This application note illustrates the use of a Phosphopeptide Enrichment Kit that consists of an affinity extraction μElution plate, and a unique chemical reagent under the trade name of Enhancer, which is shown to improve the selectivity of the affinity solid-phase extraction (SPE) towards phosphopeptides for highly complex biological samples.
The reversible phosphorylation of serine, threonine and tyrosine, is one of the most important post-translational modifications involved in various cellular functions. Identification of phosphorylation sites by mass spectrometry is challenging due to the low abundance of phosphopeptides and their limited ionization efficiency. Therefore, it is critical to selectively enrich the phosphopeptides prior to MS analysis. In this study we illustrate the use of a Phosphopeptide Enrichment Kit that consists of an affinity extraction μElution plate, and a unique chemical reagent under the trade name of Enhancer, which is shown to improve the selectivity of the affinity solid-phase extraction (SPE) towards phosphopeptides for highly complex biological samples. Also, a vial of phosphopeptide standard is included in the kit as a control sample to validate the affinity extraction method. MALDI-ToF MS and nano-scale LC-MS were used to evaluate the performance of the affinity solid-phase extraction device. Recommended protocol for the affinity SPE μElution plate, and sample preparation for MS analysis are included in the application.
The μElution plate is operated using a vacuum manifold (The extraction plate vacuum manifold (Waters P/N 186001831 is not included in this kit).

Condition the well Condition the wells with 200 μl of Milli-Q water first, then 200 μl of MeOH.
Prepare the sample Solubilize the sample in 0.2 to 0.5% TFA in 80% MeCN solution, the final volume is between 200 to 400 μl. For highly complex samples, load the sample in the appropriate solution containing between 50 to 100 mg of Enhancer solutiona.
Sample loading Load the sample into each well (loading capacity for each well is ~100 μg), and let the gravity pull the sample through the well (no need to turn on the vacuum for this step), collect the breakthrough solution using a collection plate. It takes about 15 to 25 minutes.
Washing the well Wash the wells with 200 μl 0.2-0.5% TFA in 80% MeCN (repeat this step if necessary). Wash again using 200 μl Milli-Q water.
Elution Elute with 200 to 400 μl of 100 mM diammonium phosphate (pH~8)b or 2% (v/v) triethylamine (pH~11)b.
Lyophilization Neutralize the eluent and lypholize the eluent for further analysis.
a Enhancer solution preparation: First prepare a solution of 0.2% TFA in 80% MeCN, 19.8% water (v/v) that is used to reconstitute the Enhancer powder. Weigh 100 mg of Enhancer and mix it with 1 ml (or 2 ml) of this dilution solution to make a final concentration of 100 mg/ml (or 50 mg/ml).
b We observed that diammonium phosphate eluent recovers multiply phosphorylated peptides slightly better than triethylamine. However, diammonium phosphate must be removed prior to MS analysis due to its ion-suppression effects.
If triethylamine is used to elute the enriched phosphopeptides, the lyophilized sample can be directly analyzed via MALDI MS after reconstituting the sample with appropriate solvent. No additional sample cleanup prior to MS analysis is required since triethylamine is a volatile reagent that is eliminated during lyophilization). However, for the diammonium phosphate eluted phosphopeptides, ZipTip like devices are needed to remove diammonium phosphate that suppresses MALDI ion signals. The following procedure can be used as a guideline for removing excess diammonium phosphate prior to MALDI Tof MS analysis.
1. Reconstitute the lyophilized phosphopeptides with Milli-Q water.
2. Follow the recommended manufacturing procedure to extract the peptides if ZipTip μC18 is the choice of clean up device.
3. Prepare a 20 mg/ml solution of 2,5-dihydroxide benzoic acid (DHB) (e.g., MassPREP DHB MALDI Matrix, P/N 186002333) using pure Ethanol, with 1% H3PO4 (v/v) mixed in the DHB solution.
4. Mix the ZipTip cleaned sample with DHB matrix in 1:1 ratio, and spot 1 μl directly onto the MassPREP MALDI target. Dry the droplet in ambient temperature.
