With the release of the 2013 Alliance HPLC System, this application note shows equivalency of the Waters Alliance System for Carbamate Analysis and 2013 Alliance HPLC System relative to linearity, precision, reproducibility, and limit of detection (LOD). The data shows that similar results are obtained on the legacy and 2013 Alliance HPLC systems for Carbamate Analysis.
Waters Alliance System for Carbamate Analysis provides a complete system solution for the analysis of N-methylcarbamate and N-methylcarbamoyloxime pesticides in drinking water and a variety of environmental and food matrices.
The Waters Alliance System for Carbamate Analysis has been offered as a system solution since 1998. With the release of the 2013 Alliance HPLC System, we wish to show equivalency of the two platforms relative to linearity, precision, reproducibility, and limit of detection (LOD).

|
System: |
Alliance HPLC for Carbamate Analysis (both legacy and 2013 systems) |
|
Run time: |
25.0 min |
|
Column: |
Waters Carbamate 3.9 x 150 mm, 4.0 μm at 30 °C |
|
Mobile phase A: |
Water |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Methanol |
|
Mobile phase C: |
Acetonitrile |
|
Flow rate: |
1.5 mL/min |
|
Injection volume: |
400 μL (1000 μL for 0.2- and 0.1-ppb levels) |
|
Detection: |
Fluorescence (Ex-339 nm, Em-445 nm) |
|
Data management: |
