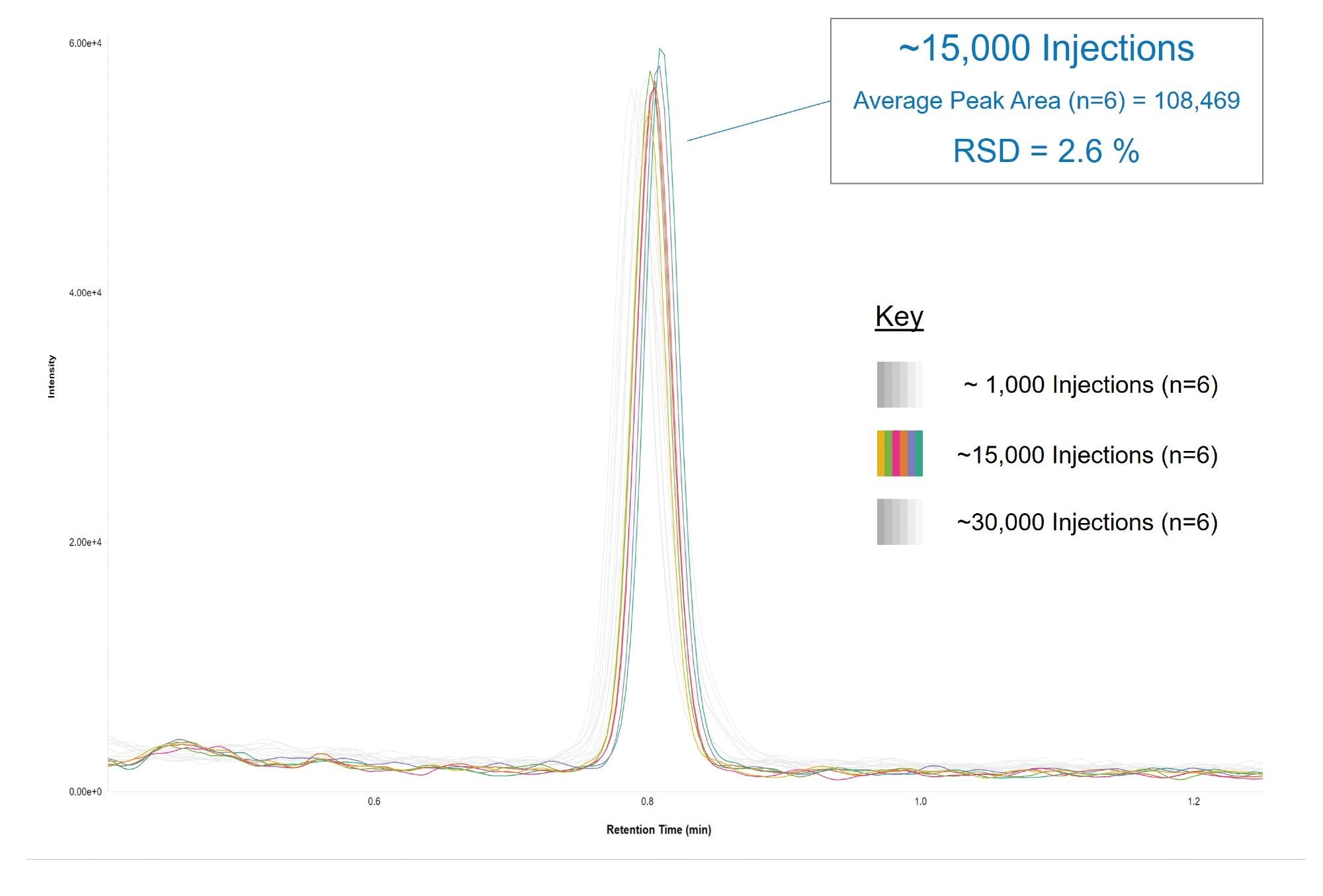
Reproducibility of peak area is a critical indicator of quantitative stability in LC–MS/MS bioanalysis, directly reflecting the precision and consistency of analyte detection across an analytical sequence. Figure 5 illustrates the reproducibility of Naltrexone peak area at the method’s lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ), showing (n=6) replicate injections of the 0.2 ng/mL QC sample acquired approximately midway through the study (~15,000 injections). For comparison, replicate injections (n=6) acquired near the beginning (~1,000 injections) and end (~30,000 injections) of the robustness sequence are overlaid in grey, highlighting the consistency of peak area throughout the analysis. Even at sub-ng/mL concentrations, the Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer maintained exceptional quantitative reproducibility, with a percent relative standard deviation (%RSD) of less than 3.0% across replicate injections.
