Les thérapies géniques à base de vecteurs viraux sont des formulations de médicaments complexes, composées de protéines et d’acides nucléiques contenant plus de 200 000 atomes. Couplée à la détection optique (UV, MALS) et à la spectrométrie de masse (MS), la chromatographie liquide (LC) de Waters offre les moyens analytiques nécessaires pour caractériser et quantifier avec exactitude ces structures hétérogènes et leurs attributs, tant au niveau des composés qu’au niveau des produits intacts, soutenant des solutions robustes pour vecteurs viraux. Elle permet de réaliser diverses mesures en routine, notamment le titrage viral, l’analyse des agrégats/impuretés, les ratios de protéines virales, la carte peptidique et l’analyse des modifications, l’efficacité de l’encapsidation et l’intégrité du génome dans vos workflows de solutions pour vecteurs viraux.
Webinaire : relier l’innovation et l’industrie grâce à la spectrométrie de masse par détection de charge (CDMS)
Accélérez le passage de l’analyse d’échantillons à la prise de décision avec waters_connect pour l’analyse biopharmaceutique et des solutions pour vecteurs viraux grâce à des applications pour l’analyse de masse intacte, la confirmation de séquence, la surveillance du processus et bien plus.
Équipez votre laboratoire du système de données chromatographiques (CDS) Empower et bénéficiez de fonctions avancées de gestion des données de laboratoire pour les analyses de vecteurs viraux, y compris l’acquisition, le traitement et la création de rapports.
Le contrôle de l’instrument, l’acquisition des données, l’analyse et la génération de rapports sont entièrement assurés par le logiciel ASTRA avec le module d’analyse des vecteurs viraux. Nous proposons une méthode SEC-MALS de plateforme, spécialement conçue pour la quantification des AAV, facilement personnalisable pour chaque produit et chaque sérotype.
Les colonnes GTxResolve Premier SEC haute efficacité de Waters permettent de mesurer plusieurs attributs, y compris les agrégats et les variants de taille, ce qui accélère l’analyse et réduit la consommation d’échantillons.
Augmentez votre rendement en utilisant une colonne AEX de Waters garnie d’une phase stationnaire non poreuse haute efficacité (p. ex.,Protein-Pak Hi Res Q) en combinaison avec des gradients de salinité optimisés pour une technique de mesure du rapport capside vide/pleine adaptée au contrôle qualité.
Identifiez et mesurez l’abondance relative des protéines virales en utilisant des colonnes MaxPeak Premier BEH C4 avec appariement d’ions par DFA pour des performances LC et MS optimales.
Phase stationnaire amide conçue pour une reproductibilité inter-lots élevée des vecteurs viraux, des protéines de capside et des acides nucléiques. Les variants oxydés et phosphorylés peuvent être facilement distingués de leurs équivalents non modifiés grâce à une séparation HILIC appliquée de manière optimale.
Confirmez la séquence, les modifications post-traductionnelles (PTM) ou la dégradation de protéines virales en établissant une carte peptidique à l’aide des colonnes CSH™ hautement résolutives de Waters.
Optimisez la productivité et le succès de votre laboratoire avec Waters Global Services, pour maintenir une performance optimale des systèmes, minimiser les temps d’immobilisation, prendre en charge les applications les plus complexes et répondre aux strictes exigences de conformité.
Maximisez les ressources et minimisez les risques grâce aux options de paiement proposées par Waters Capital, notamment la mise à niveau des équipements vieillissants, une assistance adaptée et le regroupement de l’ensemble de vos services en un seul forfait mensuel.