Empower 2 Software |
|
Time (min) |
Flow rate (mL/min) |
%A |
%B |
%C |
Curve |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Initial |
1.5 |
88 |
12 |
0 |
* |
|
5.3 |
1.5 |
88 |
12 |
0 |
1 |
|
5.4 |
1.5 |
68 |
16 |
16 |
5 |
|
14.0 |
1.5 |
68 |
16 |
16 |
3 |
|
16.1 |
1.5 |
50 |
25 |
25 |
7 |
|
20.0 |
1.5 |
50 |
25 |
25 |
6 |
|
22.0 |
1.5 |
88 |
12 |
0 |
5 |
The basic system, components, and experimental procedure are described in the Waters Alliance System for Carbamate Analysis Method Manual.1
Two reference materials, M531M and M531-IS, were purchased from AccuStandard. These were diluted with preservation solution2 to prepare the following levels: 100-, 75-, 50-, 25-, 10-, 5-, and 1-ppb. 0.2- and 0.1-ppb mixes were also prepared. These levels were also run as unknowns for the tests described in this study.
The seven levels described above were injected in triplicate to construct a linear calibration curve.
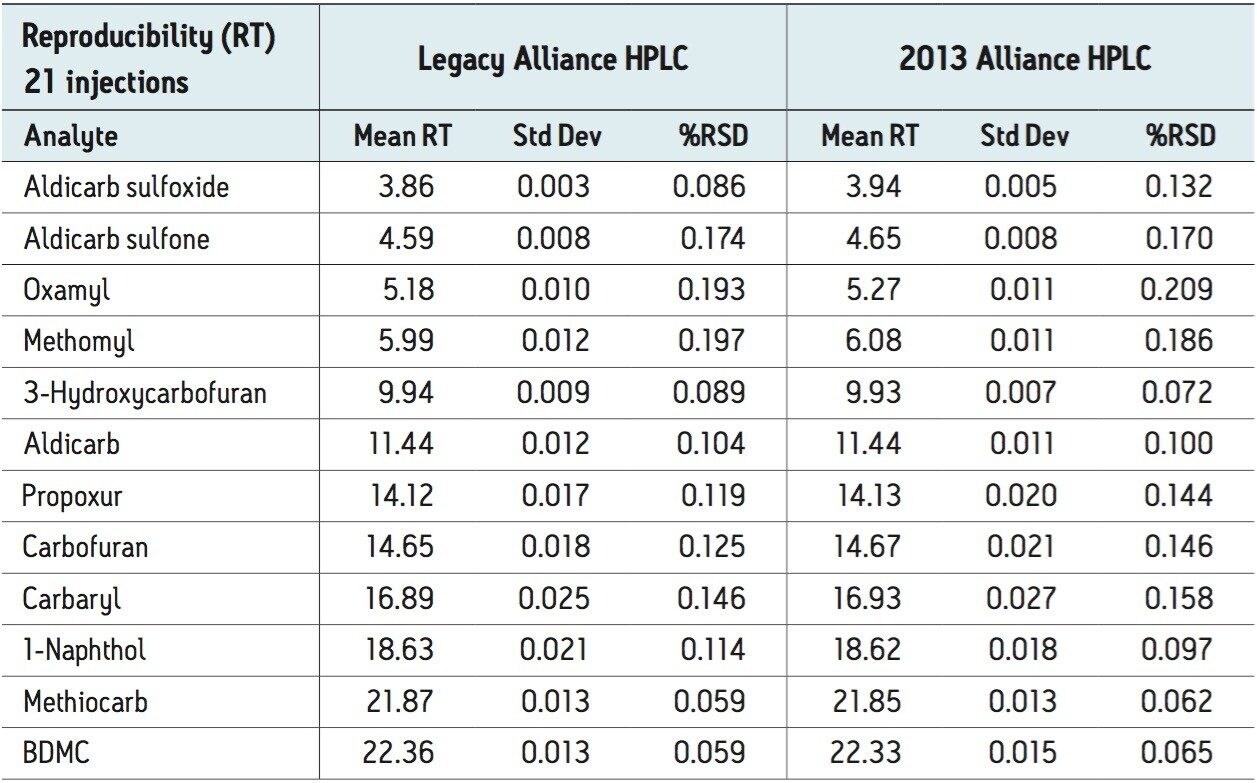
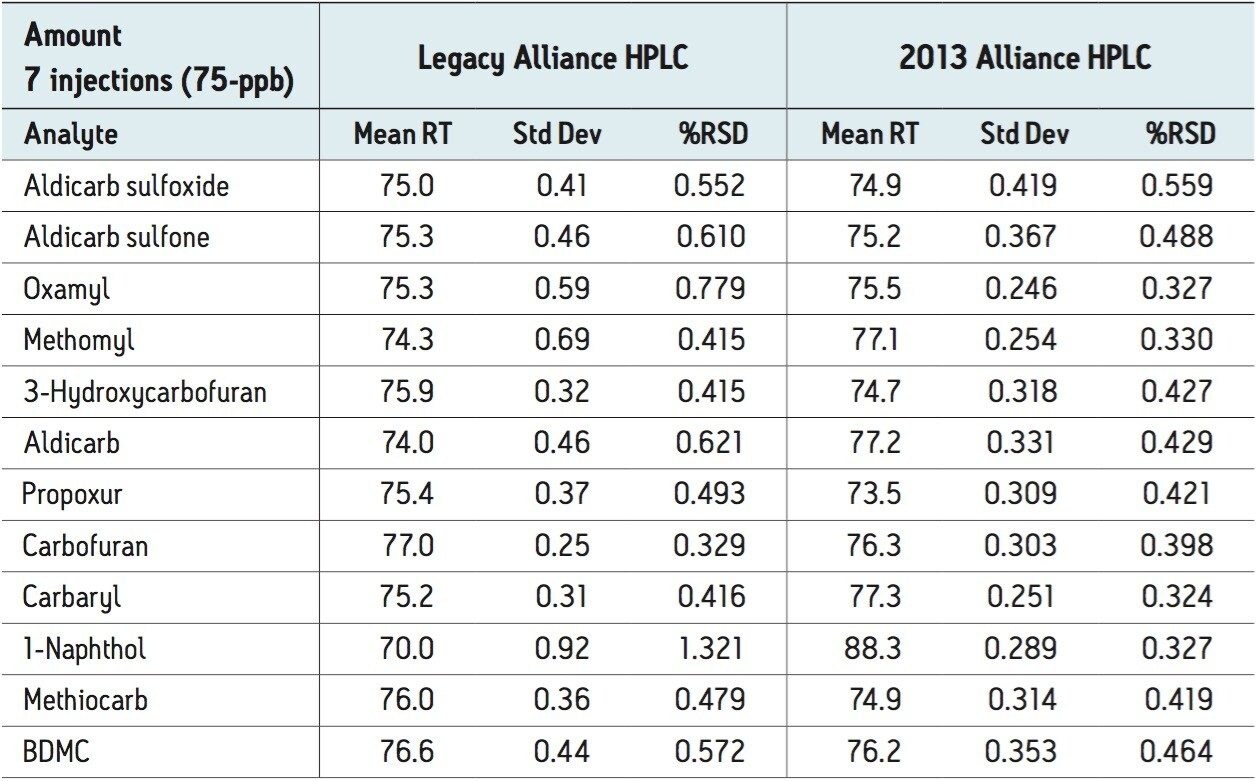
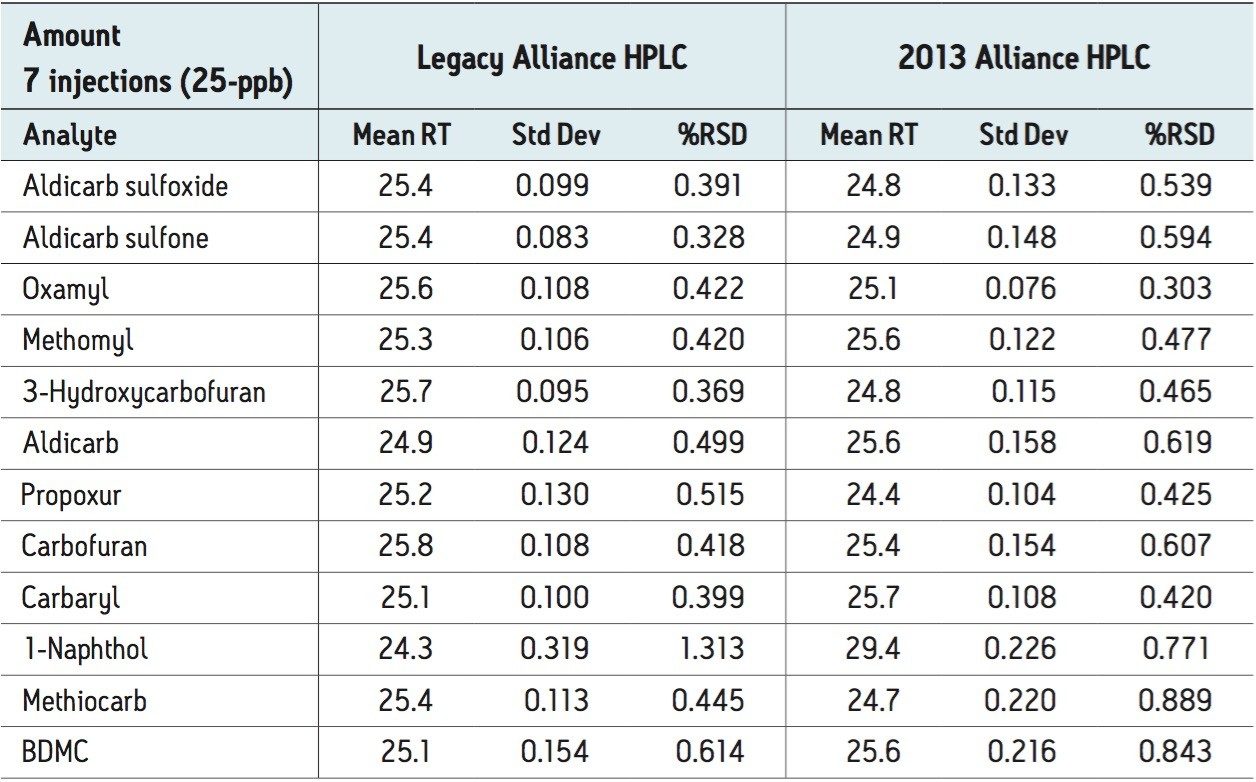
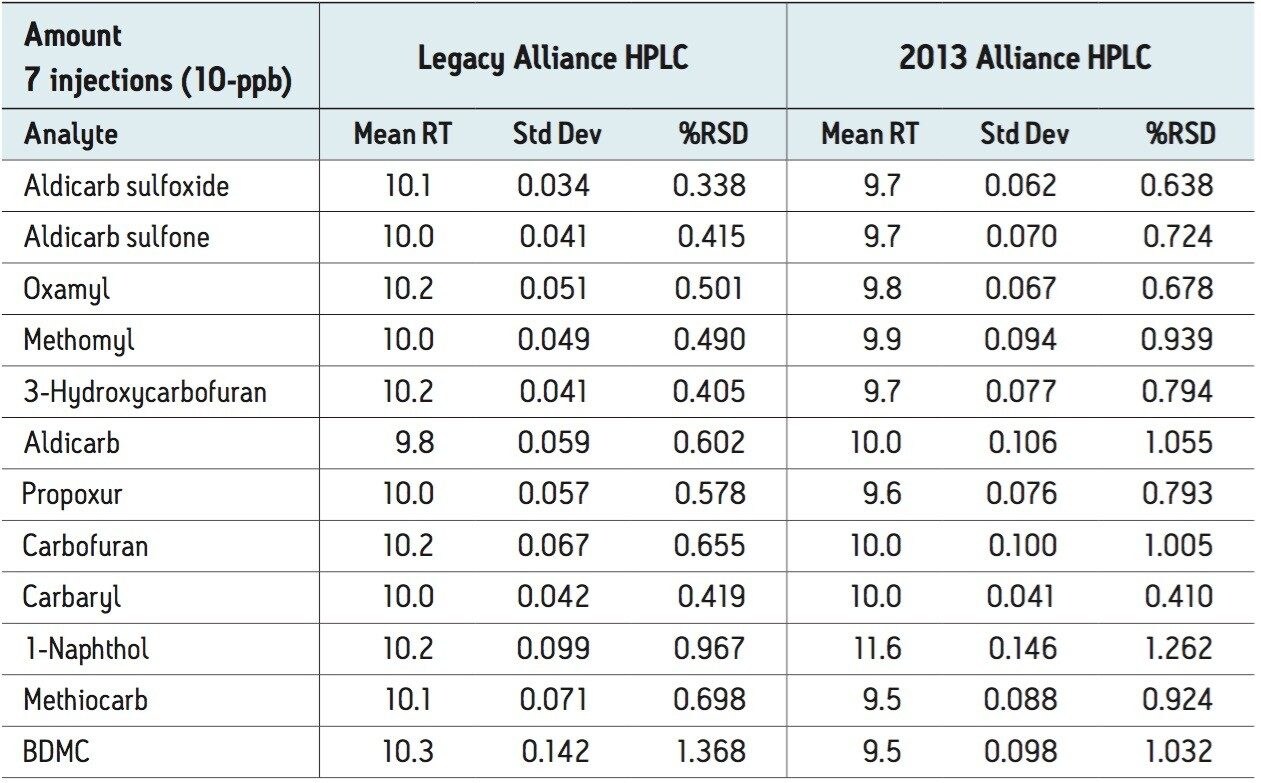
The 75-, 25-, and 10-ppb levels were injected seven times as unknowns to determine precision and reproducibility for amount. The 21 injections (seven of each of the three levels) were used to determine precision and reproducibility for retention time.
