Accelerating GLP-1 Development with High-Throughput LC-MS Using the BioAccord™ LC MS System and the INTACT Mass Application
Jonathan Fox, Laetitia Denbigh, Scott Berger, Nick Pittman
Waters Corporation, United States
Published on December 17, 2025
Abstract
High-quality analysis of GLP-1 analogs is essential to support process control, ensure product integrity, maintain batch-to-batch consistency, and meet regulatory standards throughout development and manufacturing. This application note presents a streamlined solution using the Waters BioAccord LC-MS System operated under the waters_connect™ Informatics Platform, utilizing the INTACT Mass Application, to deliver automated mass confirmation and purity determination of synthetic peptides such as GLP-1 analogs. By integrating robust LC-MS capabilities with intelligent and automated data processing, the system enabled acquisition and analysis in under one minute per sample. The automated workflow minimizes manual interventions, enhances result consistency, and enables scientists to make faster, more informed decisions in early-stage development.
Benefits
Whether screening early candidates or assaying batches of a commercial product, the BioAccord LC-MS System, combined with the waters_connect INTACT Mass Application, delivers speed, automation, and precision.
1. Ability to deploy an automated sample to report workflow for synthetic peptides.
- This study demonstrates higher-throughput performance utilizing a 1-minute LC-MS method with automated post-acquisition data processing, enabling rapid analysis across large sample batches.
- Automated data processing eliminates manual steps for peak detection, mass spectral deconvolution, impurity identification, and report generation, eliminating risks of human error and standardizing processing across samples.
2. Data quality enables rapid review of results and confident interpretation of sample failures.
- Confident identification was achieved using BayesSpray deconvolution and chemical formulas for target confirmation in each sample, improving deconvolution accuracy and resulting in a low average error of −0.34 ppm and a standard deviation of 1.43 ppm for the identified targets across the 48-well sample tray.
- Embedded purity calculations were applied to optical chromatograms, total ion chromatograms (TICs), and mass spectra within the INTACT Mass Application to deliver consistent and reliable results.
- Targeted impurities were identified with delta masses reported for novel, non-targeted species, simplifying downstream investigations.
3. User interface design facilitates review by exception for rapid processing of large data sets.
- Color-coded dashboards for mass confirmation and purity thresholds streamlined sample review, helping identify failed samples and eliminate bottlenecks in higher-throughput workflows.
- Exceptions to expected results are automatically flagged, with a view grouping failed samples presented for efficient review.
Introduction
GLP-1 receptor agonists are reshaping the treatment landscape for type 2 diabetes and obesity, with new synthetic analogs offering improved pharmacokinetics and stability. As these therapies transition from development to commercial operations, companies face growing pressure to deliver consistent quality, turn results around faster, and meet increased expectation for data integrity and regulatory scrutiny. Synthetic peptides are typically produced using solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), which enables precise control over sequence and structural integrity and expectations of consistent impurity profiles. Despite the robustness of optimized synthesis protocols, it remains critical to confirm molecular mass, evaluate purity, and detect potential failure sequences or synthetic impurities to continually ensure product quality and consistency.
In this application note, a higher throughput LC-MS workflow, using the Waters BioAccord LC-MS System and INTACT Mass Application on the waters_connect Informatics Platform, designed to automate the routine analysis of synthetic GLP-1 analogs is described (Figure 1). The results confirmed the ability to analyze GLP-1 analogs such as tirzepatide, liraglutide, and semaglutide.

Experimental results demonstrated the system’s ability to deliver rapid and accurate mass confirmation and impurity profiling, with minimal user review. In this study, acquisition and processing times were under one minute per sample using a ballistic LC-MS gradient. Throughput can be further scaled to 30 seconds per sample with trap/elute methods, enabling analysis of more than 100 samples per hour when needed.3 This facilitates scalable and reliable analysis for method screening, product development, and quality control analysis of synthetic peptides, enabling researchers to make confident decisions at every stage of the product lifecycle.
Experimental
A reversed-phase, one-minute LC-MS method was developed to enable higher throughput intact mass confirmation of synthetic peptides without the need for manual method adjustments between samples. To demonstrate the method’s versatility, different GLP-1 analogs at concentrations ranging from 0.1 mg/ml to 0.001 mg/ml were analyzed. The study highlights the capability of the workflow to acquire and process data for synthetic peptide samples in a single batch, using a single method, and delivering rapid and reliable mass confirmation and impurity results.
