
This application note describes how Waters Xevo G2 QTof can be used to determine polymer end groups, using Poly Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA) as a model example. The Xevo G2 QTof is a hybrid Quadrupole Time-of-Flight mass spectrometer. The quadrupole allows precursor ions to be selected for fragmentation, which provides the analyst with additional structural information, a cleaner spectrum, and increases confidence in the origin of the ions detected.
Polymers have incredibly diverse applications including paints, cosmetics, plastics, textiles, and food packaging. This range of applications requires a broad spectrum of properties that can be created by varying many aspects of the polymer, such as chain length, terminating and initiating end groups, polymer chemistry, cross linking, and the inclusion of additives during the manufacturing process.
In recent years, Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) have become increasingly important for the analysis of polymers. These ionization techniques within mass spectrometry have allowed information to be collected on a range of polymer properties including end group analysis, backbone structure, and in some cases average molecular weight.1,2
The ability to accurately and reliably carry out end group analysis provides valuable information to both polymer manufacturers and polymer research scientists. Information about the end groups can be used to indicate the synthetic process followed and guide how further chemical modifications can be carried out.3
Some synthetic polymers, such as poly ethylene glycol, will ionize in ESI mode with the right settings by simply dissolving and infusing. Other polymers become much easier to analyze if they are mixed with a salt before analysis so that the polymer becomes cationized (gains a charge by bonding with the cation from an added salt). The fragmentation pattern of the polymer can be affected by the specific cation present,2 and hence the structural information that can be gained from an MS/MS experiment.
