Peptide and oligonucleotide mapping are essential processes for confirming identity, purity, and sequence of complex biomolecules like proteins and RNA therapeutics. Designed for LC-MS analysis of modern biotherapeutics, RapiZyme enzymes deliver fast, reproducible digestions for:
These tools enable robust, high-resolution characterization workflows for modern biotherapeutics for LC-MS users. Improve your sample turnaround time, lab operations, and make critical decisions confidently and quickly with Waters solutions.

Comparison of 1:5 digests, another industry-leading competitor (top panel) vs. RapiZyme trypsin (bottom panel), with zoomed section of retention time window 14 to 40 min. Red arrows highlight trypsin autolysis and unknown peaks.
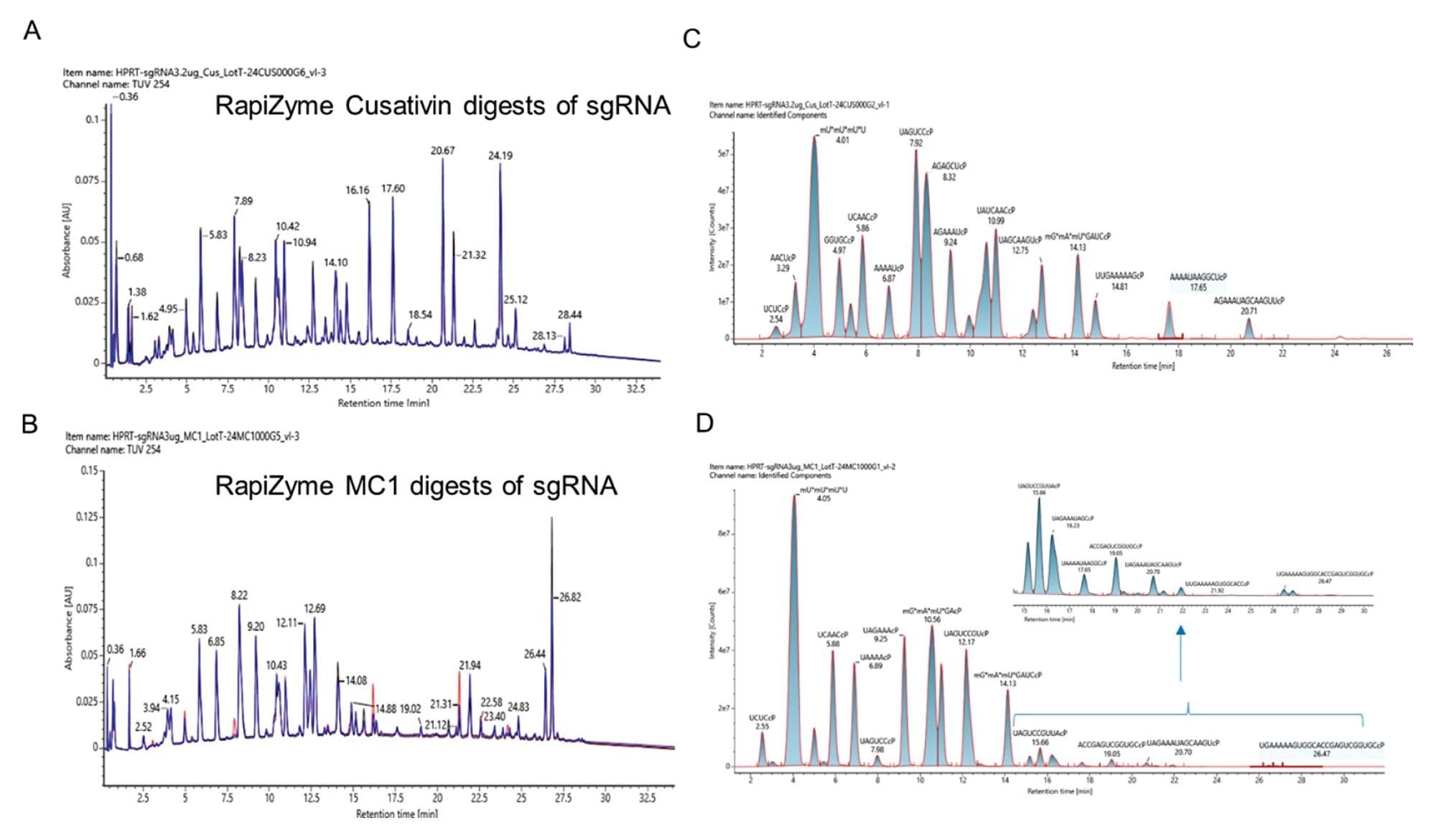
LC-UV-MS analysis of the HPRT sgRNA digested with recombinant RapiZyme Cusativin and MC1. Three independent recombinant enzyme batches of RapiZyme Cusativin (A) and RapiZyme MC1 (B) were used to digest HPRT sgRNA and the three UV chromatograms (black, blue and red traces) are overlayed on top of each other to indicate the reproducible digestion behavior of three preparations. (C) Extracted ion chromatogram overlay of the identified RapiZyme Cusativin digestion products indicating their abundance in the representative TUV trace. (D) Extracted ion chromatogram overlay of the identified RapiZyme MC1 digestion products indicating their abundance in the representative TUV trace. Low abundant digestion product profile of RapiZyme MC1 digestion products are shown in the inset figure.