Consistency in calculated concentrations and precision across repeated injections are direct indicators of instrument stability and method robustness, particularly at trace concentration levels where analytical variability can have a disproportionate impact on pharmacokinetic interpretation. Maintaining such performance is especially critical near the method LLOQ, where accurate measurement informs the terminal elimination phase of a drug’s pharmacokinetic profile.
Figure 6 presents the calculated concentrations for the 0.2 ng/mL LLOQ QC samples of Naltrexone and 6β-Naltrexol monitored over the course of the 30,000-injection robustness study. Both analytes demonstrated excellent quantitative stability, with the majority of calculated concentrations falling within ±10 % of the target concentration. 99.6% and 99.8% of LLOQ QC data points for Naltrexone and 6β-Naltrexol, respectively, fell inside the 20 % acceptance range criteria, underscoring the consistency of quantitative performance over the entire analytical sequence.
This trend was demonstrated across all QC levels, with 99.7% of all QC samples analyzed within the set acceptance criteria (± 15 % in all cases except at the LLOQ, where a ± 20 % criterion was used). This can also be illustrated by the precision plots as shown in Figure 6. Calculated as (Standard Deviation x 100 / Mean), the most precision values for both Naltrexone and 6β-Naltrexol were below 3.5% for all QC levels across the entire workflow. Calculated precision values were below 10 % for both compounds across all QC levels and sample batches, except for a single datapoint for QCL (0.6 ng/mL) observed midway through the sequence, which is likely attributable to sample preparation variability rather than instrumental drift.
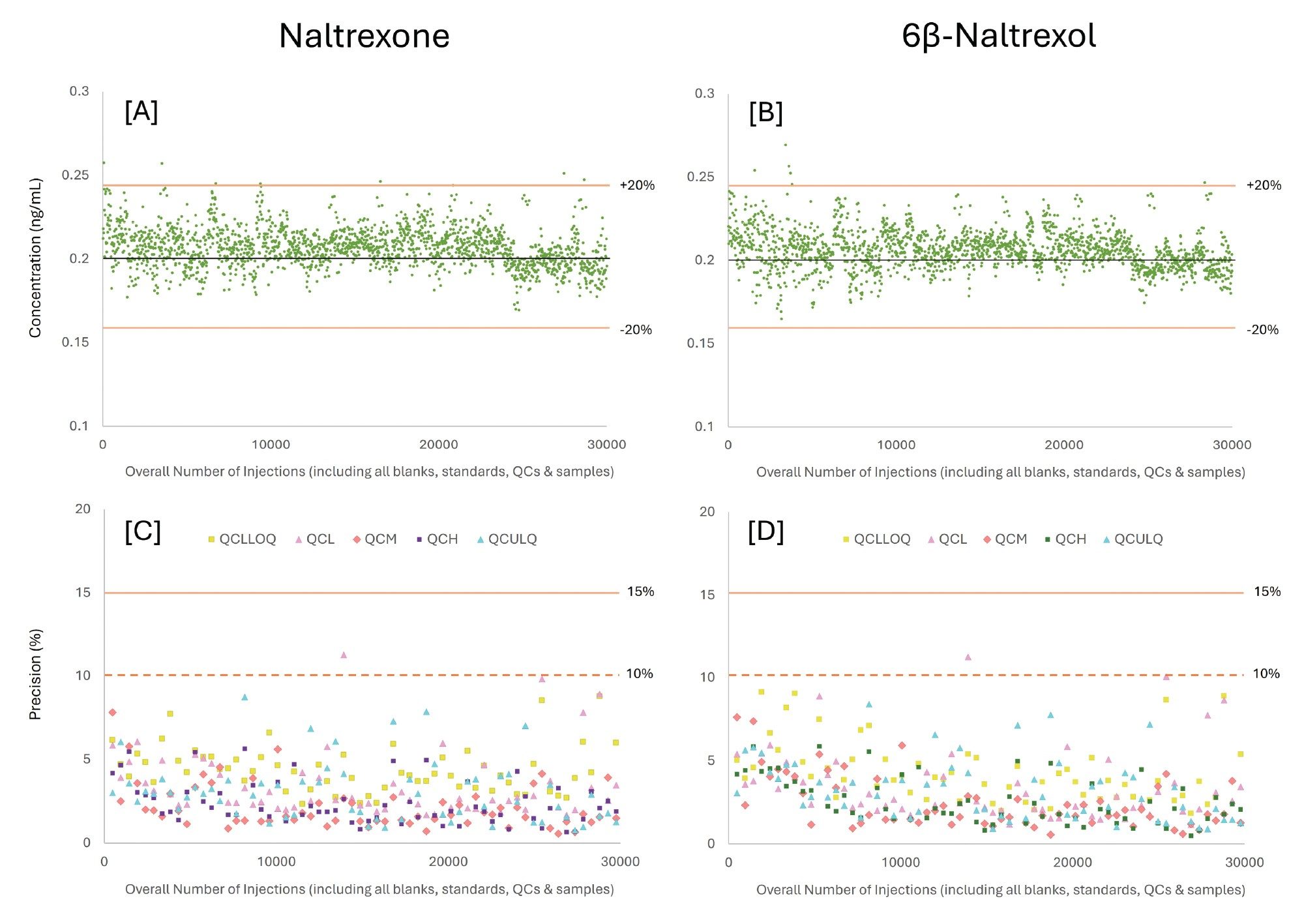
Together, these results illustrate that the Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer is capable of sustained quantitative accuracy and precision across a 30,000-injection bioanalytical workflow, even at sub-ng/mL levels. Bias and precision values generated across the duration of the study were well within the acceptance criteria of the FDA M10 guidelines.