LC Conditions
|
LC system: |
Waters ACQUITY Premier UPLC System (Binary) |
|
Detection: |
UV 280 nm |
|
Vials: |
Waters QuanRecovery™ with MaxPeak™ HPS 12 x 32 mm Screw Neck Vials (p/n: 186009186) |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY Premier Peptide C18 Column, 130 Å, 1.7 µm, 2.1 x 50 mm (p/n: 186009481) |
|
Column temperature: |
60 °C |
|
Sample temperature: |
6 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
1–10 µL |
|
Flow rate: |
0.8 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase A1: |
H2O 0.1% formic acid |
|
Mobile phase B1: |
ACN 0.1% formic acid |
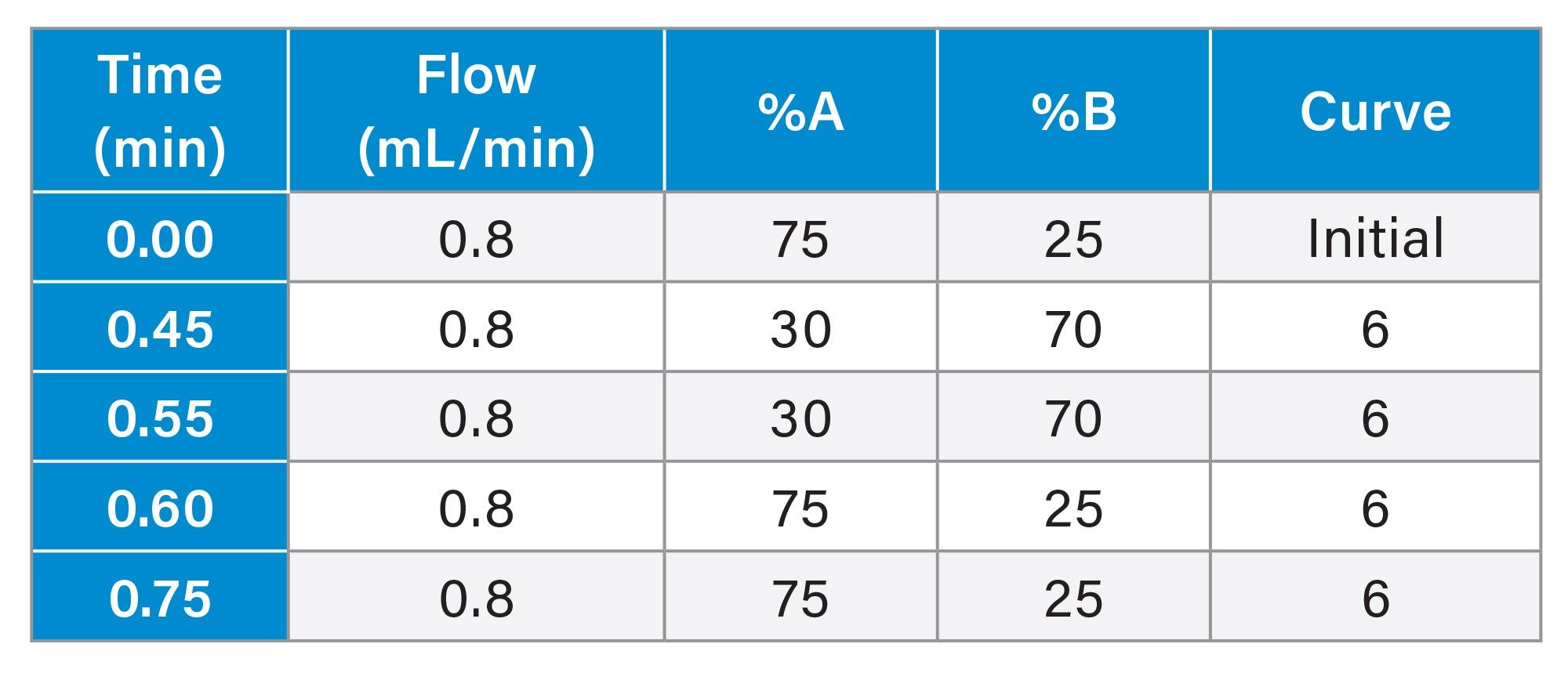
Gradient Table
MS Conditions
|
MS system: |
Waters BioAccord LC-MS System |
|
Mode: |
MSE |
|
Mass range: |
50–2000 m/z |
|
Polarity: |
Positive |
|
Scan rate |
10 Hz |
|
Cone voltage: |
30 V |
|
Source temperature: |
120 °C |
|
Desolvation temperature: |
550 °C |
|
Capillary voltage: |
1.5 kV |
|
MSE collision energy ramp: |
80–120 eV |
|
Lockmass correction: |
Scheduled lockmass |
The “scheduled lockmass” option was selected in the MS method for this experiment to shorten the total acquisition time; by reducing inter-sample system check activities from a per-injection basis to once every 60 minutes.