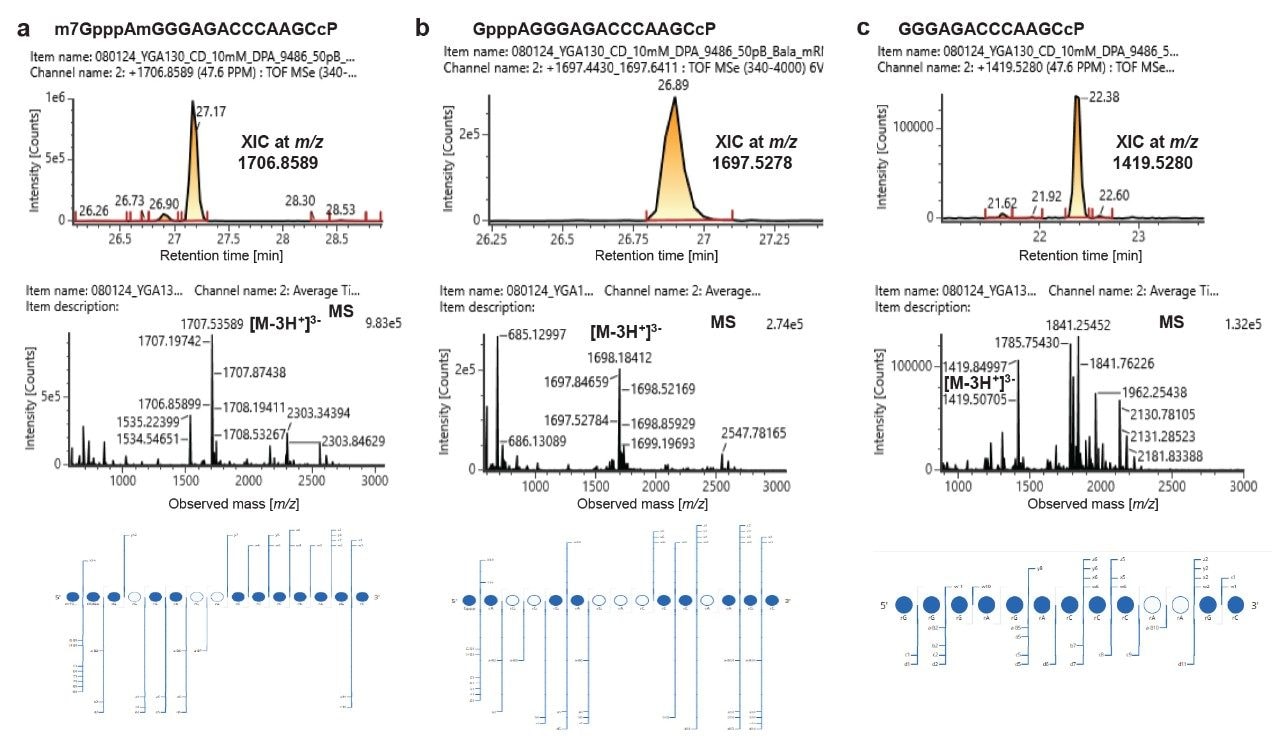
Characterization of different forms of 5’-capped oligonucleotides in the RNase MC1 digest of mRNA 1 (XIC is top panel, mass spectrum is middle panel, dotmap of MSE fragment ions is bottom panel). Detection of capped oligonucleotide (a), unmethylated form of cap version (b), and uncapped version (c).
