
This application note describes the use of the Ostro Plate for multi-residue screening for veterinary drugs in milk. Using this plate, milk samples are prepared using a few simple steps to effectively precipitate protein and remove potential interferences.
The Ostro Pass-through Sample Preparation Plate allows for simple and rapid LC-MS determination of basic drugs and related compounds in biological fluids. The Ostro Plate provides a convenient platform for liquid extraction, protein precipitation, filtration, and subsequent removal of phospholipids from the resulting extract. This application note describes the use of the Ostro Plate for multi-residue screening for veterinary drugs in milk. Using this plate, milk samples are prepared using a few simple steps to effectively precipitate protein and remove potential interferences. As the extracted sample is passed through the plate the precipitated proteins are removed by filtration and phospholipid interferences are removed by retention to a proprietary sorbent. After this simple sample preparation, the reconstituted sample is analyzed using UPLC-MS/MS. To demonstrate the suitability of this method, representative compounds were chosen from major classes of veterinary drugs including tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides, macrolides, beta-lactams, and beta-andrenergics.
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY UPLC |
|
Column: |
CORTECS UPLC CSH C18+, 1.6 μm, 100 x 2.1 mm |
|
Mobile phase A: |
0.1% formic in water |
|
Mobile phase B: |
0.1% formic acid acetonitrile |
|
Injection volume: |
7 μL |
|
Injection mode: |
Partial loop injection |
|
Column temp.: |
30 °C |
|
Weak needle wash: |
10:90 acetonitrile:water (600µl) |
|
Strong needle wash: |
50:30:40 water:acetonitrile:IPA (200µl) |
|
Seal wash: |
10:90 acetonitrile:water |
|
Time (min) |
Flow (min) |
%A |
%B |
Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Initial |
0.4 |
85 |
15 |
Initial |
|
2.5 |
0.4 |
60 |
406 |
6 |
|
3.9 |
0.4 |
5 |
95 |
6 |
|
4.9 |
0.4 |
5 |
95 |
6 |
|
5.0 |
0.4 |
85 |
15 |
6 |
|
7.0 |
0.4 |
85 |
15 |
6 |
|
Mass spectrometer: |
Xevo TQ MS |
|
Source temp.: |
150°C |
|
Desolvation temp.: |
500°C |
|
Desolvation gas flow: |
1000 L/hr |
|
Cone gas flow: |
30 L/hr |
|
Collision gas flow: |
0.15 ml/min |
|
Data management: |
MassLynxv4.1 |
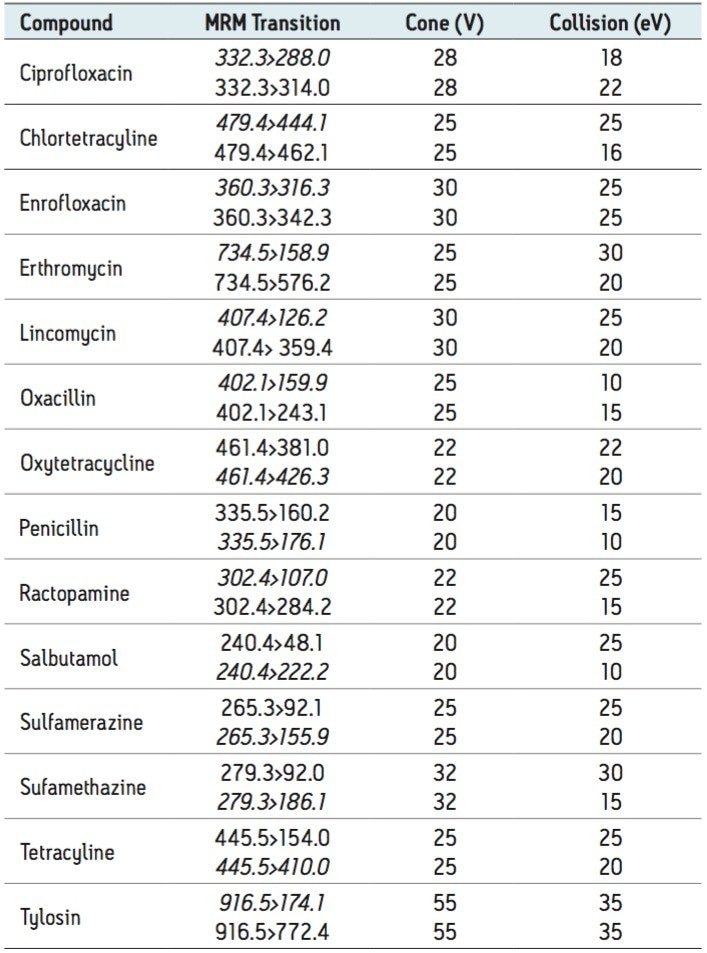
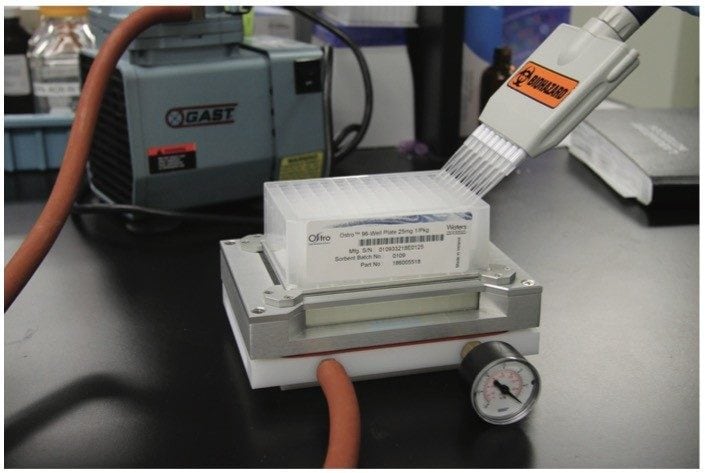
Transfer 125 μL milk to a sample well (do not use a sample volume greater than 125 μL). Add 375 μL .2% formic acid in acetonitrile (ACN). Mix well with aspiration. Elute into collection plate well. Add 100 μL 200 mM ammonium formate in 50:50 methanol/ACN and mix well. Evaporate and reconstitute in 100 μL 25:75 ACN/25 mM aqueous ammonium formate. Figure 1 shows a typical setup for SPE using the Ostro Plate.

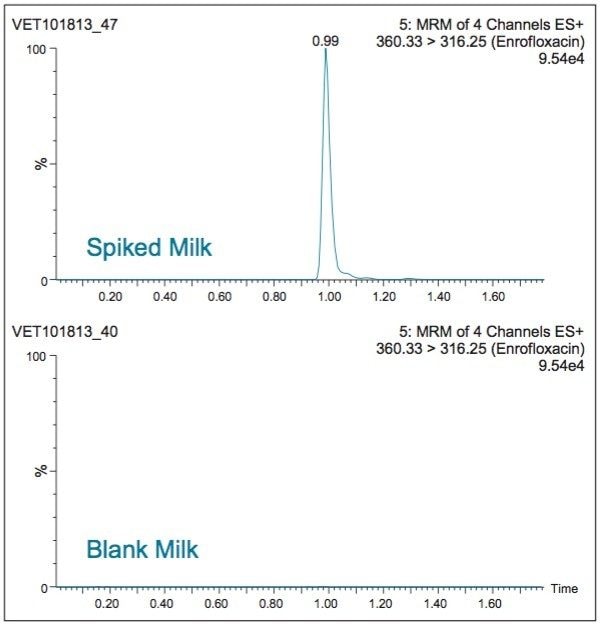
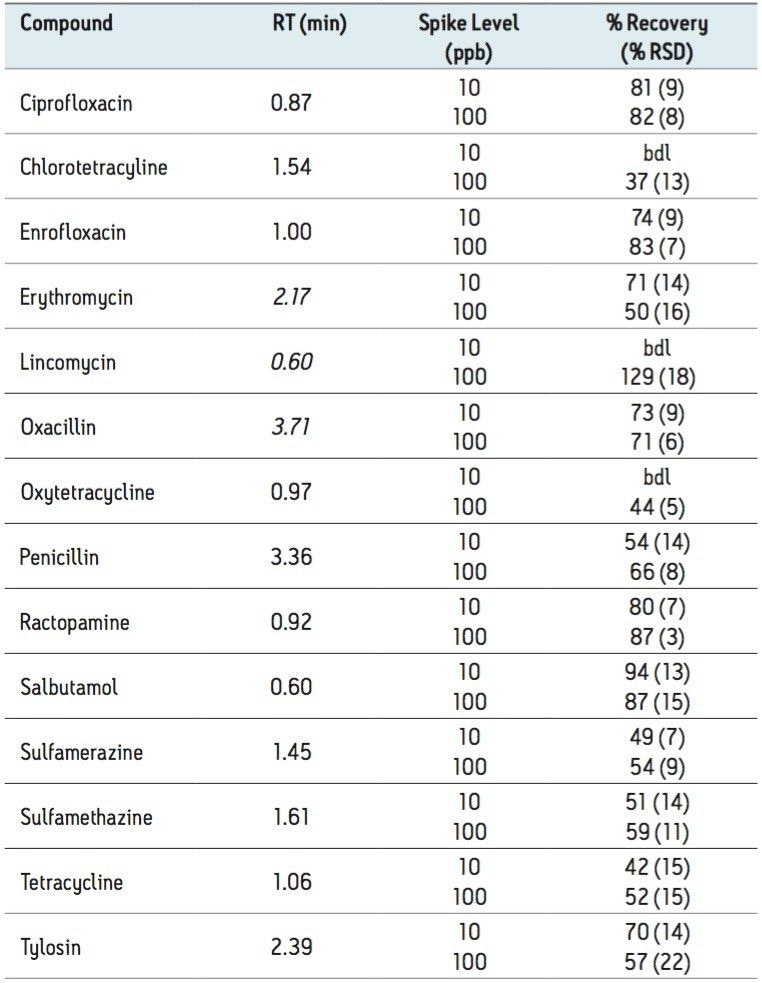
