This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
This application brief demonstrates the simultaneous acquisition, and subsequent processing, of qualitative and quantitative information for a parent drug and its metabolites utilizing an ACQUITY UPLC-SYNAPT G2 HDMS System.
Confidently and efficiently identifying metabolites is a key aspect of successful drug development. Merging qualitative and quantitative workflows into a single Met ID analysis offers enhanced levels of information, while increasing productivity.
An effective metabolism study workflow should ideally include both high quality qualitative and quantitative information, such that the identities of major metabolites are revealed, and the clearance rate and metabolic routes of the parent drug can be effectively determined.
Typically, tandem quadrupole instruments, operated in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode are employed for quantitative studies while full scan, exact mass measurement instruments are used for identification experiments. The SYNAPT G2 HDMS System, with its novel QuanTof Technology, allows sensitive, exact mass quantitative and qualitative experiments to be performed simultaneously.
In this work, we used the model drug verapamil to demonstrate how a qual/quan workflow can enhance metabolite identification, delivering a new level of productivity and performance for one of the most analytically-challenging and timesensitive applications in the R&D process.
An ACQUITY UPLC System was used with an ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 Column (1.7 μm, 2.1 x 100 mm). Mobile phase was water with 0.1% formic acid (A) and acetonitrile (B). The injection volume was 10 μL. The SYNAPT G2 HDMS System was operated in +ESI mode using MSE, a novel method of data acquisition which enables both precursor and product ion data to be acquired for virtually every detectable ion in the sample from one injection.
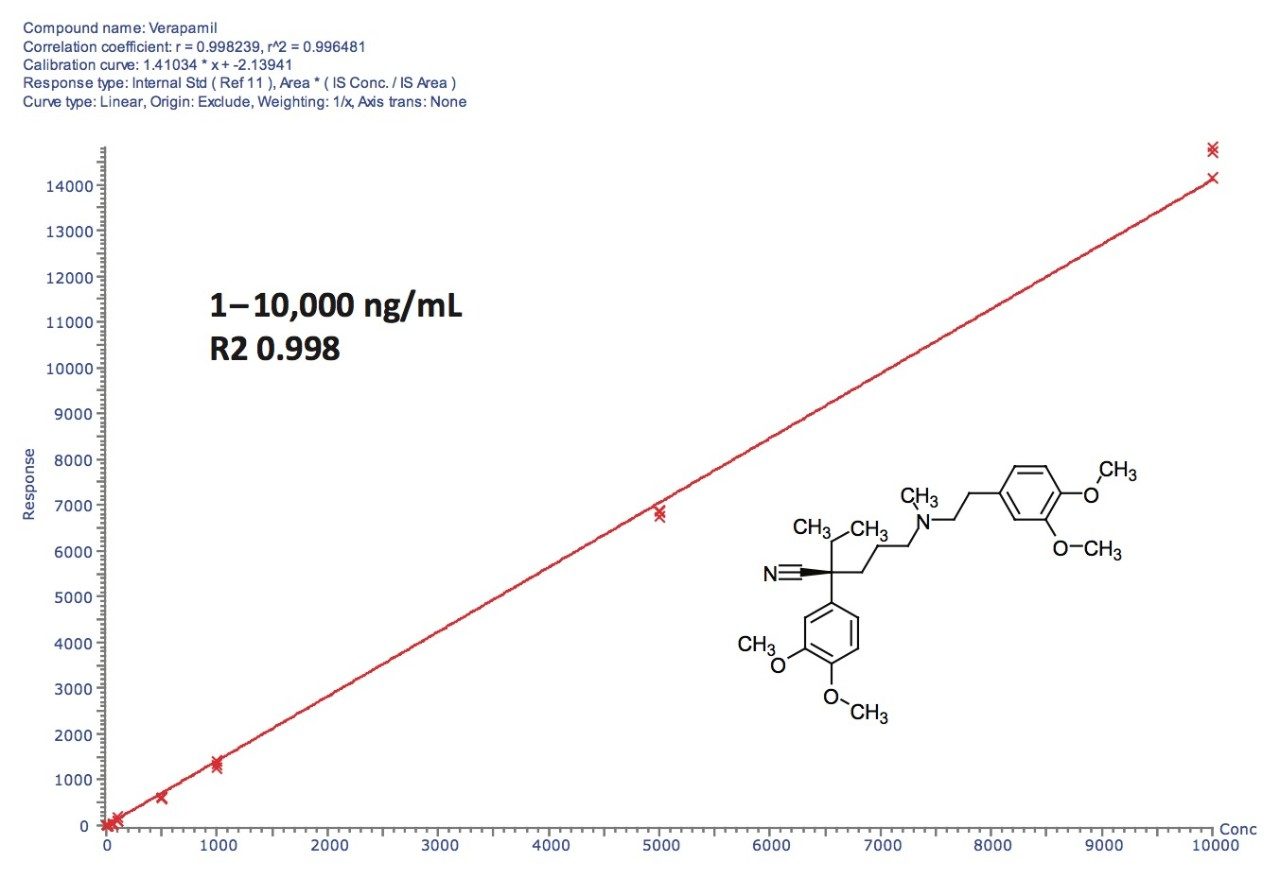
Standard verapamil stock solution was made with DMSO at 20 mM. It was then diluted into a concentration series from 10,000 to 1 ng/mL with rat plasma. A standard calibration curve for verapamil was acquired and processed by the TargetLynx Application Manager, as shown in Figure 1.