This application note describes how Waters Xevo G2 QTof can be used to determine polymer end groups, using Poly Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA) as a model example. The Xevo G2 QTof is a hybrid Quadrupole Time-of-Flight mass spectrometer. The quadrupole allows precursor ions to be selected for fragmentation, which provides the analyst with additional structural information, a cleaner spectrum, and increases confidence in the origin of the ions detected.
Three separate solutions were prepared of PMMA 4000, LiCl, and NaI, each at 1.0 mg/mL in methanol. These solutions were mixed and diluted to make the following:
100 ppm PMMA 4000 and 100 ppm LiCl in methanol
100 ppm PMMA 4000 and 100 ppm NaI in methanol
|
MS system: |
Xevo G2 QTof |
|
Ionization mode: |
ESI+ |
|
Analyzer: |
Resolution mode |
|
Infusion rate: |
10 μL/min |
|
Acquisition rate: |
1 spectrum/sec |
|
Capillary voltage: |
2.5 kV |
|
Sample cone: |
150 V |
|
Extraction cone: |
4.0 V |
|
Source temp.: |
150 °C |
|
Desolvation temp.: |
200 °C |
|
Cone gas: |
Nitrogen, 20 L/hr |
|
Desolvation gas: |
Nitrogen, 600 L/hr |
|
Compound: |
Leucine enkephalin |
|
Mass: |
m/z 556.2771 |
|
Flow rate: |
20 μL/min |
|
Capillary voltage: |
3.0 kV |
|
Collision energy: |
6.0 V |
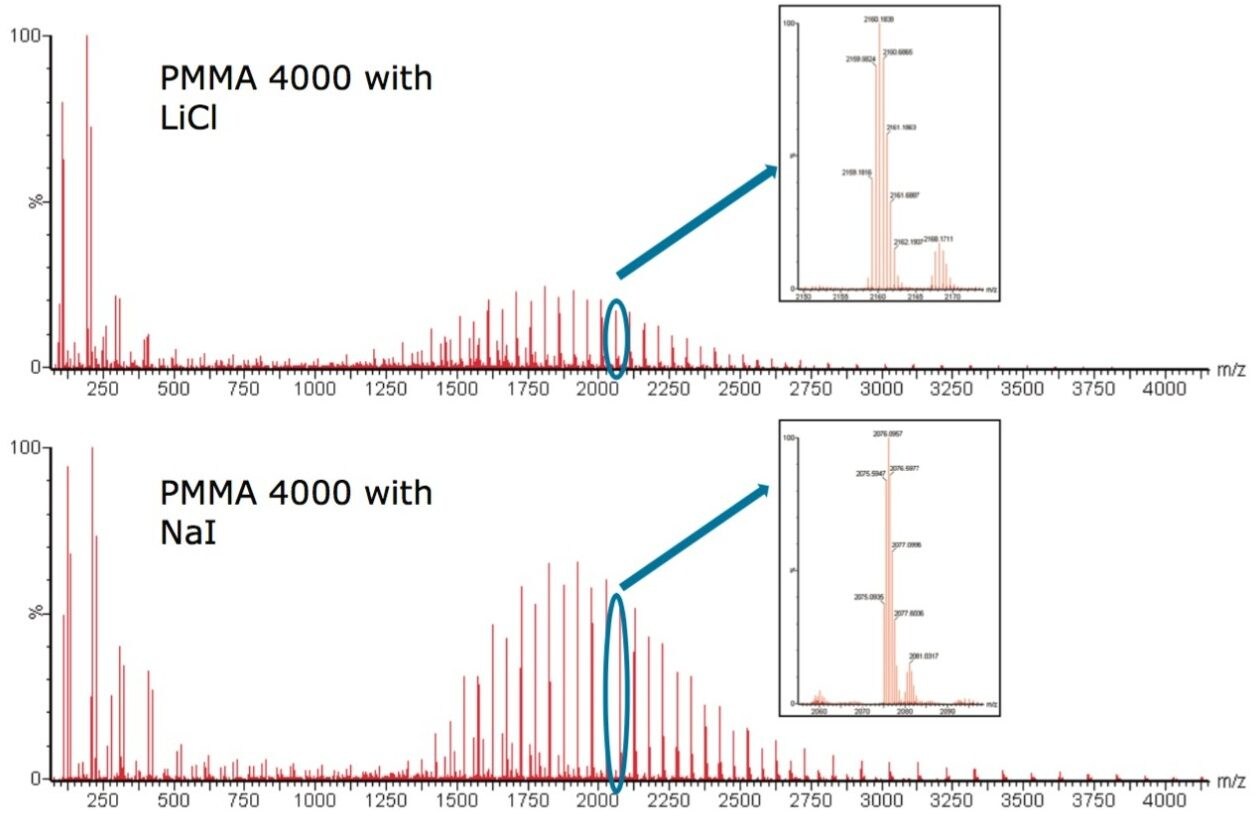
Figure 1 shows PMMA 4000 cationized with Li+ and PMMA 4000 cationized with Na+. Both singly and doubly charged ions are present in both spectra. The inserts show two ion clusters in more detail, the 0.5 m/z difference between the isotopes confirms this is a doubly charged species. We can see the majority of PMMA is present as [M + 2Li]2+ and [M + 2Na]2+.
MS/MS experiments were carried out on the abundant oligomeric ions of the 38-mer for both the lithiated and sodiated PMMA, with m/z 1910 and 1926 respectively. The spectra from the MS/MS experiments are shown in Figure 2.