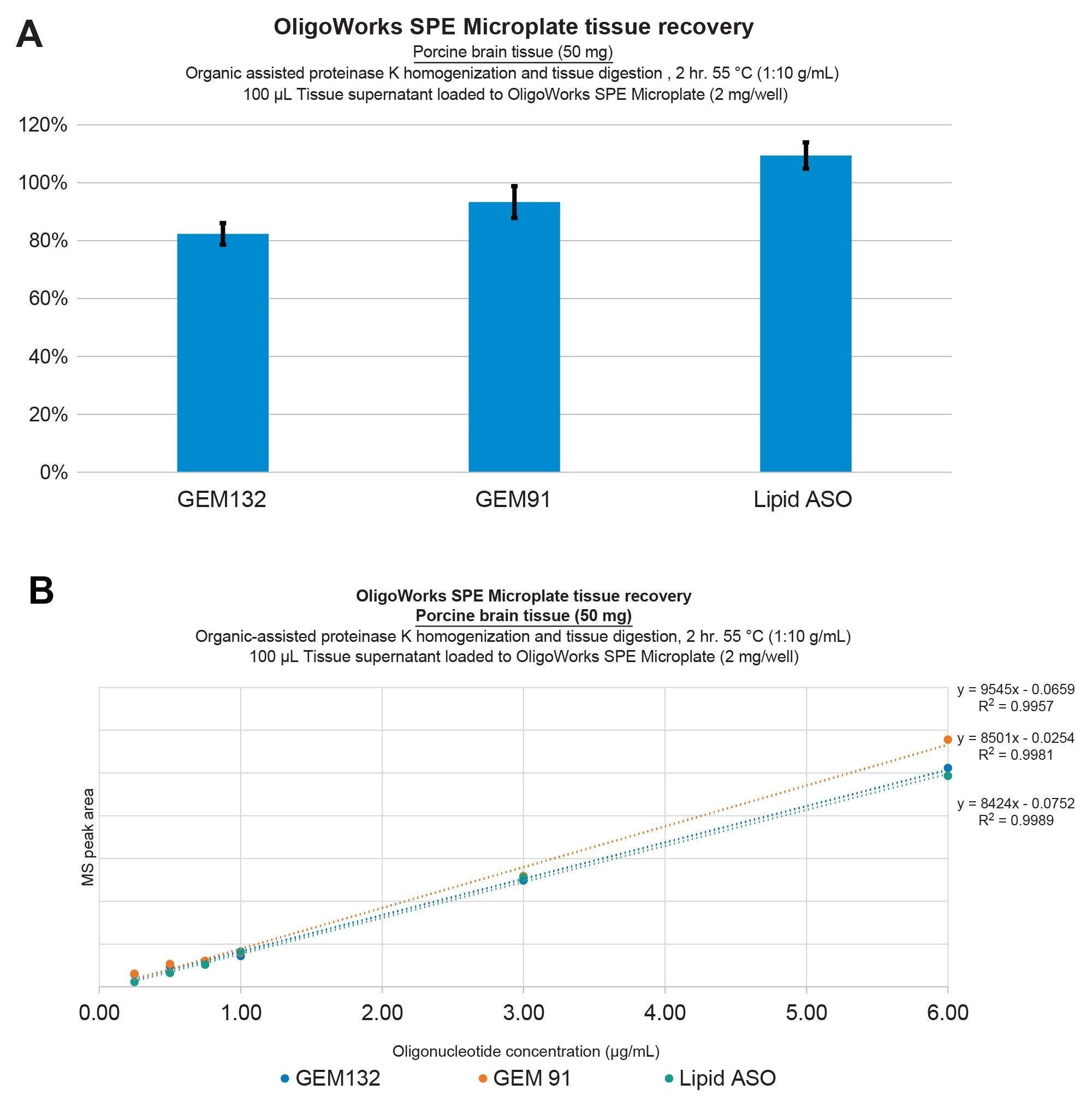
Demonstration of oligonucleotide extraction performance for GEM91, GEM132, and the lipid conjugated ASO from Porcine Brain Tissue. Recoveries were determined to be ≥80% with excellent repeatability (SDs ≤10%) (A) Extraction linearity was determined to be ≥0.99 with no internal standard correction (B) using solvent-assisted Proteinase K tissue homogenization and digestion, followed by mixed-mode SPE purification using the OligoWorks SPE Microplate and reagents.
