For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
This application brief demonstrates that the use of an online SPE system, ACQUITY UPLC Online SPE Manager (OSM), enables simultaneous and analytically sensitive measurement of a panel of steroid hormones.
Online SPE has a dramatic impact on the measurement of steroid hormones in serum.
Many of the currently available measurement procedures for steroid hormones suffer from poor analytical sensitivity, selectivity, and a lack of harmonization, making it difficult to achieve an accurate assessment of their circulating levels. Additionally, tests for many of the steroid hormones or steroid precursors are not readily available or can require expensive and time consuming test regimes. Therefore, clinical research laboratories are increasingly turning to LC-MS as an alternative technique for measurement of steroid hormones. But, even this powerful analytical technique can struggle to measure steroid hormones with sufficient analytical sensitivity as many existing methods require extensive sample pre-treatment, derivatization, and lengthy chromatography.
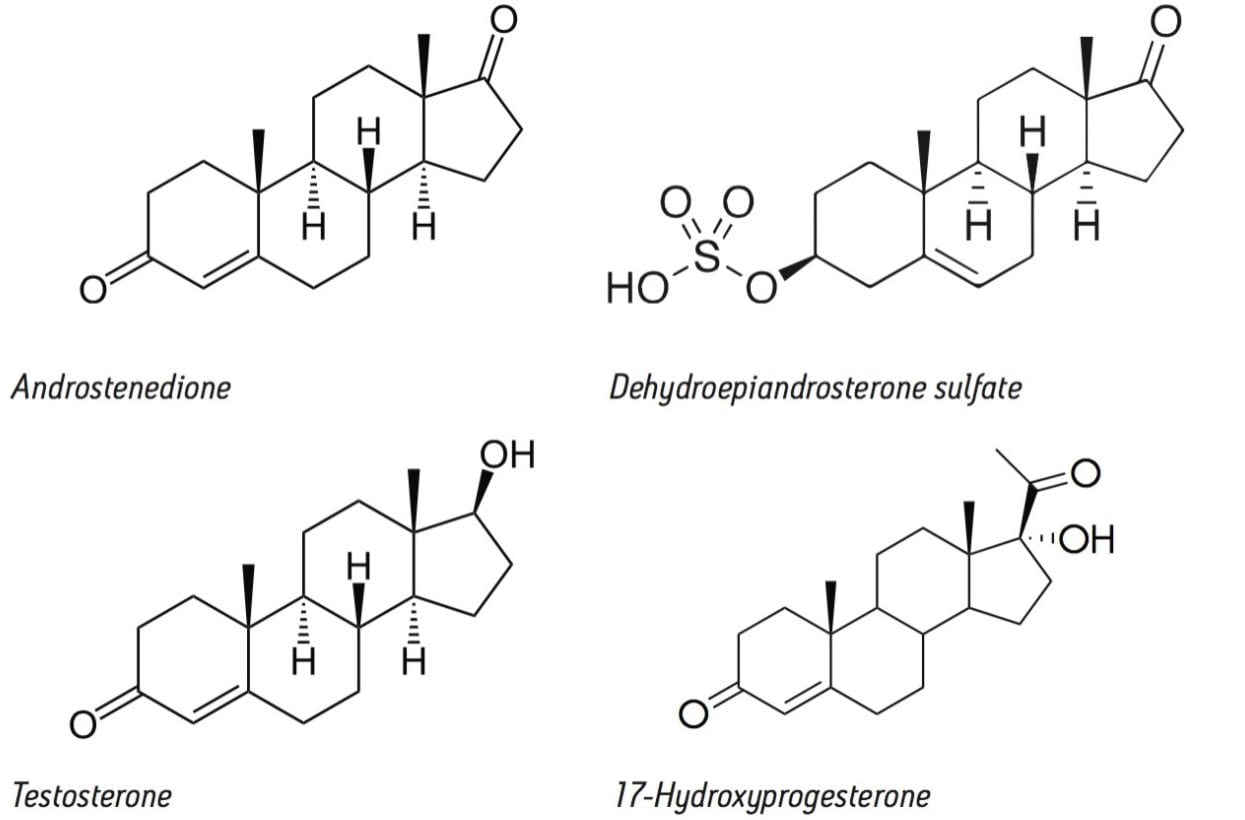
Typically, measurements of serum testosterone (T) and other androgens such as dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEAS), androstenedione (A4), and the progestin, 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) are performed in individual LC-MS methods.