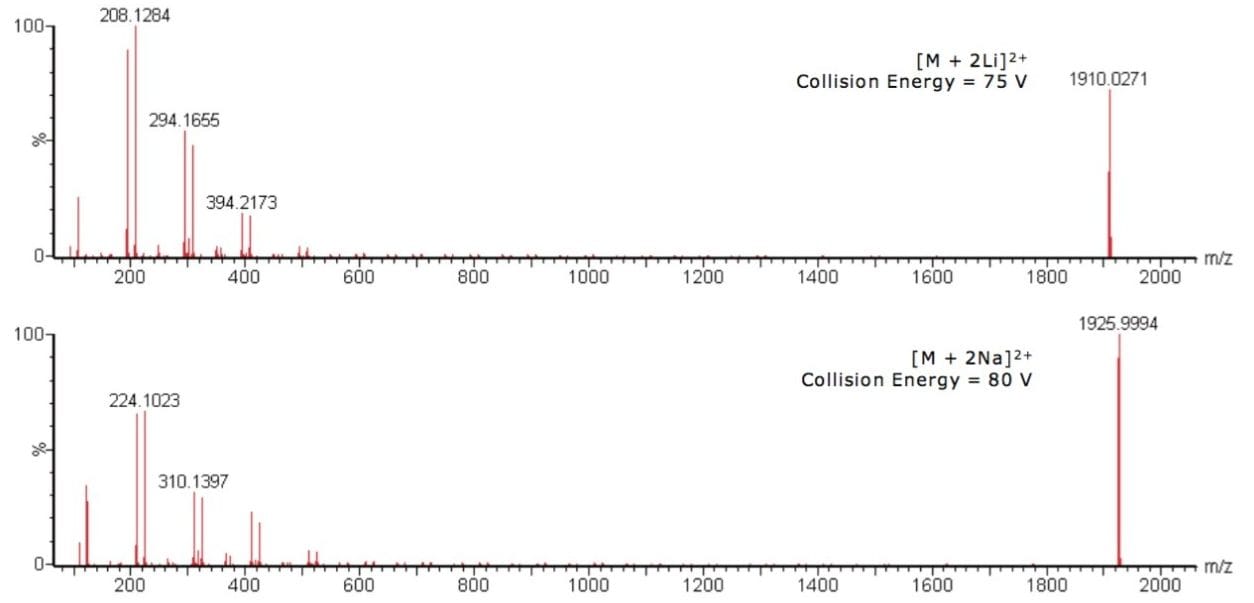
MS/MS results for the lithiated and sodiated PMMA show the same trend, each having two series of ions 100 m/z units apart. Figure 3 shows the PMMA monomer repeat unit, which has a mass of 100 Da. The sodiated results are 16 m/z units higher than the lithiated, which is consistent with the mass difference between the two cations.

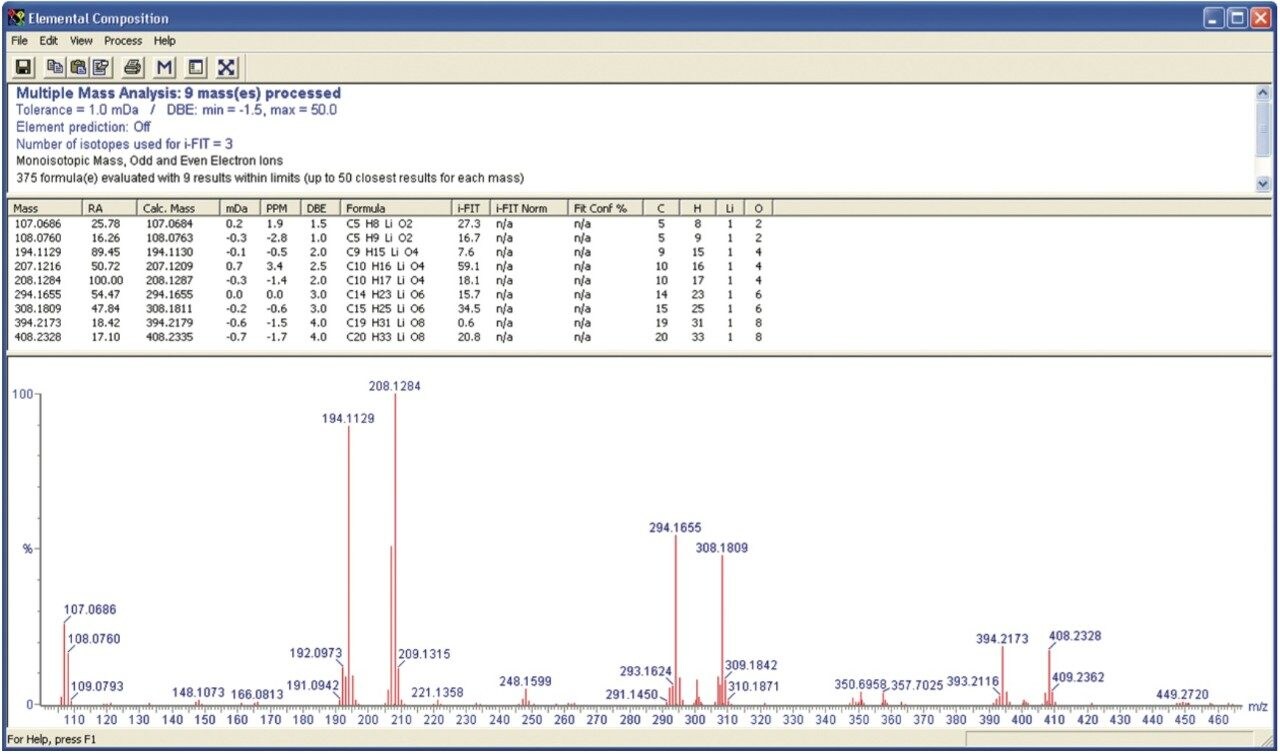
The results for lithiated PMMA have been considered in more detail using an option within MassLynx Software called Elemental Composition (EleComp). EleComp can be found