Results and Discussion
High-throughput analyses required development of robust analytical methods and automated data workflows that reduce or eliminate manual interventions. Software supporting higher throughput must also be flexible enough to handle analyte diversity within a batch without making methods unnecessarily cumbersome. To address these analytical challenges, the waters_connect INTACT Mass Application version 1.9, combined with enhancements to the Sample Submission App 2.7.0, simplifies higher throughput analyses by allowing users to specify target analytes either by their expected masses or chemical formulas within the sample list (Figure 2). This significantly simplifies setup, rather than requiring individual methods for each analyte. Additionally, specifying chemical formulas for target molecule assignments refines the deconvolution model, improving mass accuracy following mass spectral deconvolution.
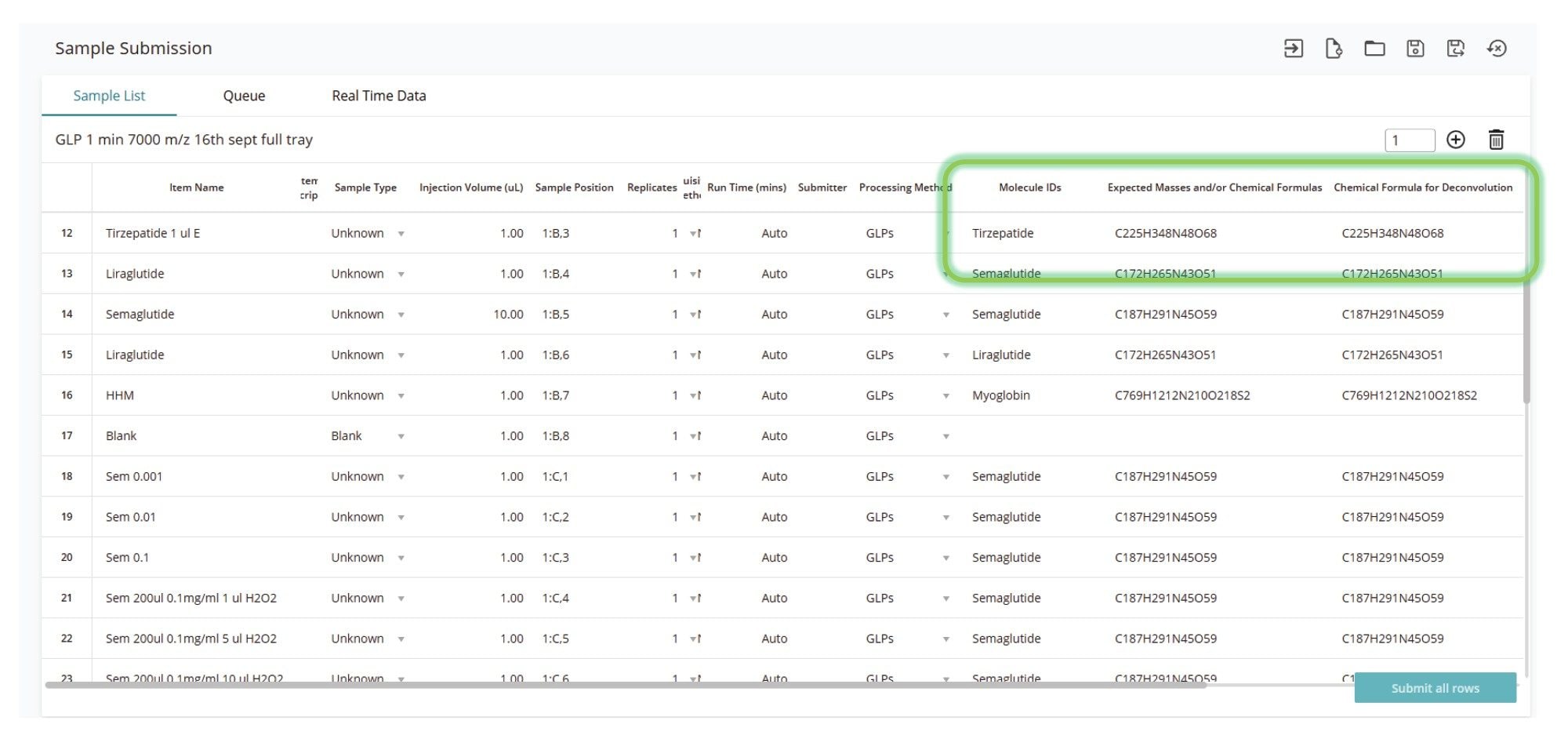
In this study, specifying target chemical formulas enabled successful batch analysis of a diverse range of synthetic peptide samples using a single acquire and process method. This approach enabled processing of chemically varied analytes within the same analysis, delivering optimized results for each sample, without the need for manual intervention. To accomplish this processing, the BayesSpray deconvolution algorithm with monoisotopic result outputs was used to deliver high-precision results for the analyzed synthetic peptide samples.