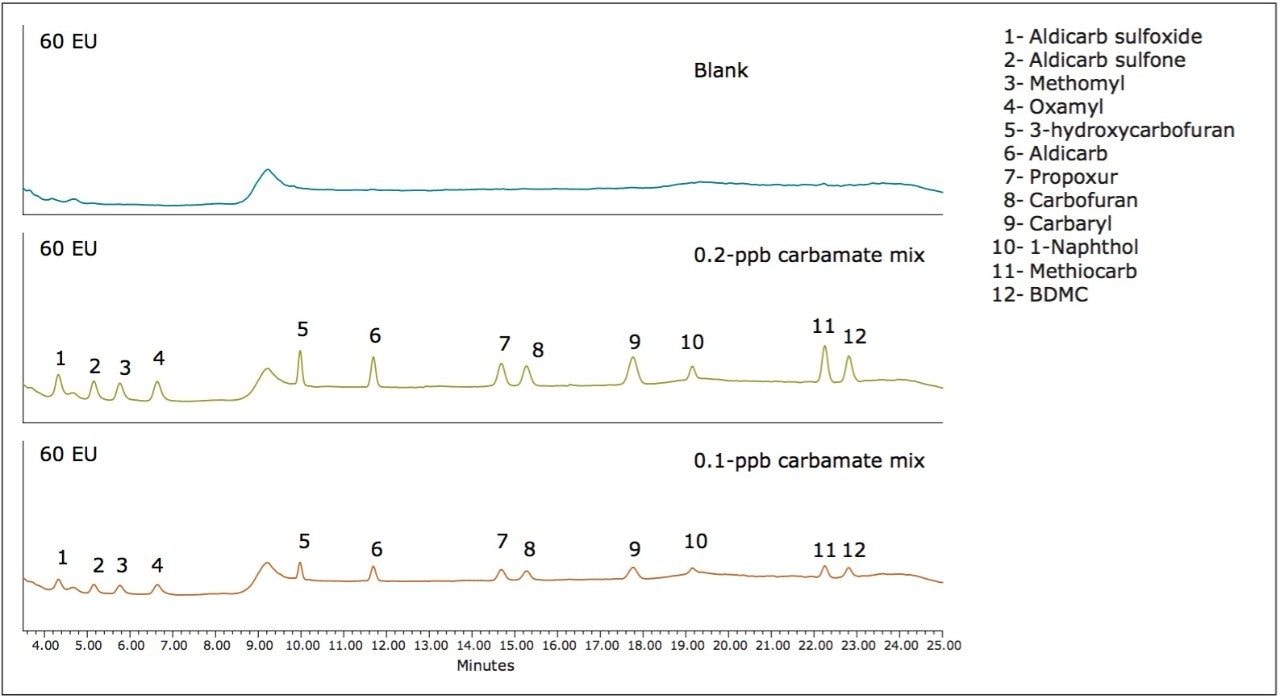
A 0.2-ppb carbamate mix was run three times as a standard, then seven times as an unknown to determine a limit of detection per 40 CFR pt 136 App, B3. A 0.1-ppb mix was also run for comparative purposes.
A Performance Evaluation Carbamate mix was purchased from ERA. The mix was prepared as directed, and quantified using both systems.
