
This application note summarizes the performance and verification of the USP Fluconazole Related Compounds method on the Alliance HPLC System with a Waters 2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector.
Fluconazole is a synthetic bis-triazole fungicide. It works by inhibiting a fungal P450 enzyme involved in the synthesis of a specific membrane component, blocking its formation. The overall action of fluconazole is primarily fungistatic, though fungicidal activity is seen in some species of fungi at higher dosing levels. This increased dosing is the usual treatment path for systemic Candida spp. infections. As these higher doses of fluconazole are used in the treatment of systemic infections, the purity of the drug compound, already critically important, becomes paramount.
USP related compound analysis in the QC lab requires a sensitive and repeatable assay performed on a robust and reliable instrument.
Precise pumping, stable mixing, and accurate sample injection, among others, are important characteristics of an LC system in the QC lab. The Waters Alliance HPLC System delivers this high level of performance.
When a compendial assay is first adopted into a QC laboratory, it is customary and prudent to perform method verification. This is to achieve compliance with regulatory guidelines, but it is also sound science. Fulfilling the suitability/acceptance criteria of the USP monograph for the method is a good first step, but further documentation of selected, meaningful analytical parameters can provide a valuable understanding of the assay.
This application note summarizes the performance and verification of the USP Fluconazole Related Compounds method on the Alliance HPLC System with a Waters 2998 Photodiode Array (PDA) Detector.
Standards for this analysis were procured from the United Sates Pharmacopeia (USP). All suitability, standard, and test solutions for this analysis were made according to the USP.1