Review and Reporting of Results
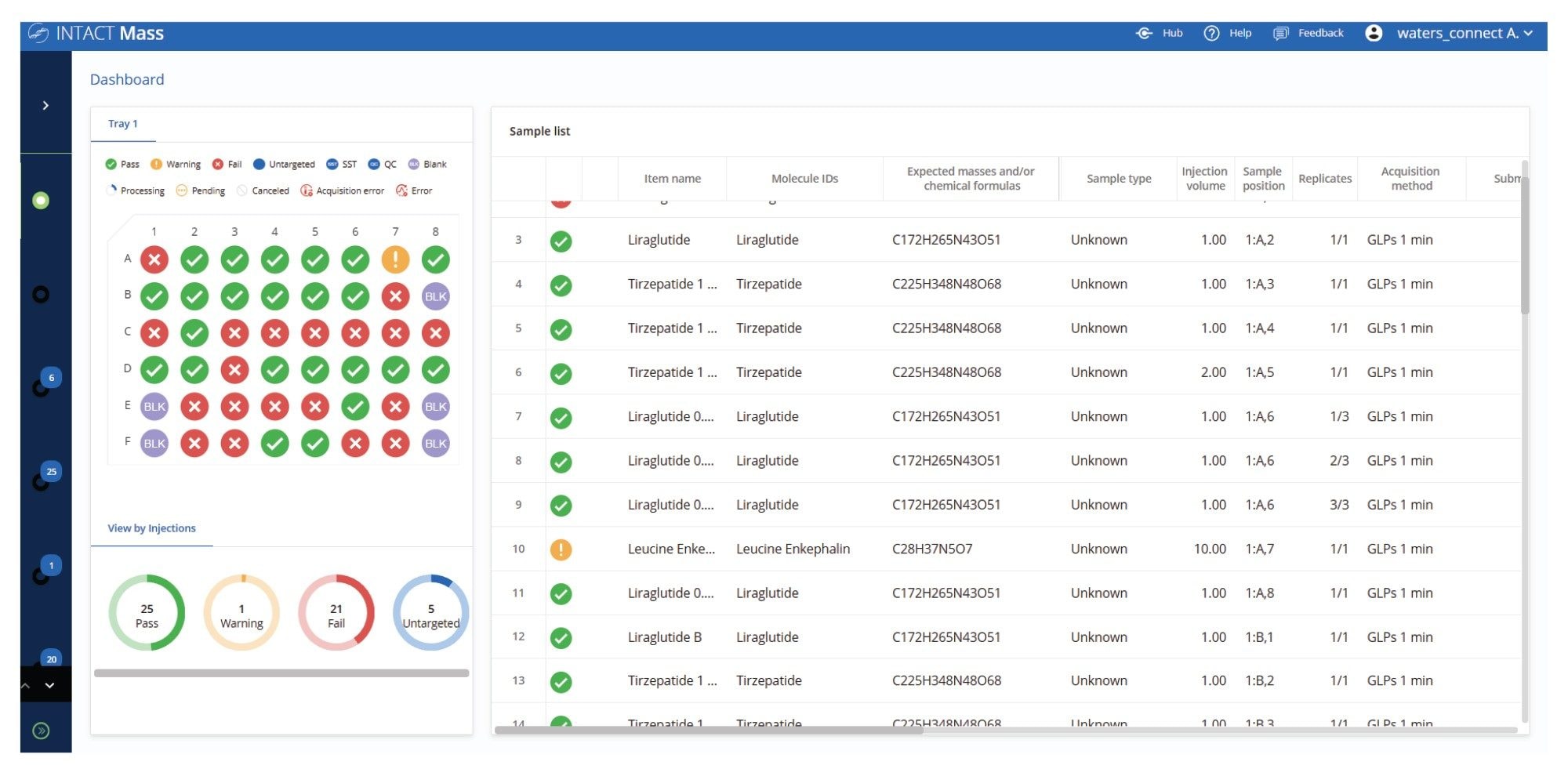
While data review can be a bottleneck in higher-throughput analysis, this challenge is addressed in the user interface of the INTACT Mass Application by generating graphical summaries and intuitive flags that quickly communicate the status of each analyzed sample. As shown in the plate analysis (Figure 3), users can easily distinguish between samples that meet both target identification and purity criteria, those that fall short of these acceptance thresholds, and those flagged for further review. The dashboard view provides a real-time summary of injections during an acquire and process run, with color-coded flags offering instant feedback on each sample’s status.
- Green: Pass — mass and purity within expected limits
- Orange: Warning — mass error or reduced purity
- Red: Fail — unmatched mass or purity below threshold
When analyzing synthetic peptides, even in higher throughput screening, the analyst is often tasked with assessing critical product attributes beyond simple mass confirmation, such as detection and reporting of impurities. Typical impurities expected for a synthetic peptide include known adducts, substitution modifications, and process-related impurities. There is also the need to recognize mobile phase adducts as product-related species and report unexpected potential impurities by indicating their delta mass from the target molecule mass.