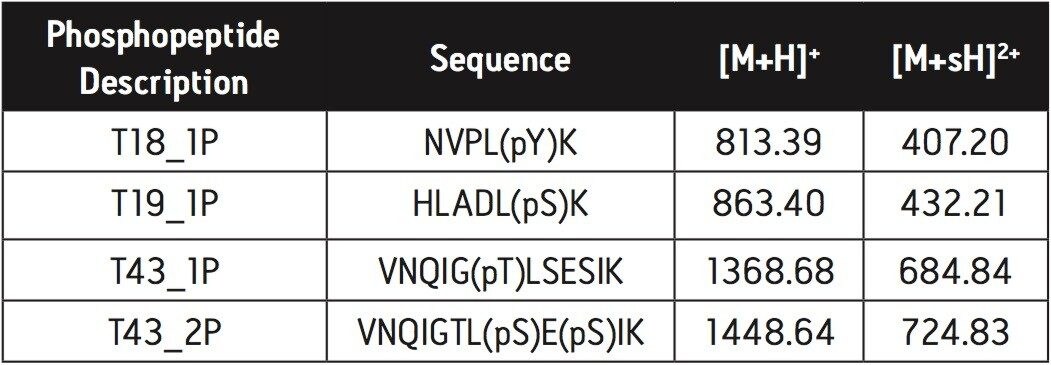
5. Proceed with MALDI MS analysis (see Figure 1). Instrument used: Waters MALDI micro MX.
The diammonium phosphate was used to elute the phosphopeptides. ZipTip μC18 tip was used to remove diammonium phosphate from the sample. Highly selective enrichment of the 4 phosphopeptides was observed.
1. Prepare a solution composed of 10-25 mM diammonium phosphate and 10-25 mM EDTA in MillQ-water.
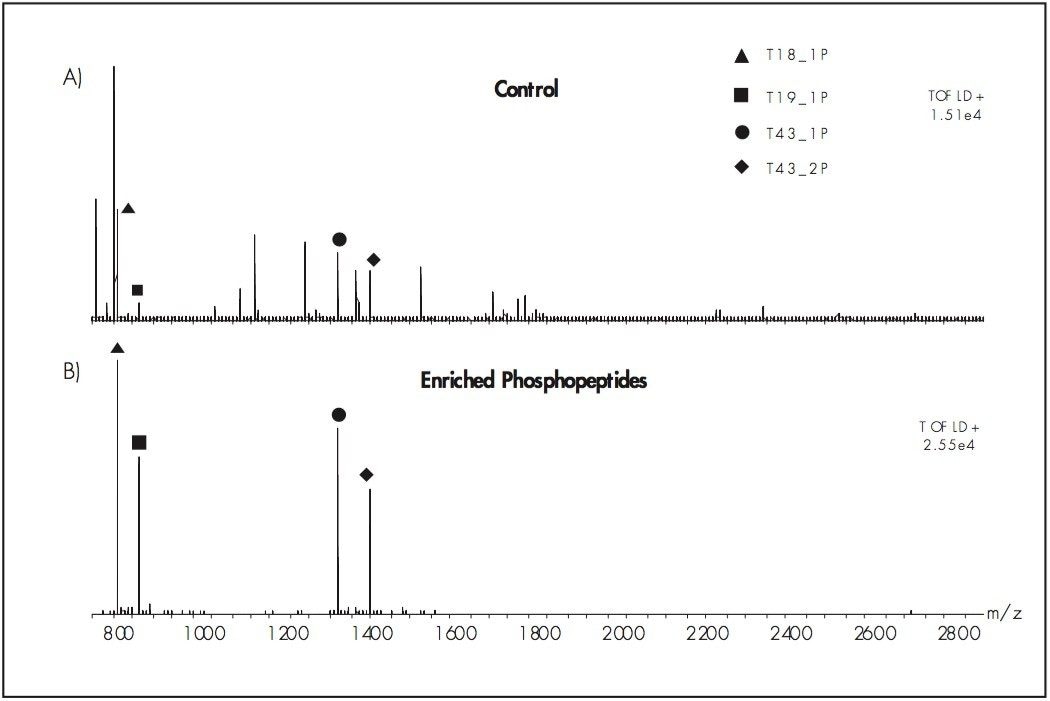
2. Solubilize the lyophilized phosphopeptides in this solution. (The combination of diammonium phosphate and EDTA was used to minimize the loss of phosphopeptides due to exposure to potential metal surfaces in the LC System fluid path.) A trap column (e.g Symmetry C18, nanoACQUITY UPLC Trap: Part Number 186002841) can to used to remove excess diammonium phosphate and EDTA from the isolated phosphopeptides prior to MS analysis.