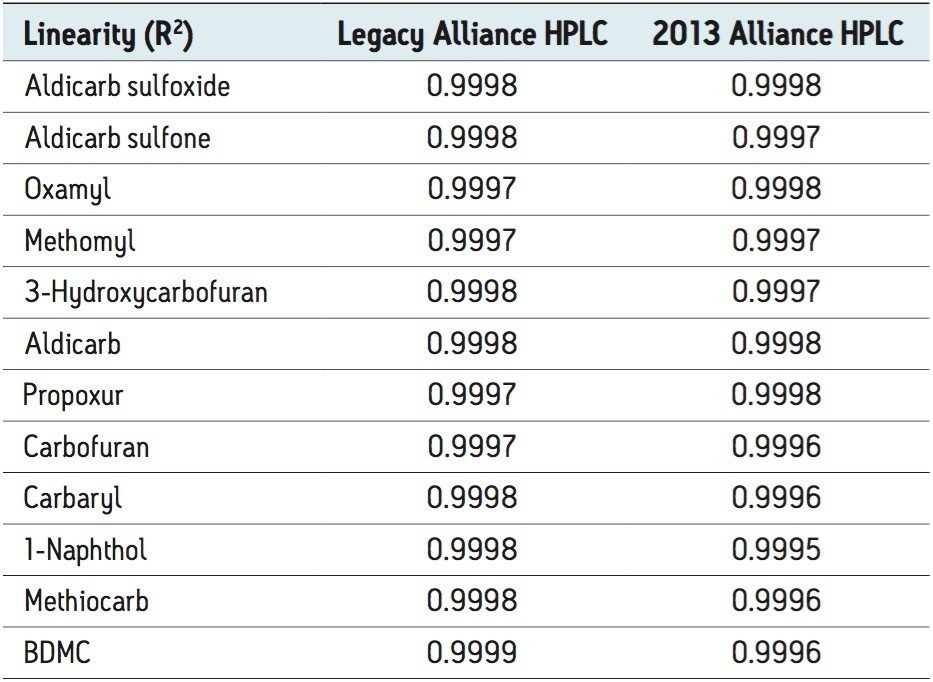
Figures 2 and 3 show overlaid chromatograms of the standards on the legacy and 2013 Alliance platforms, respectively. The linearity on both platforms is compared in Table 1. R2 is greater than 0.999 for all compounds regardless of which platform was used. The reproducibility for both retention time and concentration was investigated for both platforms using seven injections of three different standard concentrations (10-, 25-, and 75-ppb) with the results shown in Tables 2 through 5. The relative standard deviation for the retention time for the 21 injections was less than 0.25% on both platforms, as shown in Table 2. Tables 3 through 5 show