
This application note demonstrates the use of ACQUITY UPLC coupled with Xevo TQ MS for method development and high sensitivity quantification of drugs and their metabolites from dried blood spot samples.
The high sensitivity available by combining ACQUITY UPLC with the tandem quadrupole Xevo TQ MS makes it an ideal solution for analyzing samples derived from DMPK studies in a dried blood spot format.
The collection of blood from small rodent safety studies and clinical trials onto Guthrie type filter paper cards has the potential to reduce both costs and animal usage, Figure 1. This capability has been demonstrated by Spooner et al1-4 as well as others5-7 (For further explanation see sidebar, “Blood spot cards”). Typically 15 μL of blood is spotted onto the card for each sample from which a 3 or 6 mm punch is sampled, giving a sample volume in the region of 3 to 6 μL. In this application note we present the use of ACQUITY UPLC coupled with Xevo TQ MS for method development and high sensitivity quantification of drugs and their metabolites from dried blood spot samples.
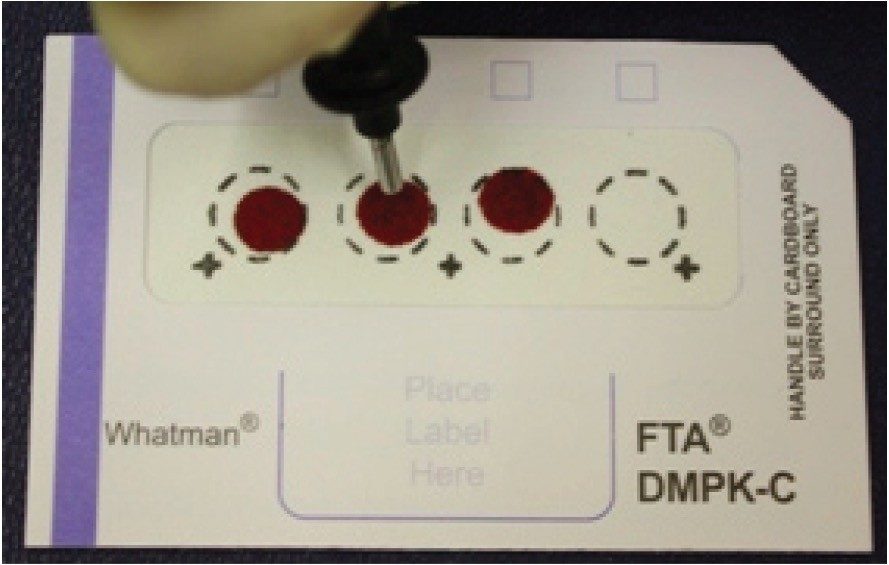

The samples, calibration line, and QCs were prepared by spiking authentic standard in solution into fresh rat blood. The samples were spotted, 15 μL, onto Whatman DMPK cards type A, B, and C. The cards were sampled using a 3-mm punch, dissolved in 100 μL of methanol, shaken for 1 hour, then centrifuged for 1 minute. The supernatant was removed and water added (1:1), before injection onto the LC-MS system.
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY UPLC System |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18, 1.7 μm, 2.1 x 50 mm |
|
Gradient: |
Reversed phase over 2 minutes |
|
MS system: |
Xevo TQ MS |
|
Ionization: |
Electrospray MS operating in positive ion mode with the simultaneous collection of both MRM and full scan MS data (RADAR mode) Collision energy, capillary voltage, and cone voltage were optimized for each individual compound |
Traditional DMPK rodent safety assessment studies produce approximately 1 mL of plasma for each sample. The plasma samples are produced from approximately 1.5 to 2 mL of blood, requiring the sacrifice of an animal for each time point. The pharmacokinetics curves produced are derived from a composite of 2 to 3 animals per time point. The use of blood spot cards as a sampling media requires that only 15 to 20 μL of blood is required for each time point. This has several advantages:
The blood spot cards are available in two main formats: treated and untreated. The treated cards are treated with chemicals to render any blood borne virus harmless, however the chemicals in the card can be dissolved during the extraction process and could interfere with the analyte signal. It is therefore critical during method development that the background signal from the card is monitored such that the chromatography can be adjusted to provide resolution from the analyte ion.