|
UPLC system: |
nanoACQUITY System |
|
Trapping column: |
Waters Symmetry C18, 5 μm, 180 μm x 20 mm |
|
Trapping mode: |
5 μl/min for 3 minutes (100% aqueous) |
|
nanoACQUITY column: |
Waters Atlantis dC18, 3 μm, 5 μm x 100 mm |
|
Solvent A: |
0.1% formic acid in 100% Milli-Q water |
|
Solvent B: |
0.1% formic acid in 100% acetonitrile |
|
Flow rate: |
300 nl/min |
|
Gradient: |
2%-40% B, 1% B per minute |
|
Injection volume: |
2 μl, full loop |
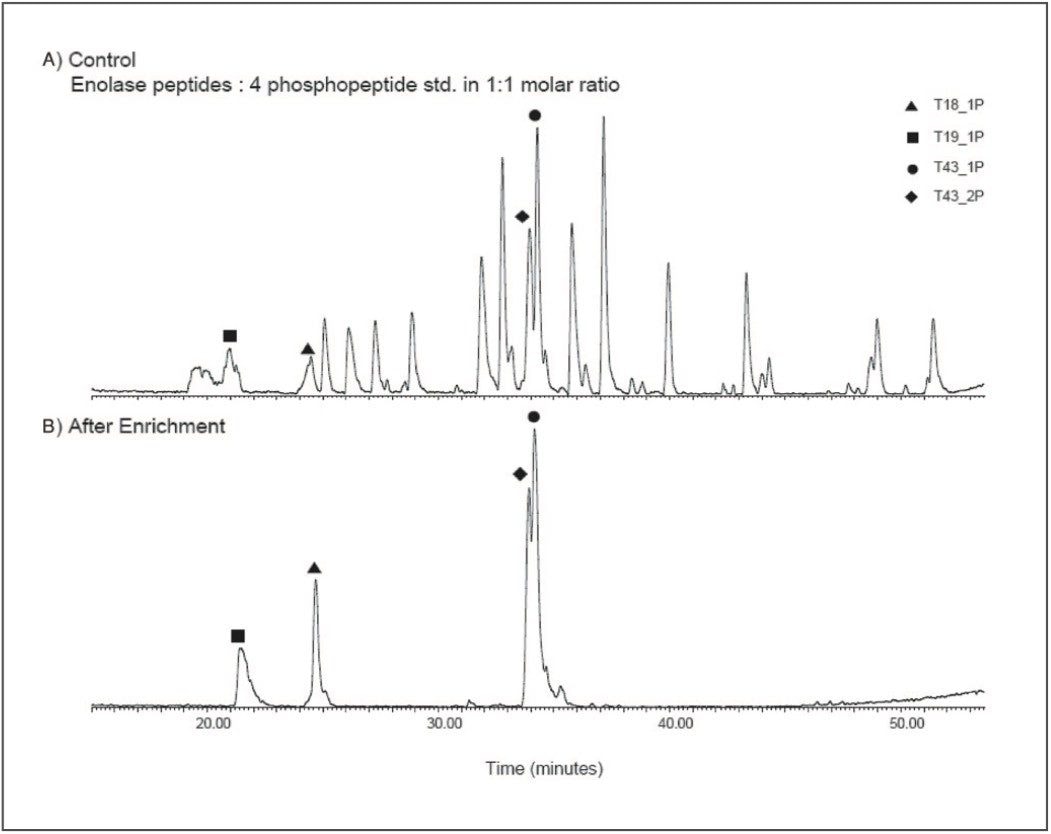
Figure 3 illustrates the use of Waters Enhancer (50 mg/ml) Reagent in the loading solution and subsequent improvement in the selectivity of the affinity extraction. The Enhancer can selectively displace acidic peptides without removing phosphopeptides from the μElution Plate and improves the selectivity towards phosphopeptides.
720002179, August 2007