Supporting this impurity logic within the automated data processing routines reduced the need for manual interventions and can accelerate decision-making, helping scientists move from raw data to processed results and actionable insights faster. If deeper insights into individual sample composition and purity profiles were required, results were reviewed on a per-sample basis. Examples from the panel of GLP-1 analogs included in this batch analysis are presented below.
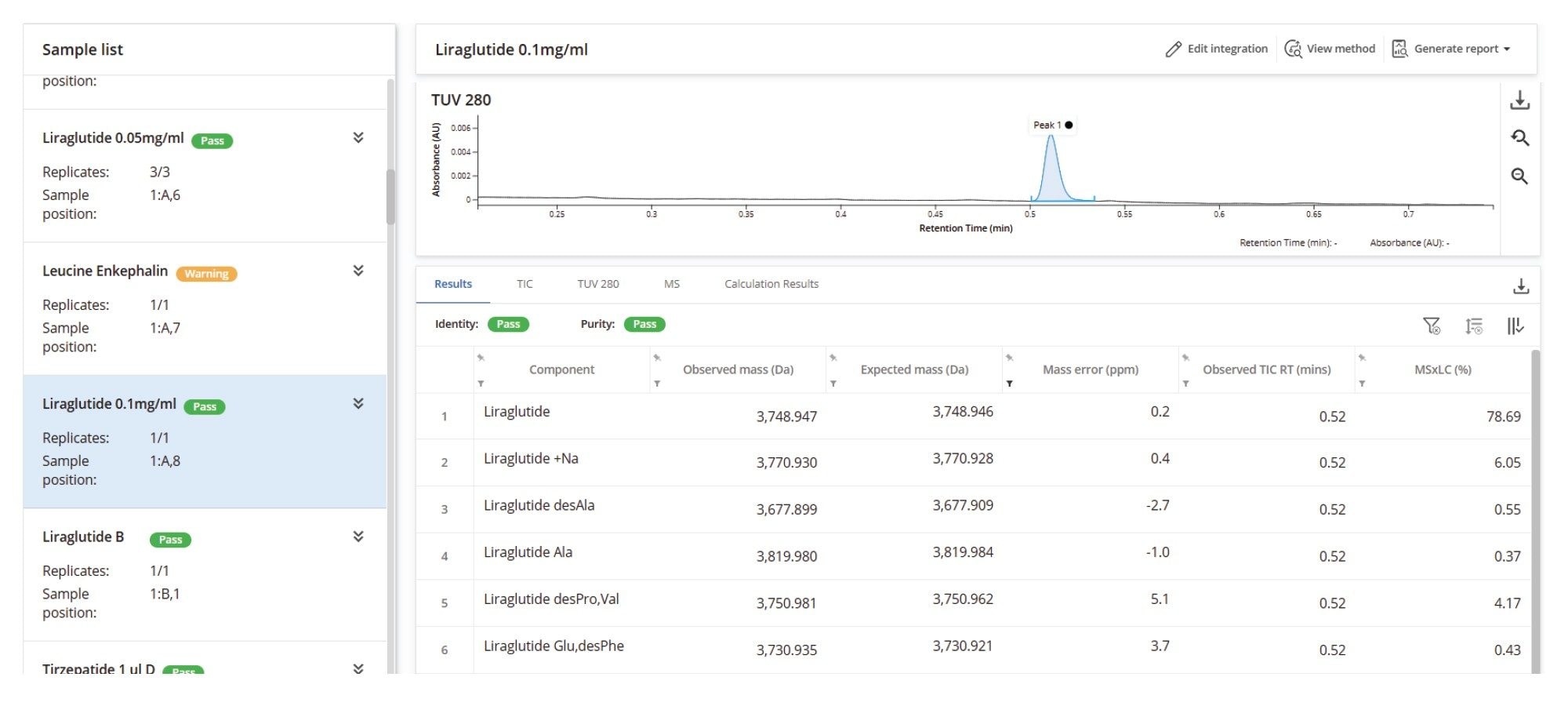
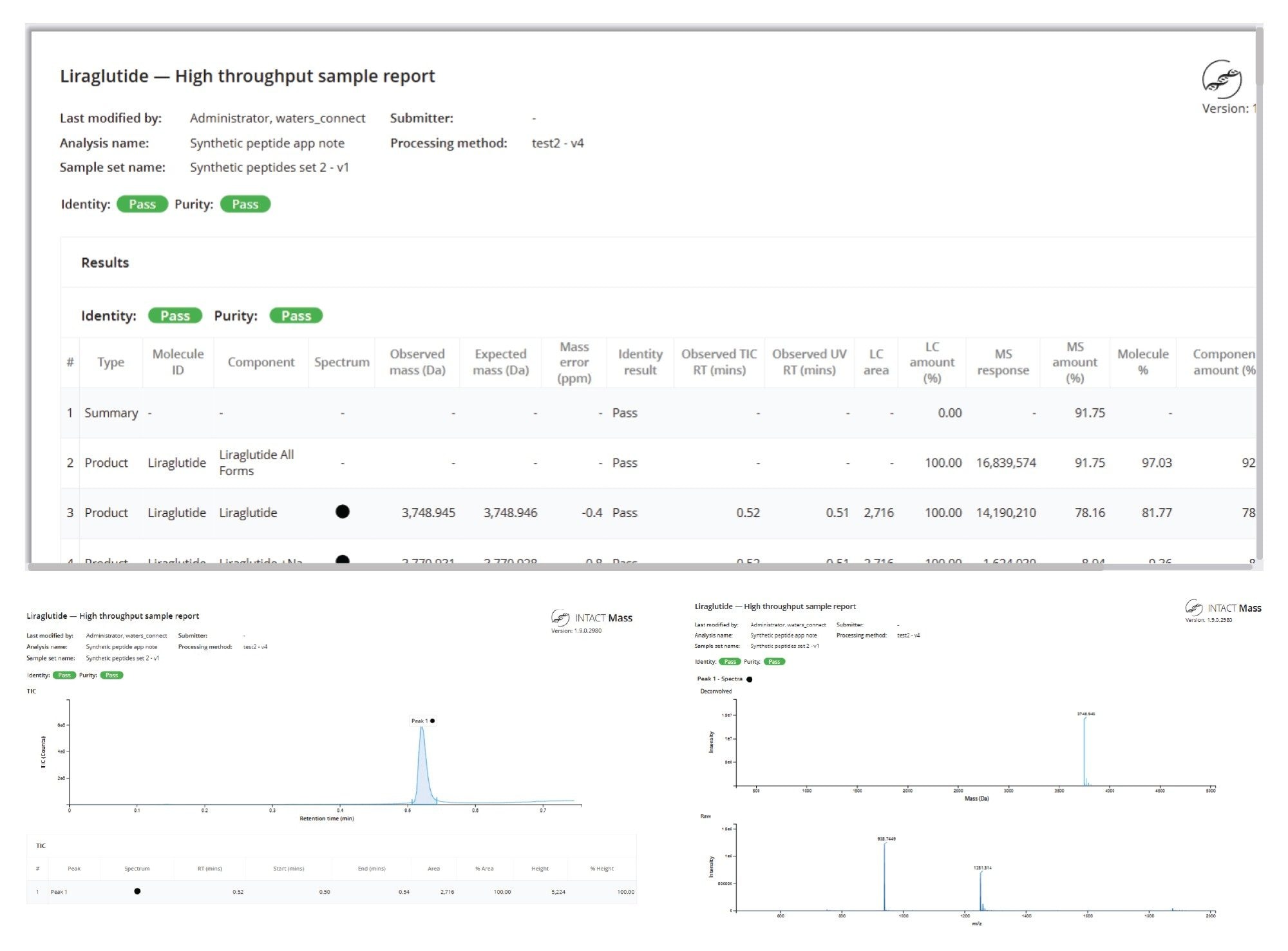
The first result features liraglutide, a GLP-1 analog composed of a synthetic peptide and a fatty acid chain. A resulting deconvoluted mass error of 0.1 ppm from the in silico predictions was achieved for the main target species. The processing method included a range of modifications and substitutions, enabling the assignment of lower-level impurities and adducts. The lowest level impurity reported was an amino acid substitution (des-Phe, Glu), quantified at 0.17% relative to the main form of the peptide (Figure 4). The INTACT Mass Application method also allowed mobile phase adducts to be treated separately from impurities. These adducts were incorporated into the overall purity percentage of the main product rather than being quantified as distinct impurities. This is detailed in Figure 4, where the reported liraglutide purity of 81.29% is combined with the quantified sodium adduct level of 7.35%, resulting in a total liraglutide MS×LC calculation, which indicated that this product represented 91.91% of quantified forms.