In this study, experiments were performed to verify and document the specificity, precision, and limit of quantitation (LOQ) of this HPLC method. These three parameters are of primary concern to those running related compounds methods and provide meaningful data for the evaluation of the assay. Only combined standards containing all three related compounds and fluconazole were used to determine assay characteristics.

|
LC System: |
Alliance e2695 Separation Module |
|
Column: |
Atlantis dC18 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 μm(Part No. 186001342) |
|
Column temperature: |
40 °C |
|
Sample temperature: |
15 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
20 μL |
|
Mobile phase: |
80/20 water/acetonitrile, isocratic with pump mixing |
|
Flow rate: |
0.5 mL/min |
|
Run time: |
15 min |
|
Detection: |
2998 PDA Detector |
|
PDA wavelength: |
260 nm at 1.2 nm |
|
Date rate: |
5 Hz, filter time constant:normal |
The Fluconazole Related Compounds method was performed smoothly on the Alliance HPLC System and the Atlantis dC18 Column, which yielded a high quality separation, as shown in Figure 2. All USP criteria for this assay were easily exceeded, detailed in Table 1.
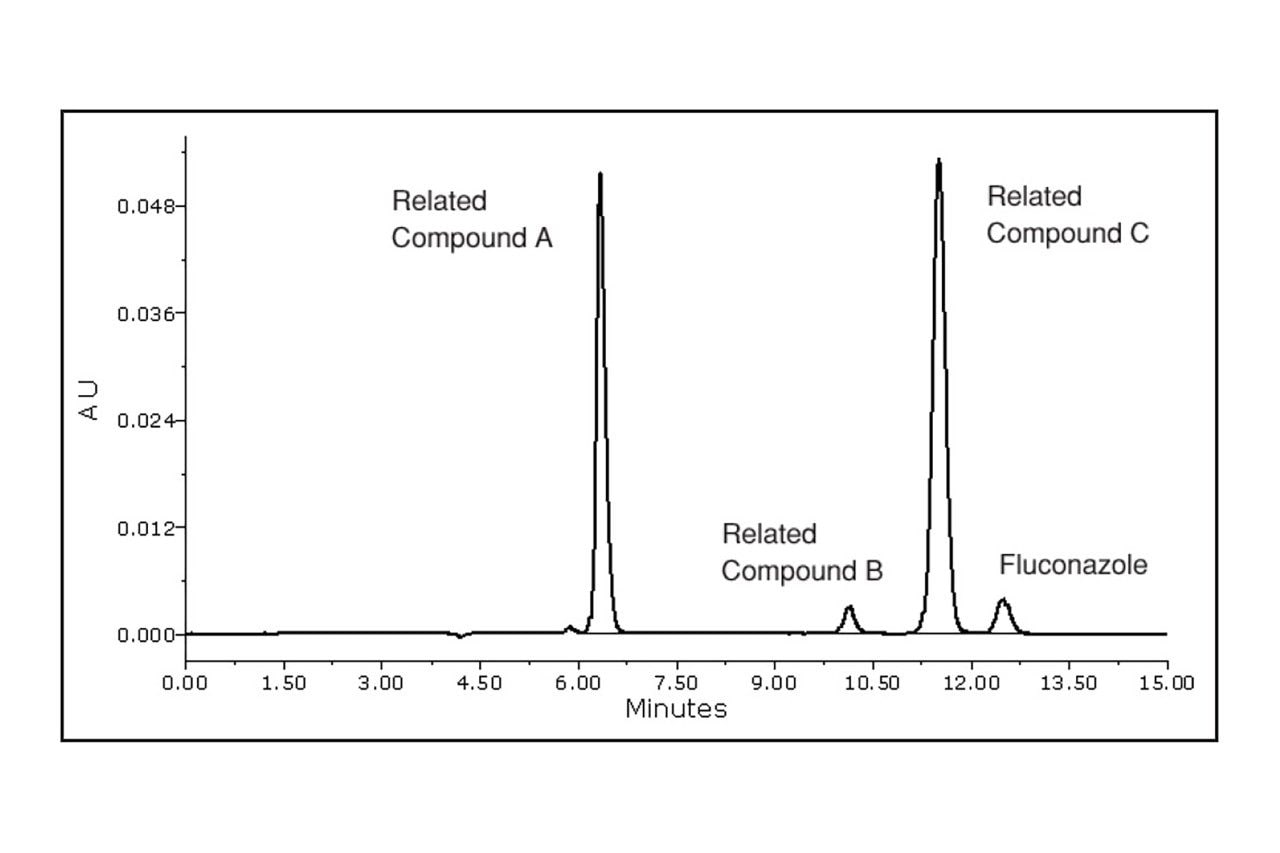
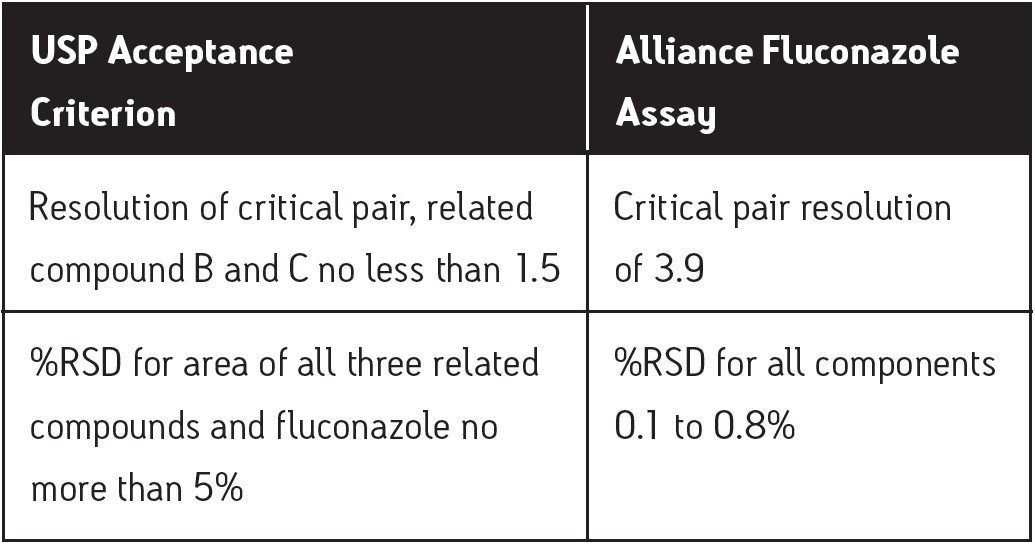
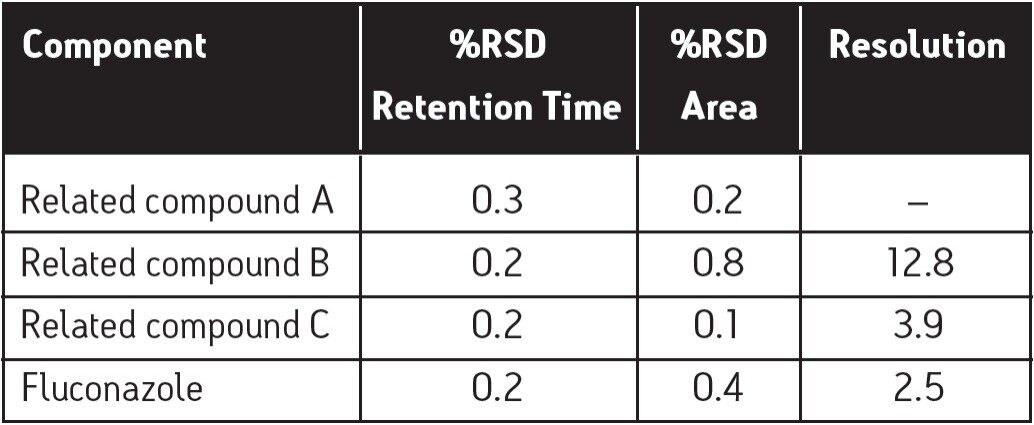
Specificity is a measure of how well a method separates an analyte of interest from possible interferences. The primary specificity parameter of the fluconazole assay is the resolution between related compounds B and C. Adequate resolution for this critical pair implies adequate resolution throughout the assay. In this study, the resolution result between B and C was 3.9, which indicates ample resolution compared to the USP criterion of 1.5. Table 2 gives the resolution results for all of the components of the suitability standard. Based upon these results, this assay demonstrates good specificity.