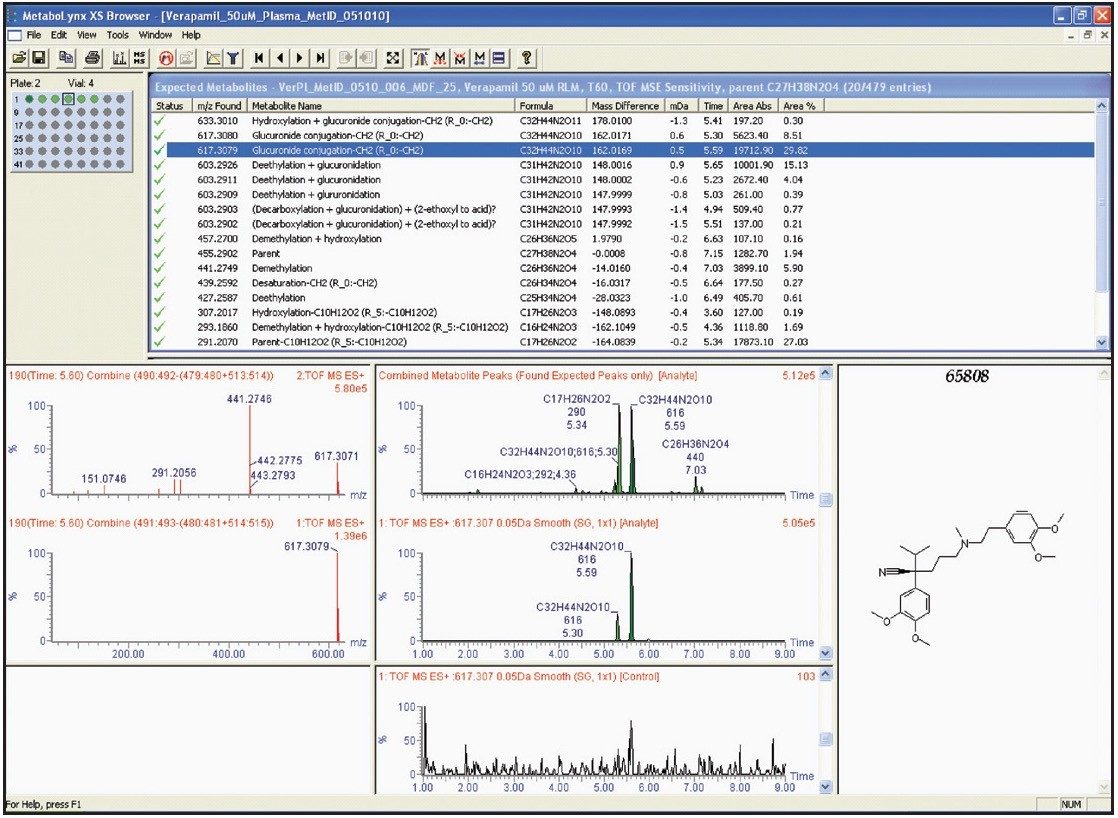
Verapamil was incubated at 37 °C with rat liver microsomes at 300 μM, the reaction terminated at 0, 15, 30, 60, 120, 240 minutes respectively. After centrifugation, 50 μL of supernatant was spiked into 450 μL of rat plasma followed by the addition of 1 mL of acetonitrile. After a second centrifugation, the supernatant (equivalent to about 10 μM of the parent drug incubation concentration) was analyzed and data subsequently processed by the MetaboLynx XS Application Manager. The identified metabolites reported in the MetaboLynx browser are shown in Figure 2.
By applying the calibration curve obtained, as outlined above, the quantification data from the parent drug and metabolites at each incubation time point are easily obtained. Since there are usually no standards available for quantitation of metabolites, use of the parent drug calibration curve is a typical practice. The curves of parent drug clearance and metabolite formation can be generated, as shown in Figure 3.

A qualitative and quantitative metabolite identification workflow using an ACQUITY UPLC- SYNAPT G2 HDMS System coupled with MetaboLynx XS and TargetLynx was demonstrated.
The combination of superb resolution from UPLC separations and high quality data from the SYNAPT G2 HDMS System allowed metabolites to be identified with ease and with high confidence. Additionally, the significantly enhanced quantitation capabilities provided by the SYNAPT G2’s QuanTof Technology enabled the acquisition of an external calibration curve of verapamil with 4 orders of magnitude of linear dynamic range. This allowed parent drug clearance and metabolite formation information to be determined in a simple and rapid manner.
Combining quantitative and qualitative workflows into a single analysis allows drug project teams to quickly obtain answers, and increase productivity.
720003492, May 2010