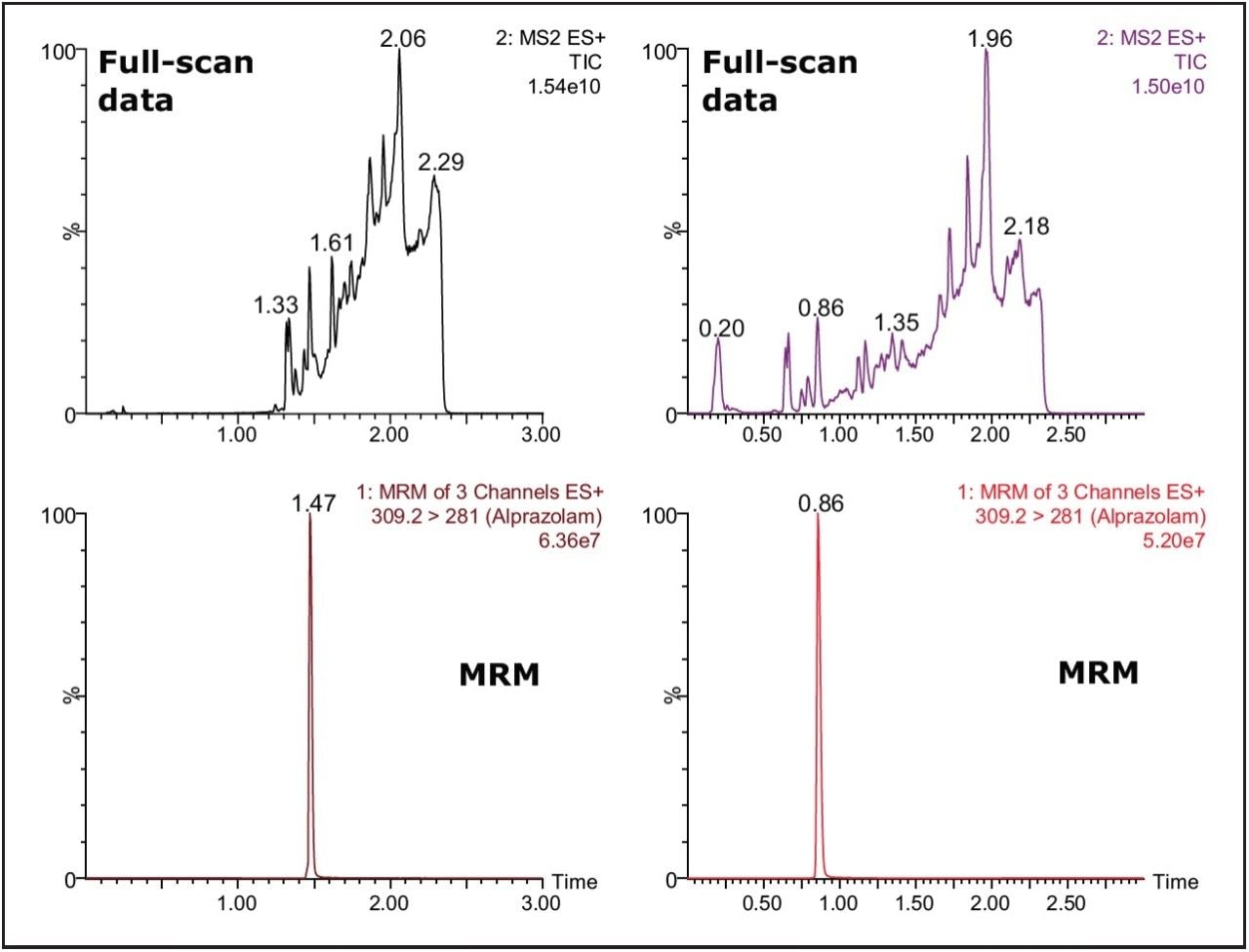
The Xevo TQ MS features a novel collision cell design, incorporating T-Wave Technology, which allows the simultaneous collection of full-scan data and MRM data using the RADAR acquisition mode. The data in Figure 2 shows the full-scan and MRM data for each of the three cards after spiking with alprazolam (1 ng/mL) in solvent and extraction with methanol.