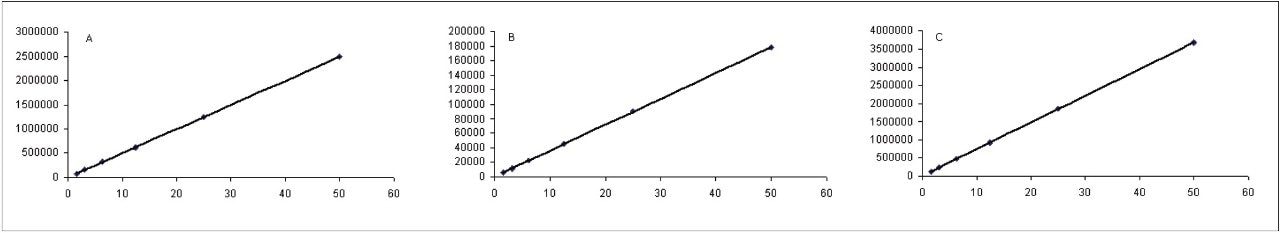
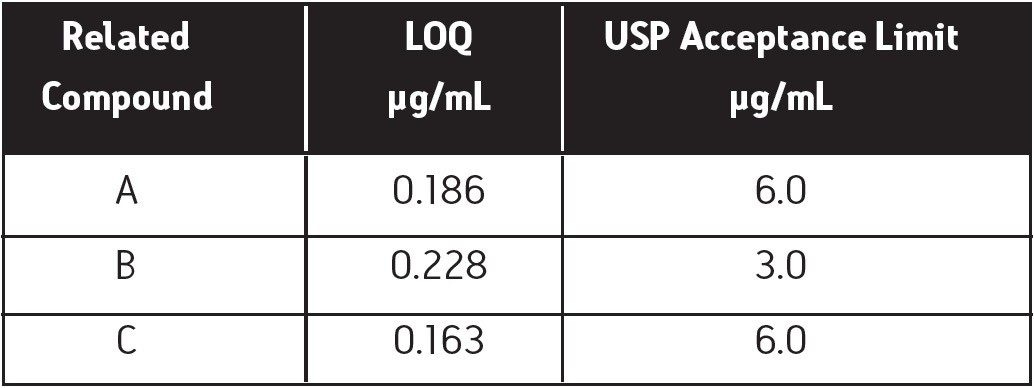
The limit of quantitation was calculated from the residual standard deviations of the linear calibration curve for each related compound. The concentration range of the plots was 0.15 to 50.00 μg/mL, with each combined standard containing the test solution concentration of fluconazole. The plots were highly linear with all R2 values above 0.999, as shown in Figure 3. Table 3 shows the LOQ for each related compound and its associated USP acceptance limit. The limits of quantitation determined from this experiment were much lower than the USP acceptance limits, which indicates the excellent sensitivity of this analysis. Analysis of a test solution of fluconazole containing spiked related compounds at their LOQs further confirms the ability of the assay to resolve and detect the fluconazole related compounds in the presence of interferences, as shown in Figure 4.

720002922, January 2009