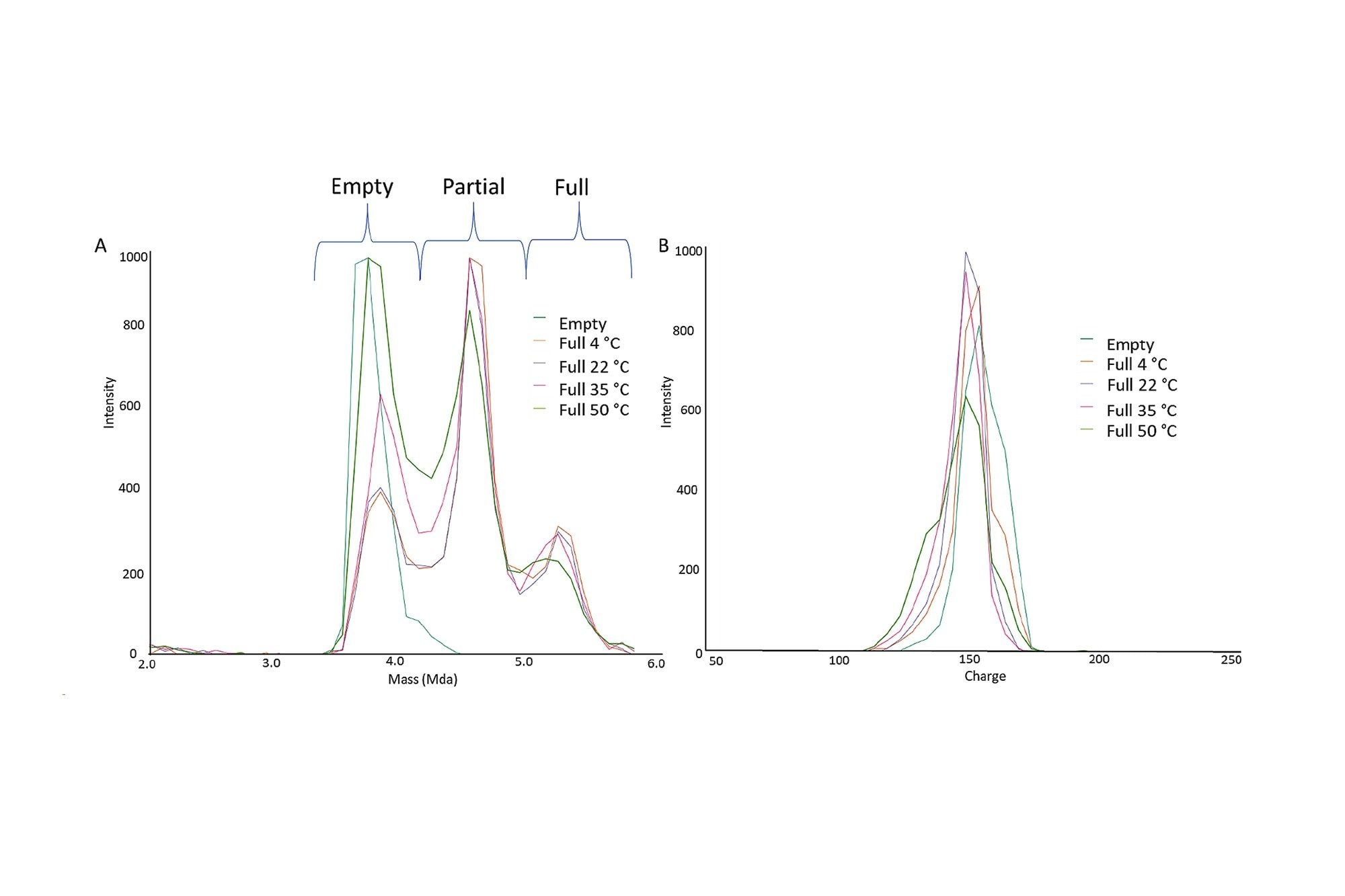
a) Superposition du spectre de masse de l’AAV8 avec un zoom sur la plage de masse de 2,5-6 MDa, avec les capsides entièrement vides et les capsides pleines traitées par incubation de 30 minutes à 4, 22, 35 et 50 °C. b) Spectre de charge de l’AAV8 avec un zoom sur la plage de masse de 2,5-6 MDa, avec les capsides entièrement vides et les capsides pleines traitées par incubation de 30 minutes à 4, 22, 35 et 50 °C.