Compared to a previously published method,1 the Ostro Pass-through Plate procedure gives comparable results. However, the Ostro Plate procedure takes significantly less time and is much more suitable for high throughput analysis. A typical analyst can prepare a batch of ten or more samples in a few minutes compared with a few hours using prior methods. Figure 2 shows a typical LC-MS chromatogram obtained from analysis of a matrix matched standard of enrofloxacin at 10 μg/L. Although performance for most of the other compounds was similar, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and lincomycin were not quantifiable at the 10 μg/L level. An alternative method for tetracylines has recently been presented.2 Table 2 shows recovery data observed for multiresidue milk analysis.
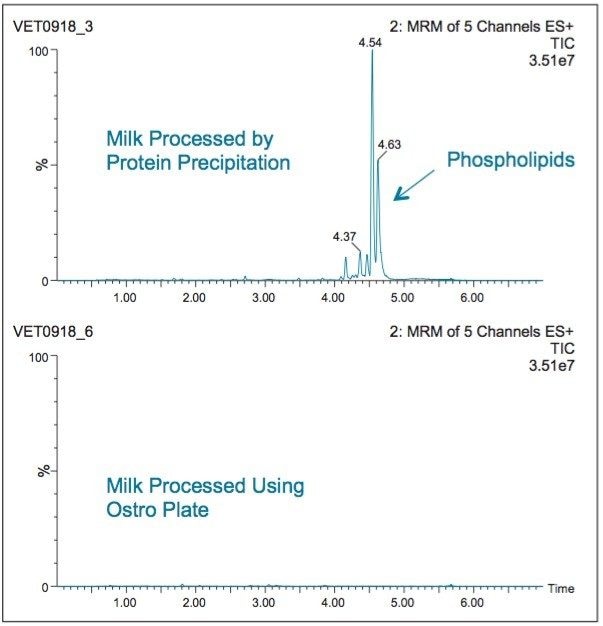
Milk contains a significant amount of phospholipids, approximately 1% of the total lipid content.3 These phospholipids can interfere directly with late eluting compounds in LC separations. Also, the buildup of phospholipid residue has been shown to result in poor or deteriorating performance in reversed-phase LC separations.4 Figure 3 shows UPLC-MS/MS analysis of milk samples using an MRM transition (m/z 184>184) chosen for identification of phospholipids. The lower trace shows the result obtained from a milk sample processed using the Ostro Pass-through Plate. The upper trace was obtained using protein precipitation with no SPE cleanup. The Ostro Plate was effective in removal of >98% of phospholipids.
720005053, November 2014