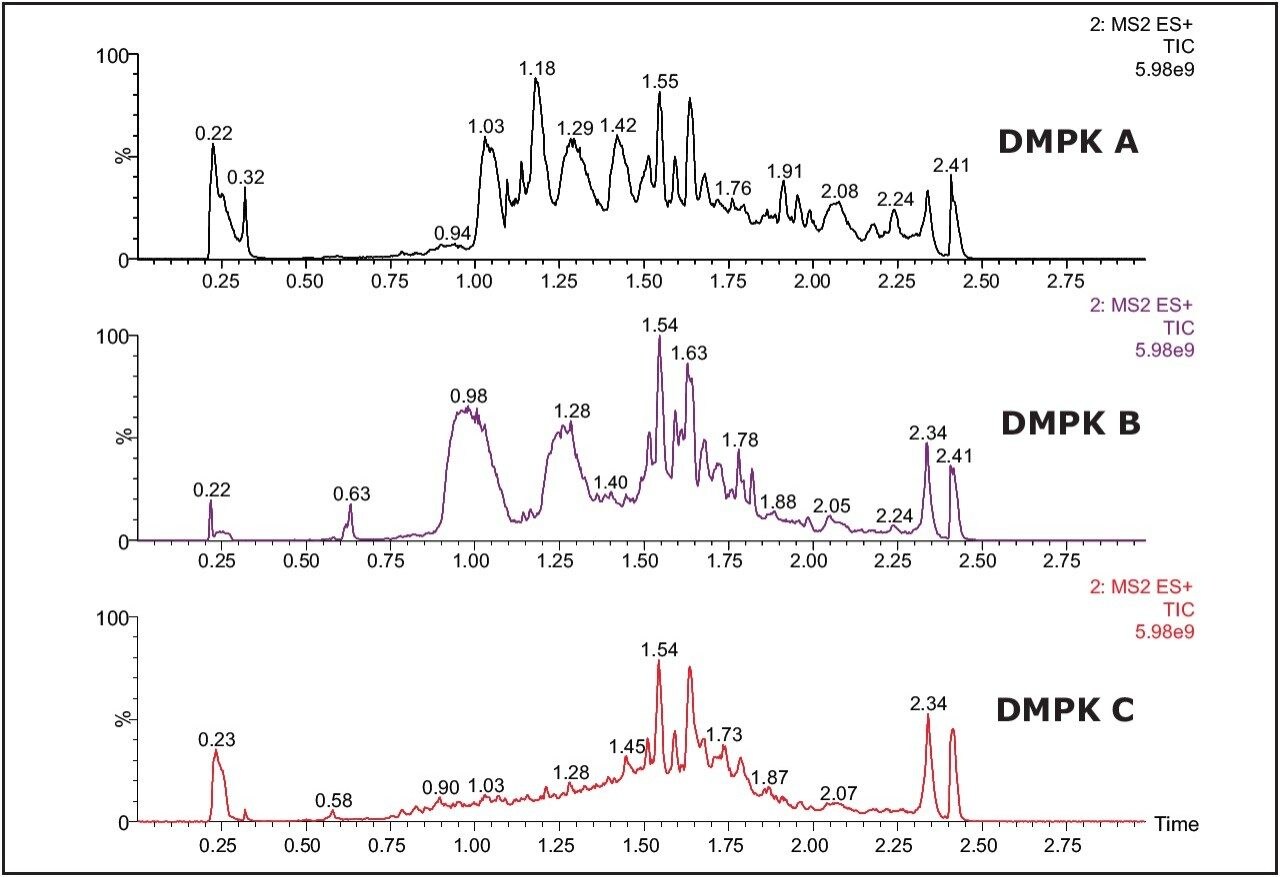
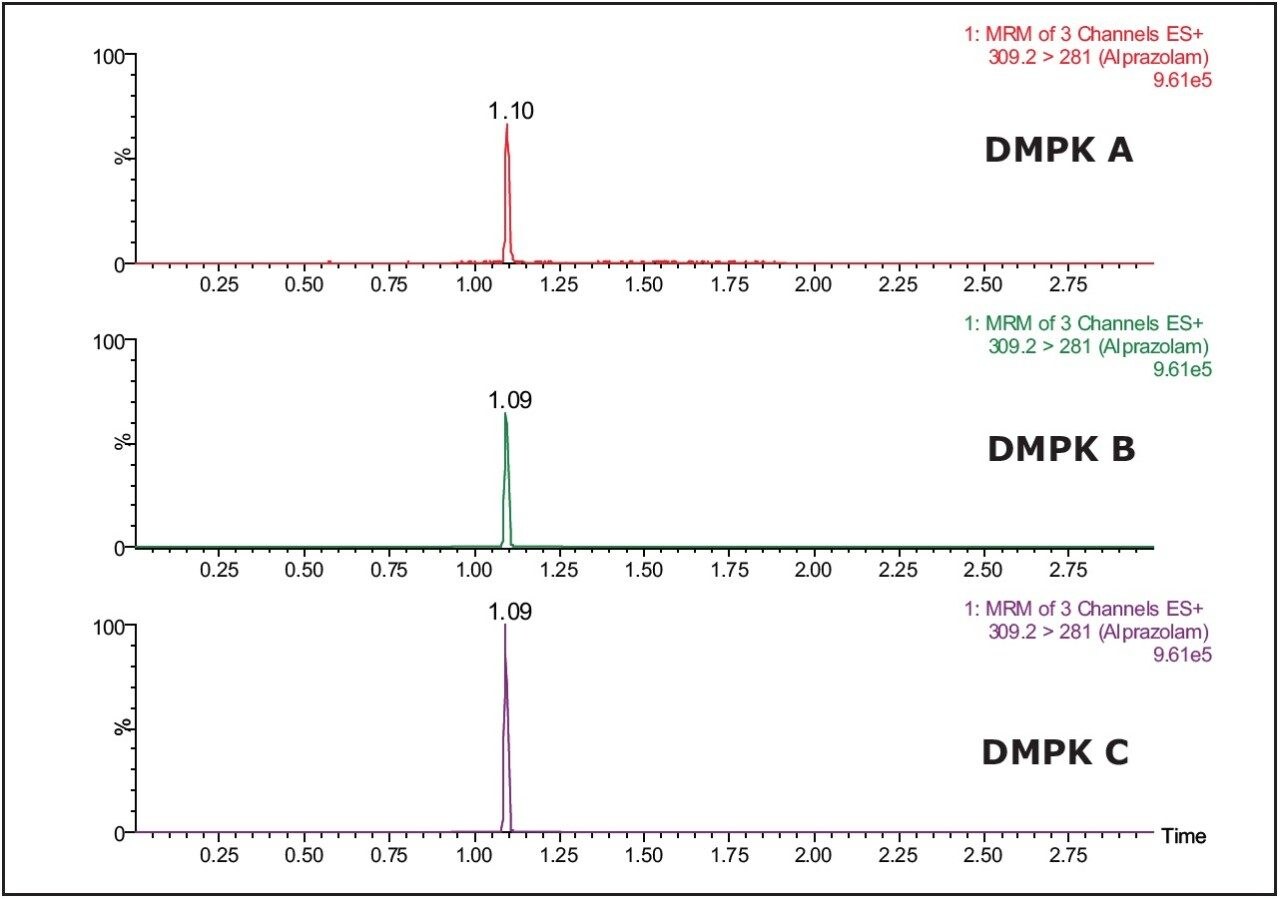
As we can see from this data, the untreated card (DMPK C) exhibits a significantly lower background signal than that of the treated cards. The full-scan MS data of each of the cards shows the treated cards have an increasingly intense ion current as the LC gradient increases. This is also reflected in the response of analyte ion where the signal is reduced with the treated cards compared to the untreated one.