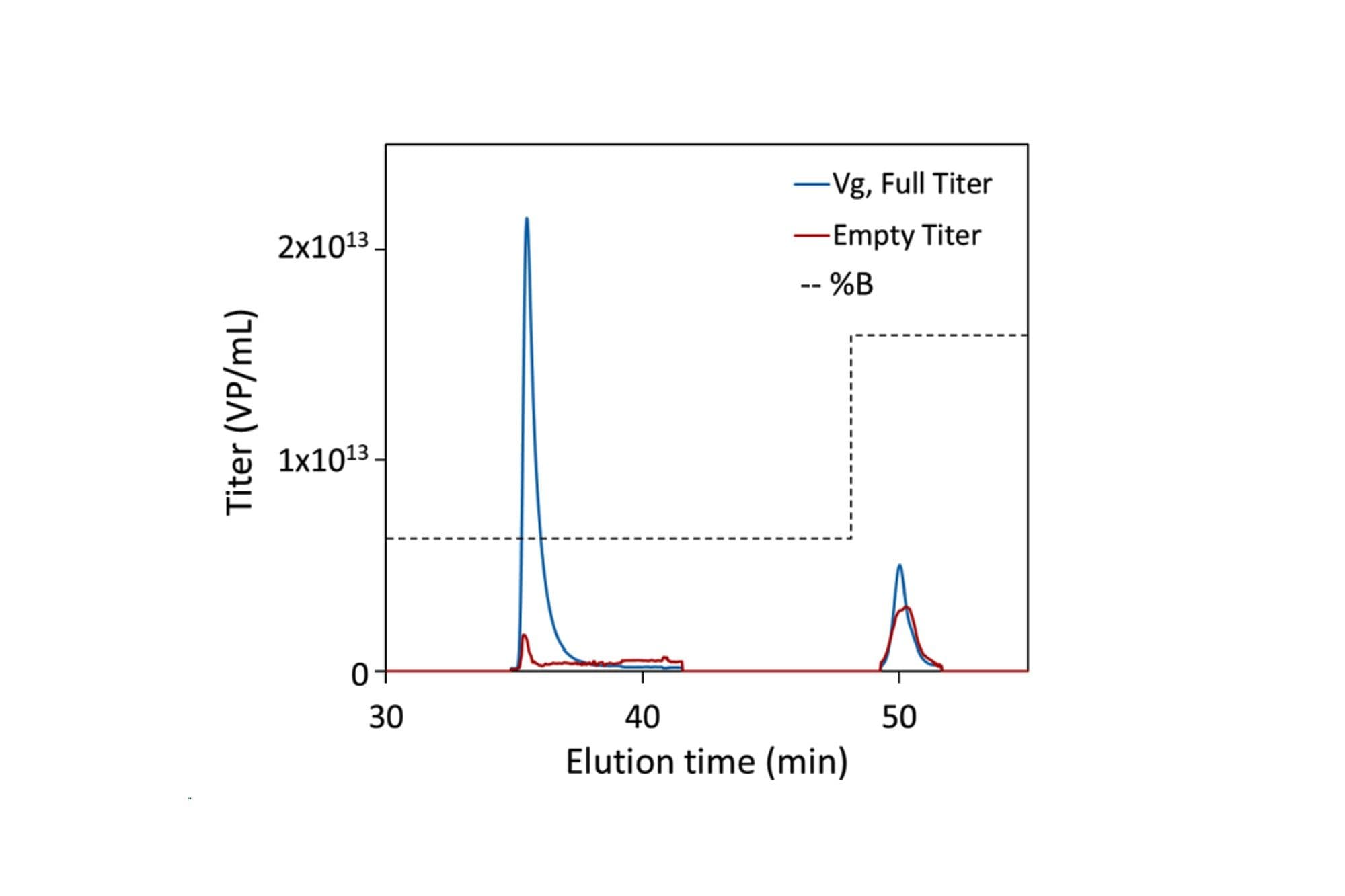
Titrages de capsides pleines (bleu) et vides (rouge) déterminés par RT-MALS lors de l’élution (34–48 minutes) et de la désorption (> 48 minutes) dans le gradient linéaire final. La force ionique du tampon est représentée par la ligne noire en pointillés.
Vues agrandies d’un chromatogramme d’AAV2 obtenu avec une colonne en acier inoxydable (4,6 x 150 mm, granulométrie de 5 µm, tracé rouge) par rapport à une colonne MaxPeak HPS (XBridge Premier GTx BEH SEC 450 Å 2,5 µm 4,6 x 150 mm, tracé noir). Les séparations ont été effectuées avec une phase mobile contenant un tampon de force ionique standard (10 mM de phosphate à pH 7,4 + 200 mM de KCl).
La quantification relative des protéines VP a été mesurée par détection optique, notamment (A) par UV et (B) par fluorescence (FLR). L’annotation des pics indique la répartition et l’abondance relative calculée des composés détectés. La détection par FLR présente un rapport signal/bruit de VP3 presque cinq fois plus élevé que la détection par UV avec une charge massique 10 fois plus importante, ce qui suggère une sensibilité environ 50 fois plus élevée.