in the Tools dropdown list in the Spectrum window. Figure 4 shows the EleComp results for masses above 15% relative abundance within the selected portion of the spectrum. EleComp has calculated possible formulae that could create ions of these masses. The results show that the ions of interest are within 1 mDa of the theoretical exact mass.
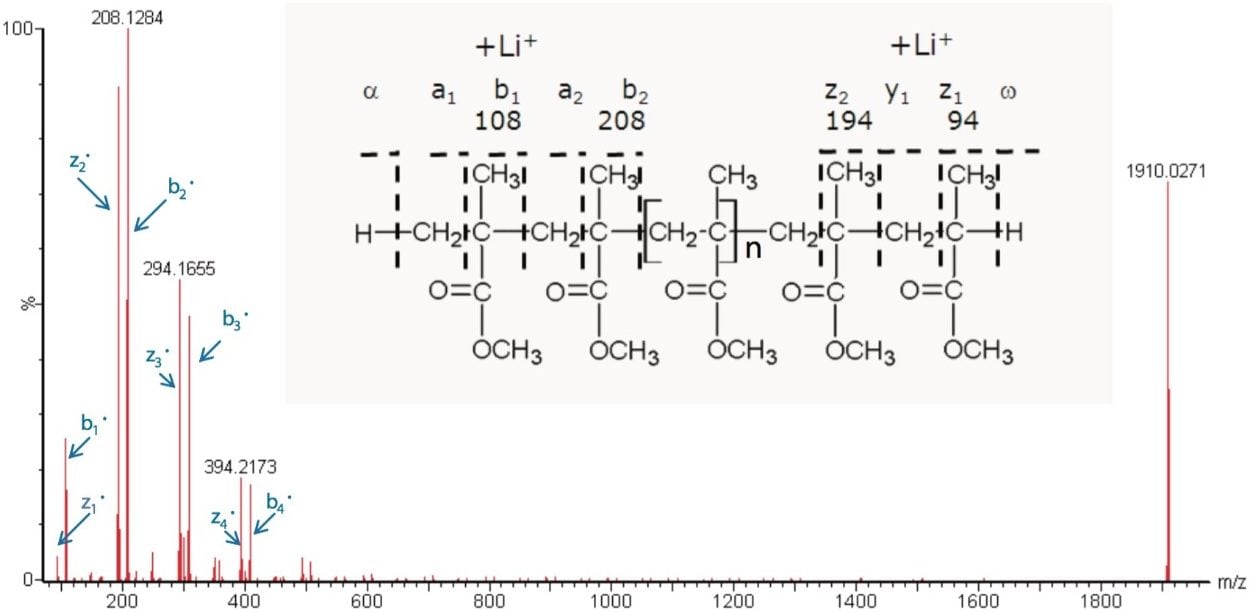
With this information it is possible to propose the structure, shown in Figure 5. Nomenclature for the fragments has been taken from the Proceedings of the 54th ASMS Conference.4
720004252, March 2012