The low sample spot and sampling volume means that only 3 to 6 μL of blood are actually used for the analysis. In a typical safety assessment study the compound under test is dosed once or twice a day intravenously or orally at levels of 3 to 200 mg/Kg. For a compound that is not sequestered into an organ/fat or rapidly eliminated, this results in circulating levels of the drug and/or metabolite thatare greater than 5 ng/mL at the later time points (24 hours). These levels are well within the detection range of today’s modern LC-MS/MS analytical systems when operated in MRM mode. However, for low dosed, rapidly cleared, or inhaled compounds, the circulating levels are typically much lower; in the 1 to 10 pg/mL range. Therefore greater levels of sensitivity are required from the analytical instrumentation to accurately quantify these types of samples from a dried blood spot.
UPLC Technology exploits the chromatographic potential of sub-2-μm porous particles, and has been demonstrated by many scientists to provide 3 to 5 fold more sensitivity than traditional HPLC8-10 (go online to www.waters.com/uplc for more details on UPLC). This extra sensitivity when combined with the best-in-class performance of the Xevo TQ MS provides the ideal analytical platform for the rapid analysis of DMPK samples from blood spot cards.
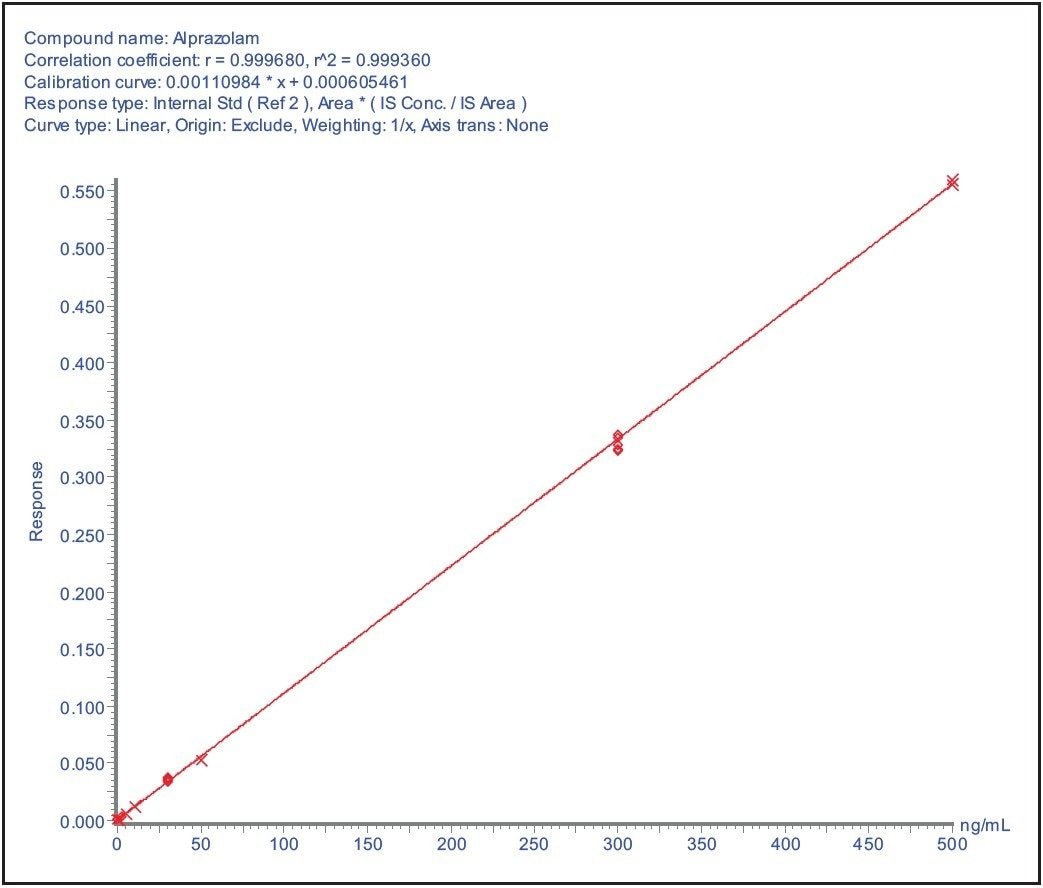
The data displayed in Figure 3A shows the LLOQ and blank from the analysis of alprazolam in spiked into blood and spotted (15 μL) onto a blood spot card. The calibration line, Figure 3B, shows that the analysis was linear over the range of 100 pg/mL to 500 ng/mL. For this assay it was not necessary to obtain a lower level of sensitivity; however the LLOQ could be lowered to 10 pg/mL by injecting a larger volume of sample. This assay sensitivity level should be sufficient to define the pharmacokinetics of all but the lowest exposure compounds.