Although it would be advantageous to measure these four steroids simultaneously using LC-MS, this is not straightforward because of the differing extraction conditions required to analyze these hormones.
|
LC System: |
ACQUITY UPLC |
|
MS: |
Xevo TQ-S |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY UPLC HSS SB C18, 2.1 x 50 mm; 1.8 μm |
|
Sample Preparation: |
ACQUITY UPLC Online SPE Manager (OSM) |
|
SPE: |
MassTrak C18 OSM Cartridge |
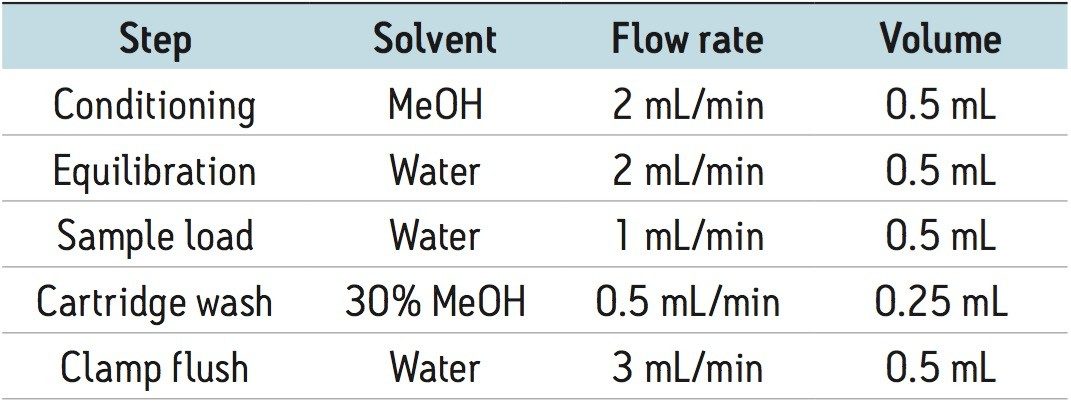
Calibrators were made by spiking methanolic standards into PBS/BSA. Initial sample pre-treatment involved the addition of 50 µL of serum to 150 µL of aqueous 0.4 M ZnSO4 and 100 µL acetonitrile (including isotopically labelled internal standards). Following centrifugation, the supernatant was extracted using the C18 cartridges for the OSM. Online SPE cartridges and samples were prepared and extracted as follows:
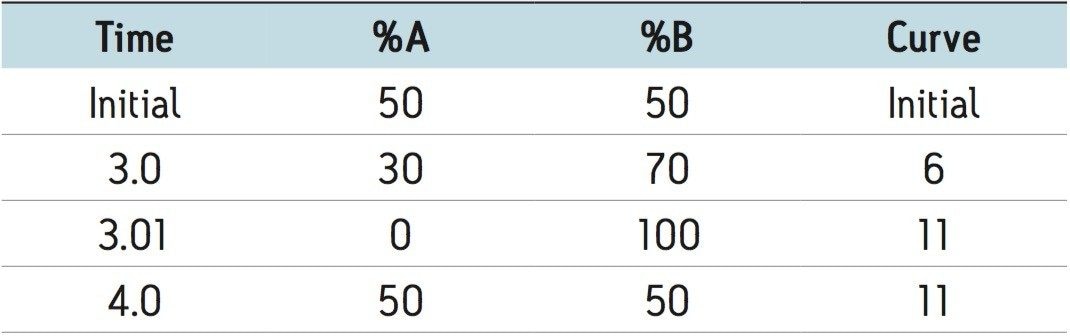
After extraction, the samples were eluted from the MassTrak C18 OSM Cartridge onto the analytical column using the following gradient of water (A) and methanol (B) both containing 2 mM ammonium acetate and 0.1 % formic acid:
Eluent was directed (without stream splitting) into the ion source of a Waters Xevo TQ-S tandem quadrupole MS, operated in the negative ion mode for DHEAS and the positive ion mode for the other steroids. The following quantifier and (qualifier) transitions were utilized:
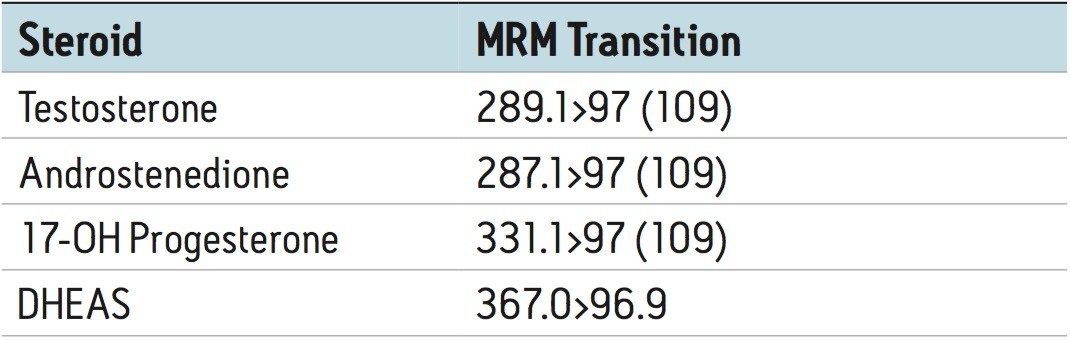
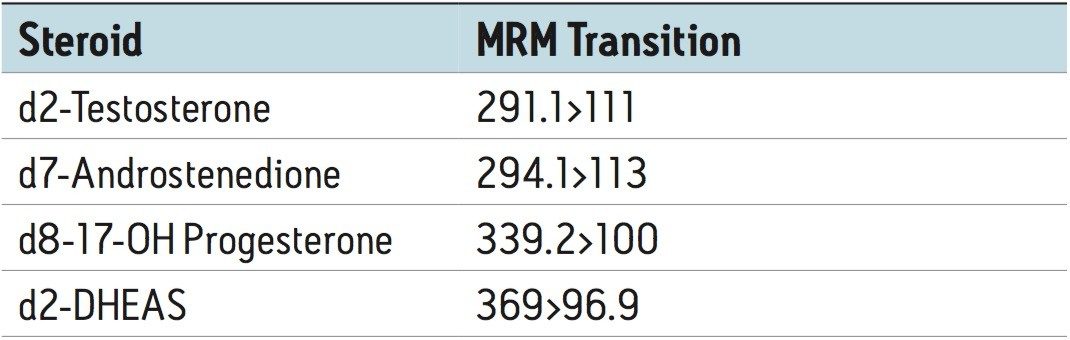
A clinical research method for simultaneously measuring four steroid hormones (T, DHEAS, A4, and 17-OHP) from serum has been developed. This method takes advantage of the unique capabilities of an online SPE system to enable analytically sensitive and reproducible measurements of these steroid hormones. The method enables direct measurement of these key steroid hormones and can provide valuable information to clinical researchers as they investigate the role these molecules play in normal biological function and disease. Simultaneous measurement of these key steroid hormones with this method can also provide valuable information to clinical researchers as they investigate novel models of disease.
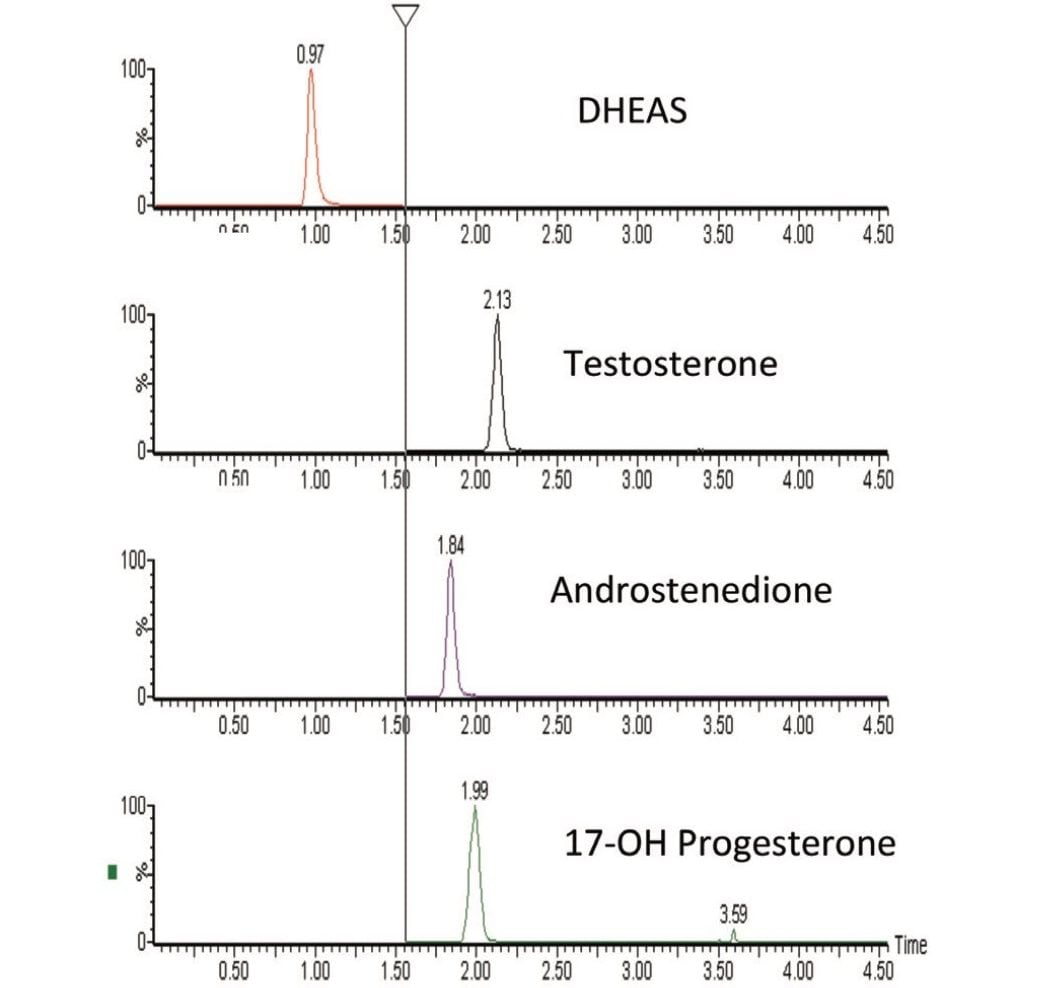
Further studies demonstrated that the lower limits of quantitation (LLOQ) for these steroids were as follows:
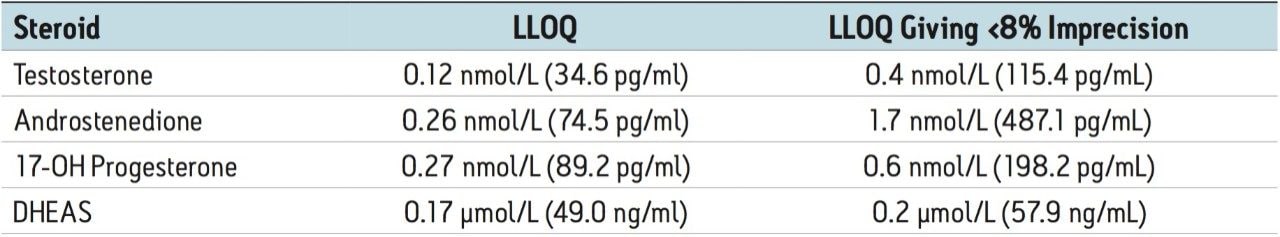

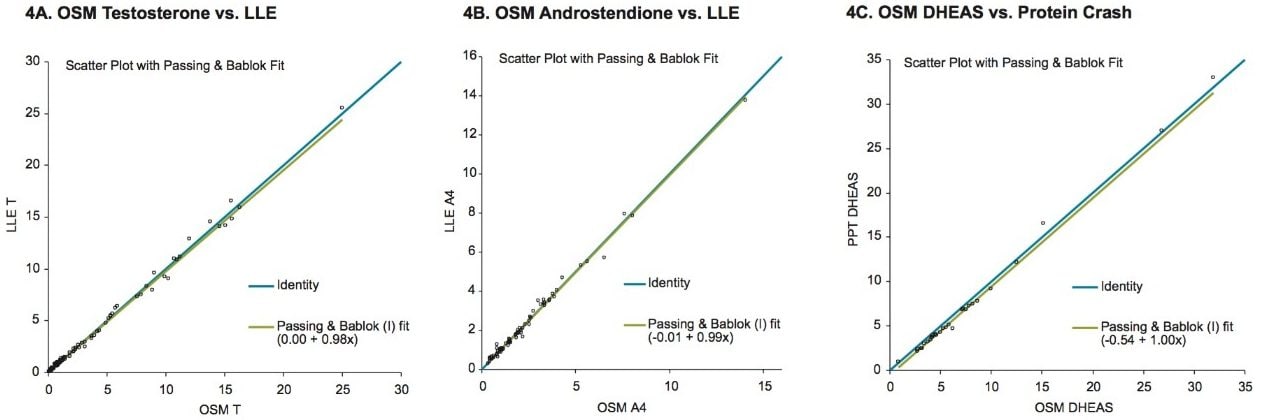
In many clinical research laboratories, two or more separate analytical runs for measuring T, A4, 17-OHP and then DHEAS have been required. Using the OSM method in conjunction with LC-MS will reduce both the direct staff and instrument time required to perform these analyses while allowing for simultaneous analysis of all four steroids. The Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS SB C18 Column used in this study showed excellent performance in terms of separation of these steroids. While the ion suppression experiment showed negligible matrix effects (Figure 3) from the serum sample matrix after treatment with online SPE. The clinical research method developed here demonstrated excellent performance when compared to existing single analyte LC-MS/MS methods incorporating various sample prep techniques such as LLE.
Sample preparation using LLE as used in many laboratories can produce clean sample extracts with minimal matrix interference. But, the use of highly flammable solvents is precluded in some laboratories because of health and safety concerns. In addition, LLE does not lend itself easily to automation and high sample throughput. Using a simple protein precipitation method, samples can be quickly and easily prepared for online sample cleanup.
This clinical research method is suitable for multiple steroid analysis and can also accommodate ionic compounds such as DHEAS which do not extract into organic solvents.
In this study, a rapid clinical research method for the LC-MS/MS measurement of T, DHEAS, A4 and 17OHP has been developed. The method is suitable for research use and the small volume of serum used (50 µL) is desirable for clinical research laboratories that are sample limited.
The method developed here provides:
720005037, August 2014