Such long-term robustness supports reliable pharmacokinetic measurement and enables laboratories to maintain high-throughput operation with confidence in data quality and consistency, without interrupting analysis for engineer intervention or any maintenance beyond routine source cleaning. Ultimately, extended instrument uptime not only preserves data quality and analytical integrity but also accelerates scientific timelines, improving decision velocity and operational efficiency across all bioanalytical environments, from early-stage discovery through to post-market monitoring.
Conclusion
The Xevo TQ Absolute XR Mass Spectrometer, which is equipped with the novel slotted bandpass StepWave XR ion guide, demonstrated exceptional robustness and uptime over more than 30,000 matrix injections for a typical bioanalysis workflow. Quantitative accuracy and reproducibility were upheld throughout the study, with continuous and reliable operation enabling seamless transitions between sample assays. Sensitivity and selectivity were demonstrated across a high-throughput workflow, in a complex human plasma matrix, even at LLOQ method limits, demonstrating suitability for high-throughput discovery and regulated bioanalysis applications.
References
- Shen PT, Liu SC, Huang MC, Liu YL. Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of plasma naltrexone and its active metabolite in patients with AUD. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2025 Oct 3:14690667251384047. doi: 10.1177/14690667251384047.
- Timmerman P, McDougall S, Adcock N, Arfvidsson C, Barfield M, Blech S, Cowan KJ, Ferrari L, Greco A, Golob M, Goodwin L, Hughes R, Ivanova T, Laurén A, Nelson R, Neitzel S, Verhaeghe T, van de Merbel N, Wright M, White S. European Bioanalysis Forum recommendation on embracing a context-of-use-driven scientific validation for chromatographic assays in the light of ICH M10. Bioanalysis. 2025 Sep 7:1-10. doi: 10.1080/17576180.2025.2555774.
720009143, November 2025