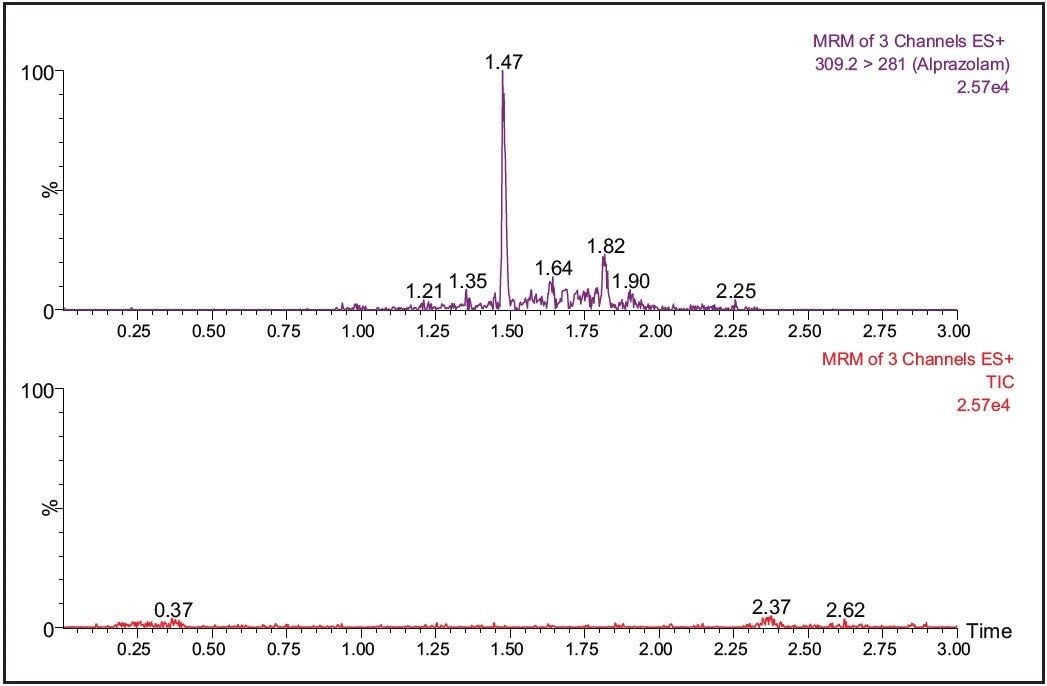
During the method development process for a conventional DMPK study, it is necessary to adjust the chromatography to minimize the coelution of the analyte of interest from endogenous components in the matrix. When developing methods for dried blood spots there is the further complication of background matrix from the card, which must also be resolved from the analyte molecule. The ability of the Xevo TQ MS to simultaneously collect MRM and full-scan data in RADAR mode allows the scientist to monitor the analyte signal and the background signal at the same time. This allows the background signal of the sample to be monitored for interferences which may cause ion suppression. The analyte peak can then be manipulated to a position in the chromatogram with minimal interference.
The data shown in Figure 4 illustrates the MRM and full-scan signal for the analyte drug molecule and background signal from two different chromatography conditions. We can see from this data that the chromatogram on the right of Figure 4 has less background interference than the chromatogram on the left.