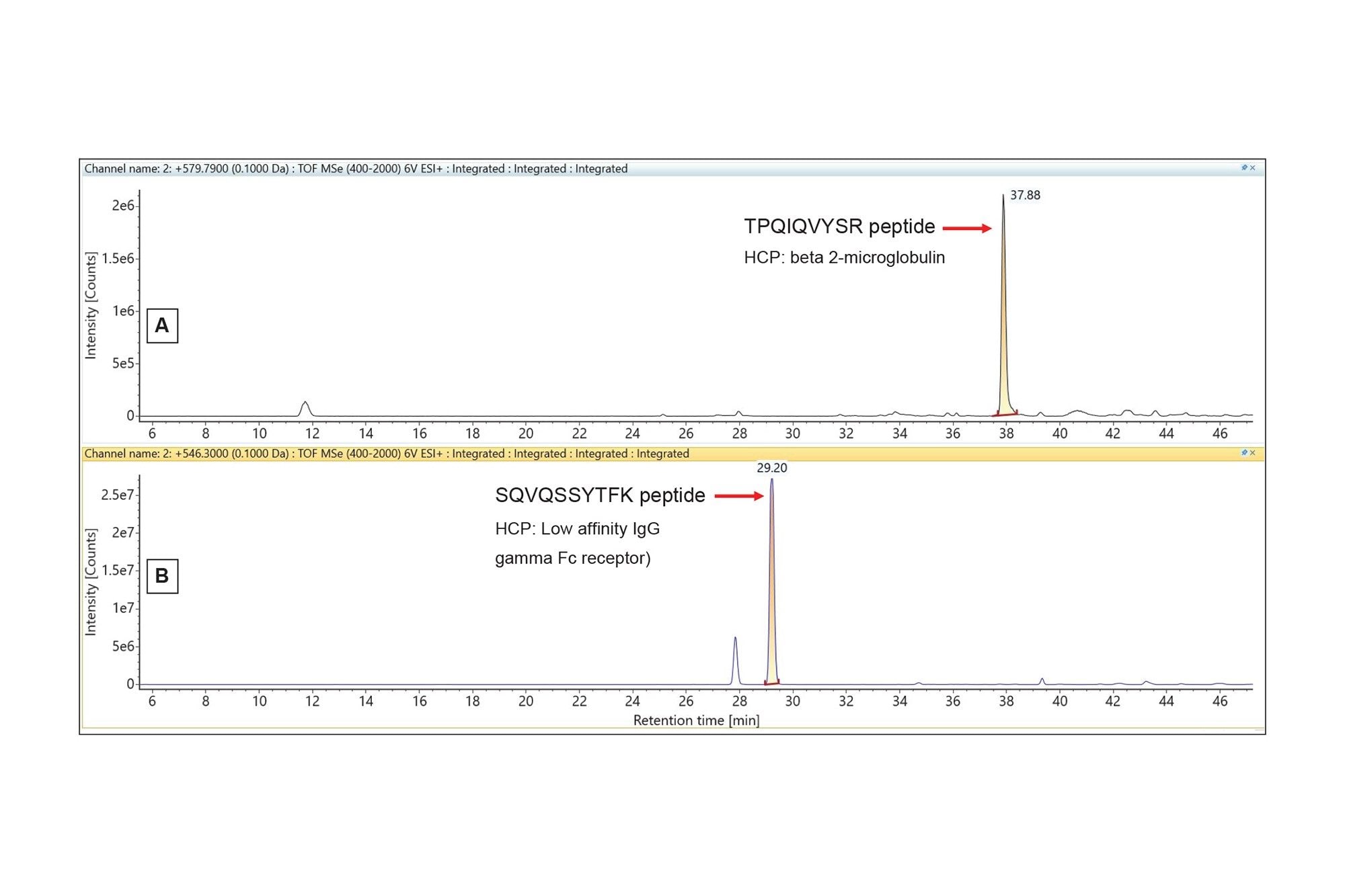
Extracted mass chromatograms for two lower-abundance HCP peptides identified in the NIST mAb digest using the Discovery HCP Assay.