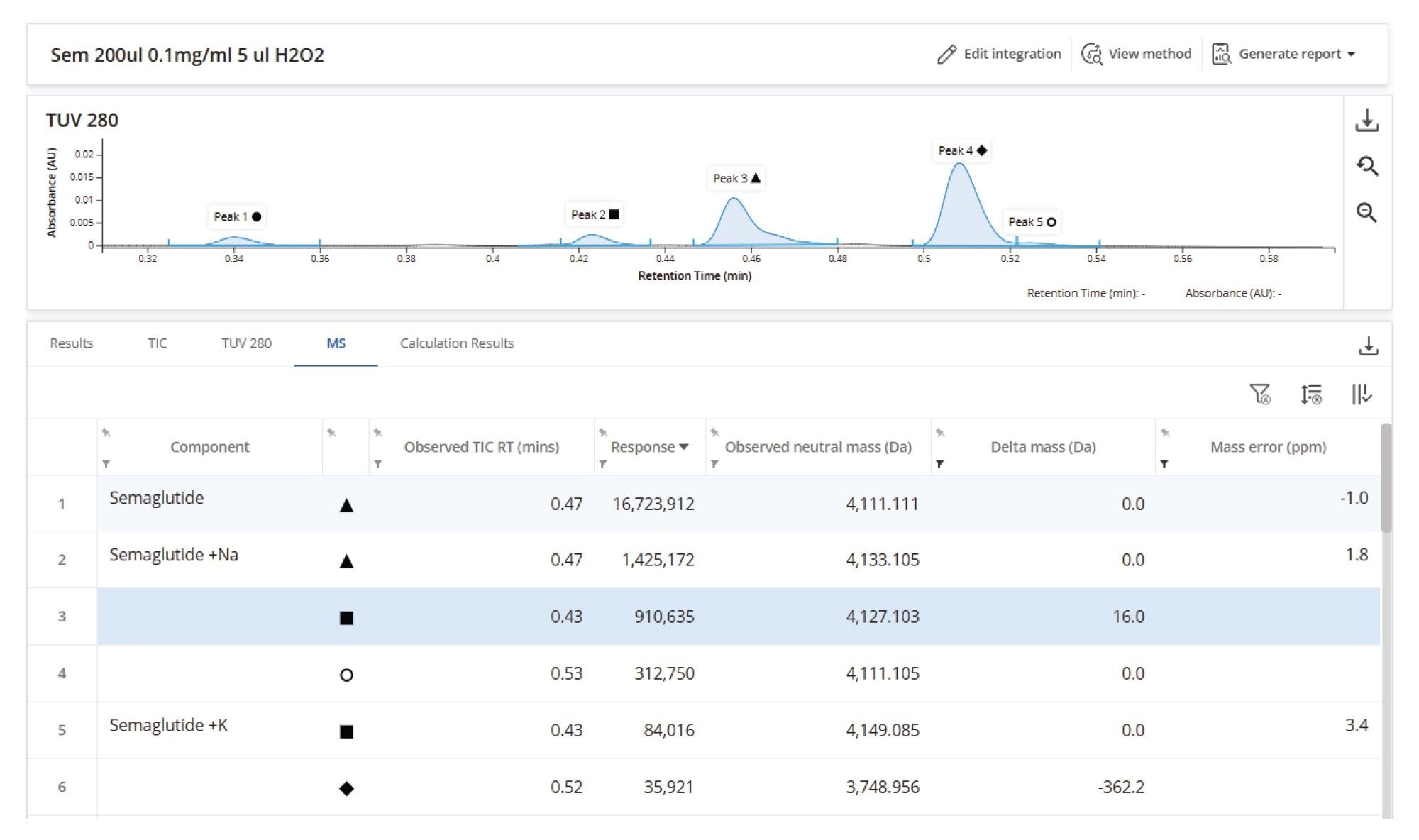
A sample containing semaglutide was identified with a deconvoluted mass error of 1.2 ppm alongside several known impurities and an unassigned component with a neutral mass of 4124.123 and a delta mass to the target molecule of +13 Da (Figure 5). A delta mass calculation is automatically applied to all MS peaks that are not targeted or otherwise identified. This hierarchy of automated assignments streamlines the characterization of novel impurities by highlighting the unexpected species present in the sample and providing results that guide the user to their elucidation.
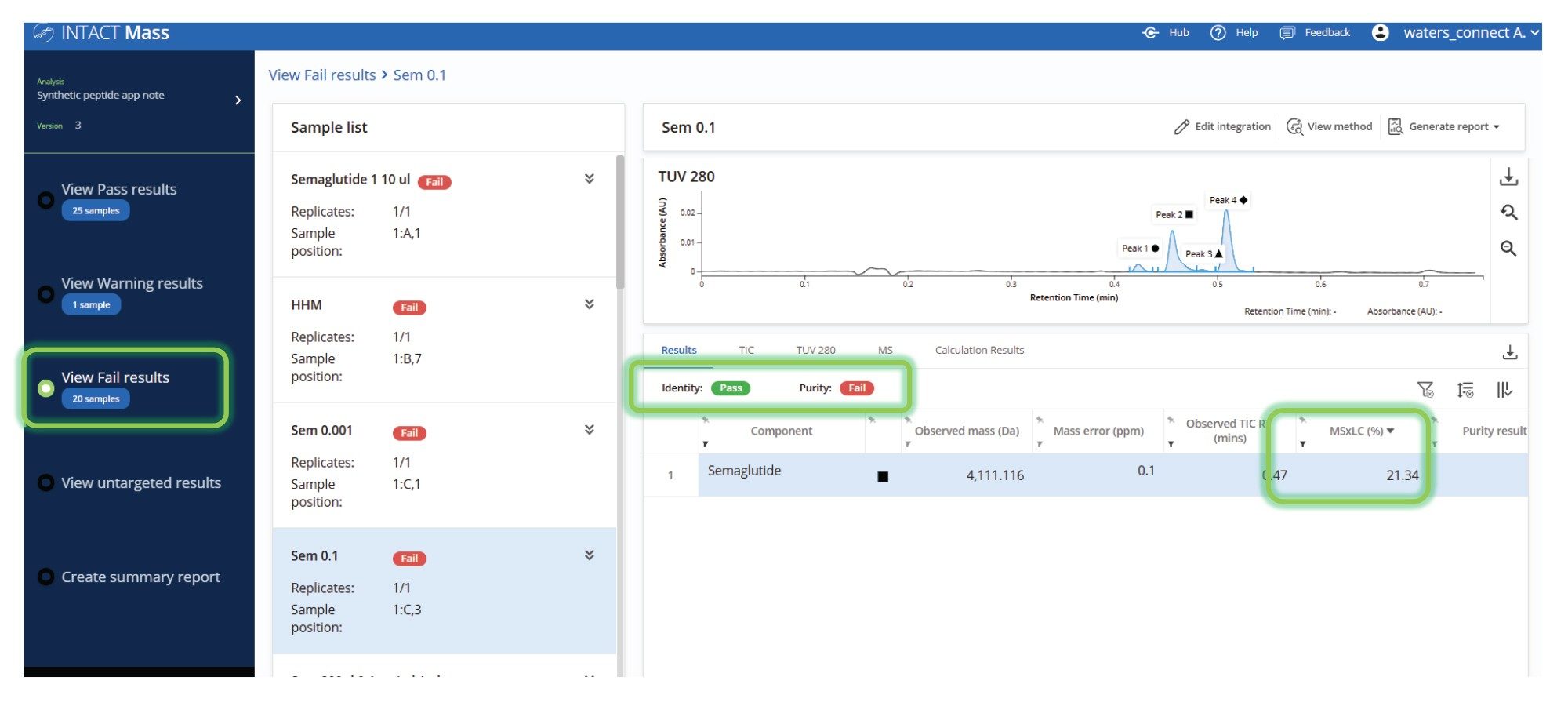
The ability to select a grouped display of failed samples in the user interface facilitated their rapid summary and detailed review (Figure 6). Samples were automatically flagged based on key criteria such as mass accuracy, absence of the target mass, or low calculated target purity. These grouped exceptions allowed a focus on problematic data and accelerated decision-making when reviewing large batches. In this example, although the target species was successfully identified, the sample was flagged due to failing to achieve the predefined purity threshold.
Reporting
Automated reporting ensures a consistent format for communication of results, ensures traceability, and simplifies the process of demonstrating data integrity and regulatory review. When configuring the acquire and process method in the INTACT Mass Application, users can opt to automatically generate a PDF report for each sample (Figure 7). Preconfigured elements of the report enabled the clear communication of analytical results and method parameters to external stakeholders and capture for documentation purposes.
Conclusion
The BioAccord LC-MS System with the waters_connect INTACT Mass Application provided a fast, automated solution for synthetic peptide and GLP-1 mass confirmation and impurity analysis screening, with several key elements directly contributing to the efficiency and quality of higher throughput screening results:
- Sub-one-minute, end-to-end acquisition and processing enabled identification of all mass spectral and chromatographic peaks above a defined threshold, including the reporting of delta masses for novel impurities. This methodology could support thousands of samples per week.
- Automated data processing with intelligent peak picking, mass spectral deconvolution parameter setting, and embedded impurity profiling logic delivered detailed insights on samples of varying abundance, a key need for robust screening protocols.
- Graphical batch summaries and review by exception logic enabled faster, simpler analyst review of data, and the ability to focus on sample results that do not conform to predefined quality criteria defined in the method.
Together, these capabilities of the BioAccord LC-MS System and INTACT Mass Application for synthetic peptide analysis can support the broad exploration of chemistry space for developing modern therapeutic peptides, higher throughput quality analyses from large-scale manufacturing operations, and rapid turnaround and cost-efficient sample analysis by contract and core laboratories.
References
- Shion, H., Berger, S. J., Yu, Y. Q. Application of a Mass Confirmation Workflow for Biotherapeutics Screening. Waters Corporation Application Note, 720007027. November 2020.
- Shion, H., Boyce, P., Berger, S. J., Yu, Y. Q. INTACT Mass™ – A Versatile waters_connect™ Application for Rapid Mass Confirmation and Purity Assessment of Biotherapeutics. Waters Corporation Application Note, 720007547. February 2022.
- Fox, J., Berger, S., Denbigh, L., Yu, K. 100 Samples per Hour: High Speed Oligonucleotide Analysis with BioAccord LC-MS and INTACT Mass™. Waters Corporation Application Note, 720009127. November 2025.
720009176, December 2025