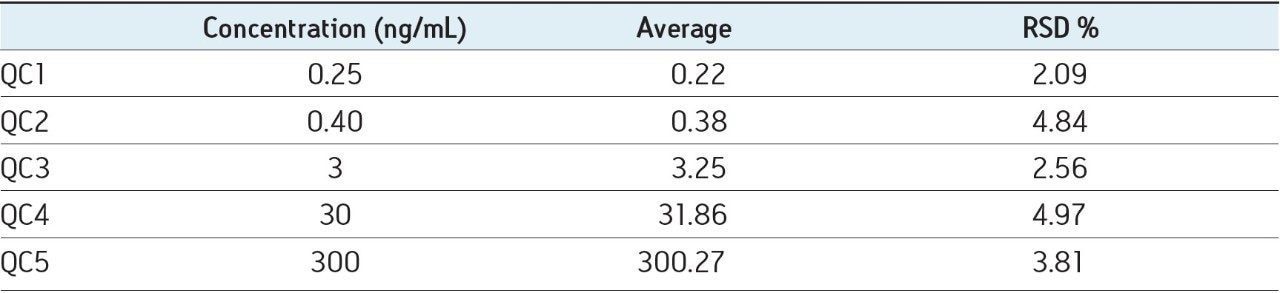
A requirement of any bioanalytical assay is that it is reliable and reproducible. To evaluate the reproducibility of the blood spot assay, a calibration line and QCs were produced in blood, spotted onto the cards, extracted, and analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS. The data presented in Table 1 show the reproducibility of the QC data. We can see from this data that the reproducibility across the QCs ranged from 2.08% to 4.9%. This data gives confidence that the high sensitivity assays can be developed with good reproducibility using blood spot cards and UPLC-MS/MS.
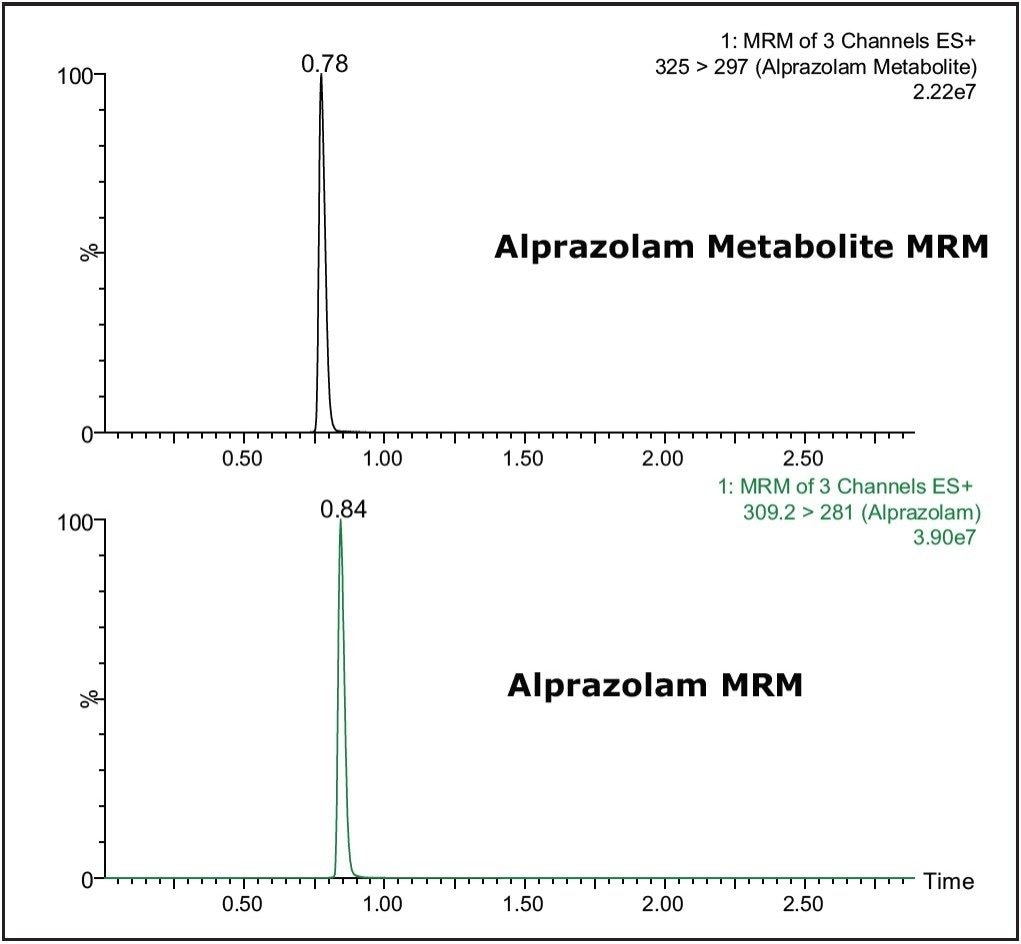
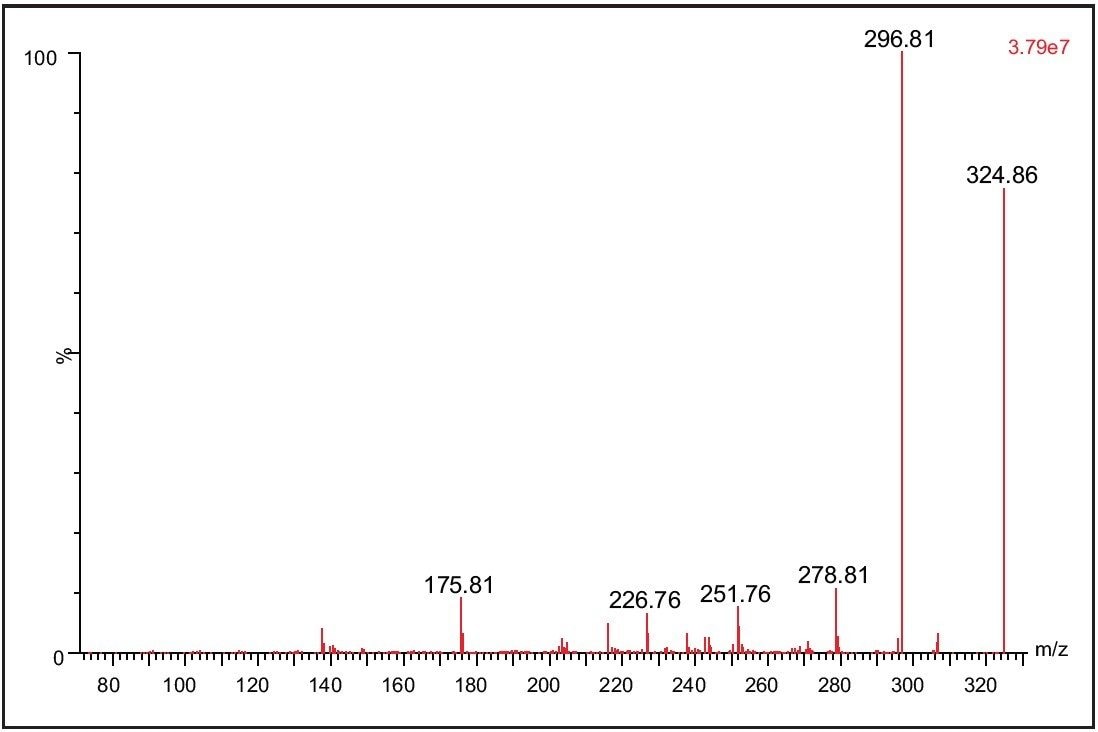
The detection and quantification of metabolites is a necessary part of modern bioanalysis. Using its RADAR acquisition mode, the Xevo TQ MS is able to collect in a single analytical run both MS and MRM data, which can be exploited to detect and confirm the identity of drug metabolites during a bioanalysis assay. The data displayed in Figure 5 show the detection of the 4-hydoxy metabolite of Alprazolam from a sample derived from a dried blood spot. The MS/MS spectra acquired from the metabolite peak was triggered from the MRM signal related to the metabolite peak. The spectrum was obtained on the trailing edge of the peak using the enhanced sensitivity mode of ScanWave. The increased sensitivity of the Scan Wave MS/MS data acquisition approach increases the scientists’ capability to confirm the identity of metabolite peaks during a bioanalysis assay.
The collection of samples derived from DMPK studies in a dried blood spot format offers a great opportunity to reduce animal usage while also reducing operating costs. The lower sample volumes produced from these dried blood spot assays requires increased assay sensitivity for low dosed and low exposure compounds. The increased sensitivity produced by the ACQUITY UPLC/Xevo TQ MS system combination addresses the issue of assay sensitivity. The system’s dual scan MRM capability simplifies methods development allowing the analyte to be resolved from the endogenous blood components and the chemicals present in the blood spot cards, while also ensuring the analyte is resolved from its metabolite(s).
720003408, March 2010