comparisons for the amount for seven injections each of the 75-, 25-, and 10-ppb carbamate mixes run as unknowns. The %RSD was less than 0.8% for the 75-ppb and 0.9% for the 25-ppb mixes using both the legacy and 2013 Alliance platforms. One exception to this is 1-Naphthol, which is a hydrolysis product of carbaryl4 and is, therefore, expected to show more variability. The %RSD was shown to be less than 1.5% for the 10-ppb mix on both platforms.
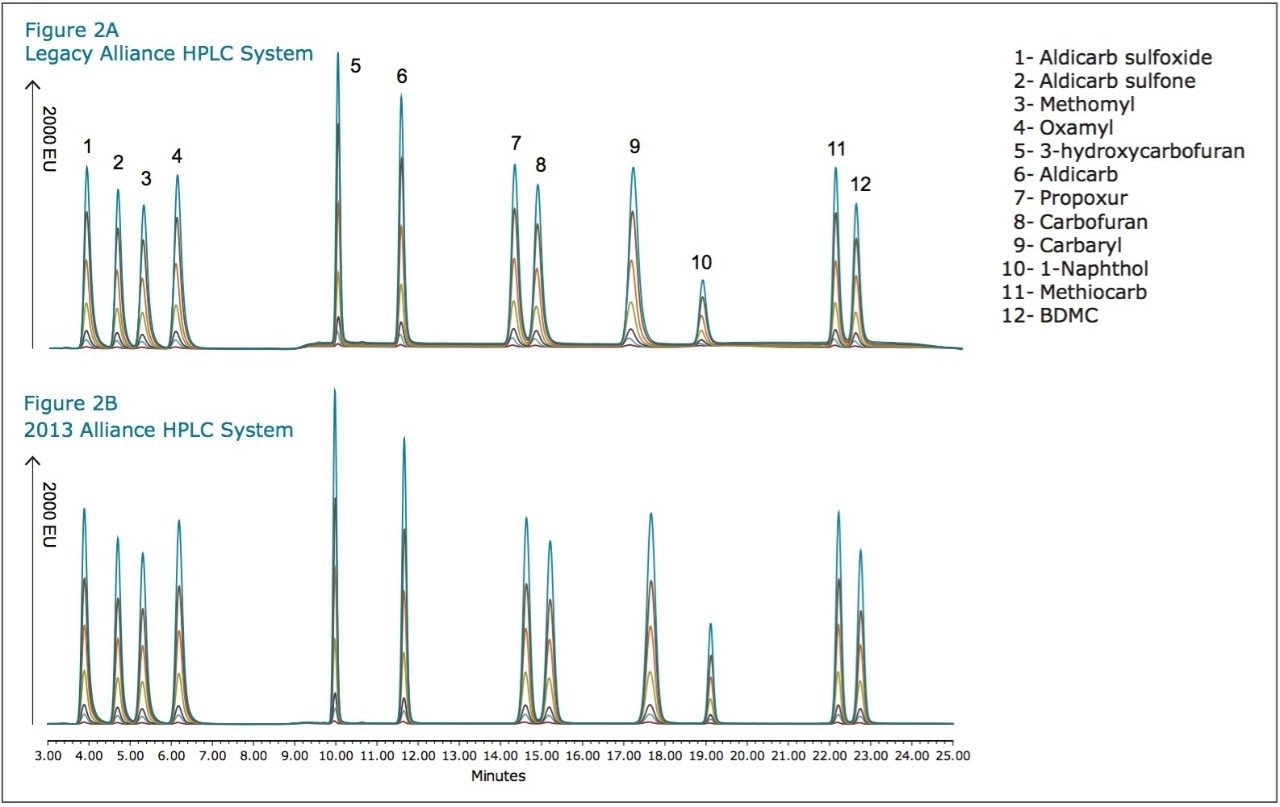
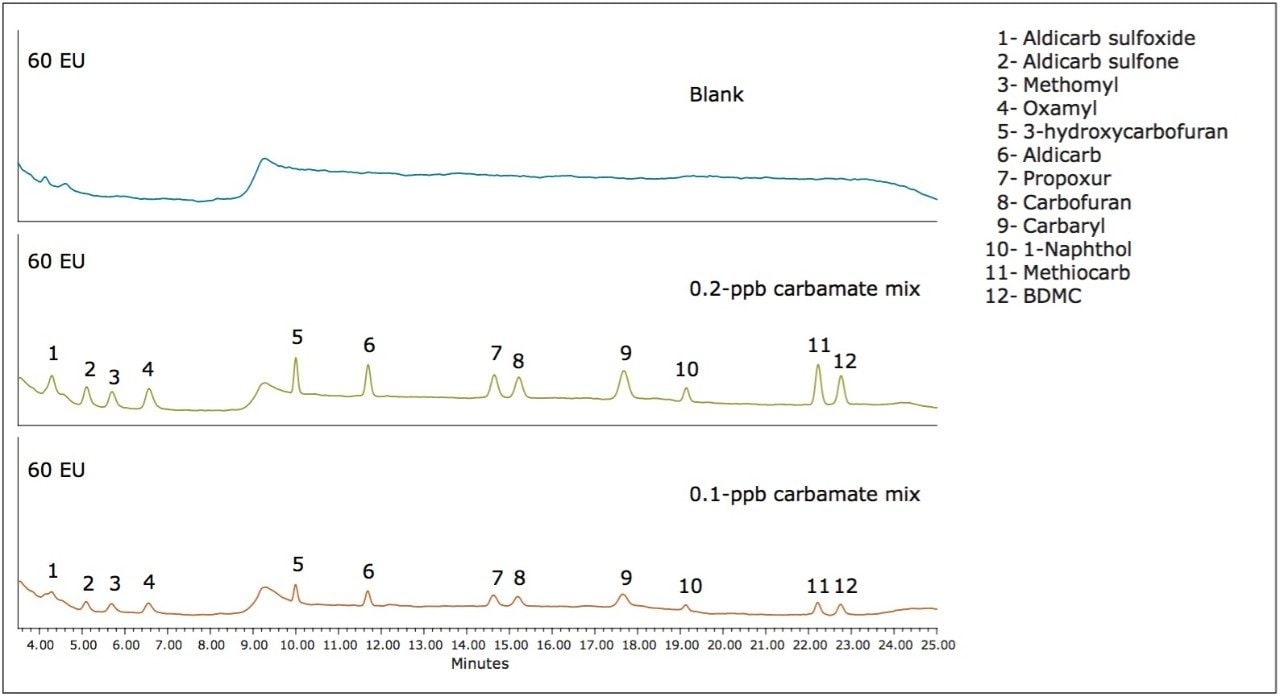
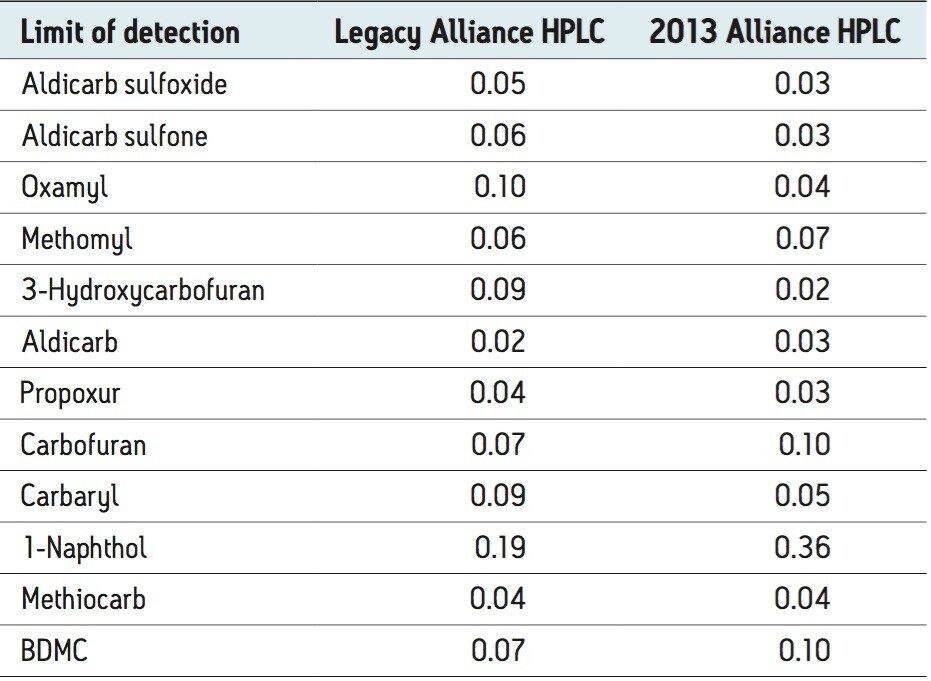
To investigate the detection of low levels of the pesticides, a blank, 0.2-ppb, and 0.1-ppb carbamate mix was injected with the resulting chromatograms shown in Figures 3 and 4. The calculated limits of detection, shown in Table 6, were 0.1-ppb or less for both systems with the exception of 1-Naphthol which, as previously mentioned, is a degradation product.
To test the two systems using a blind sample, the ERA performance evaluation sample was used. For both the previous and current systems, the calculated amounts were found to be within the acceptable QC performance limits and within 1-ppb of each other, as shown in Table 7.

The data show that similar results are obtained on the legacy and 2013 Alliance HPLC systems for Carbamate Analysis, yielding the following benefits:
720004679, May 2013