This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
In this study, a trypsin digest of trastuzumab was used to demonstrate repeatability of a peptide mapping using the ACQUITY Arc Bio System.
The retention time percent RSD for 102 peptides ranged from 0.025–0.05% for the majority of peptides. The percent RSD for the area of eight peptides selected throughout the gradient ranged from 0.26–0.93%. The percent RSD for both metrics demonstrated excellent instrument precision, which is important for generating reliable data and providing confidence in results.
The ACQUITY Arc Bio System offers biocompatible UHPLC performance for assessing repeatability of a peptide mapping method.
To date, many of the analytical methods used in development and quality control of pharmaceuticals are HPLC-based. While HPLC may provide a basic level of assurance of product quality and safety, there are noted advantages to modernizing legacy methods and instrumentation. This is especially true for complex samples, where lower dispersion LC platforms can offer better resolution between critical pairs and increased sensitivity for detecting and monitoring low-level sample components. The idea of continuously improving development and manufacturing activities is supported in ICH Q10 as part of lifecycle management with the intention of enhancing product quality for improved patient safety.1 When considering development and manufacturing activities as well as technology transfers as part of lifecycle management, it is critical that new technology be robust and easily deployable.

As with any analytical method, it is expected that the instrumentation used for analysis provides reliable data with minimal user intervention.
In this study, a trypsin digest of trastuzumab was used to demonstrate repeatability of a peptide mapping method across five injections using the ACQUITY Arc Bio System. Retention time and peak area were used as metrics for assessing instrument precision. Empower 3 Software allowed batch processing of data, eliminating user bias in integration and offering compliance when needed.
The ACQUITY Arc Bio System is a quaternary UHPLC system designed with biocompatible materials, which provide versatility for a host of routine bioseparations, including RP methods for proteins and peptides, as well as methods requiring more aggressive conditions (e.g. high salt and/or pH extremes), such as SEC, IEX, and HIC. Peptide mapping was used to assess repeatability of the system because the length of the method and the number of peaks make for a more complex separation.
A Waters XBridge BEH C18 XP Column (130 Å, 2.5 μm, 4.6 x 100 mm) in TFA was used to collect a peptide map of trastuzumab over a 60 minute gradient. An overlay of the five injections can be seen in Figure 1. From visual inspection, each of the five injections align with one another. To further assess this data, the retention time was determined for 102 peaks in each of the five injections. Results were batch processed using Empower 3 to eliminate any bias in treatment of the data. The distribution of retention time percent RSD is reported in Figure 2. The data was observed to approximately fit a Gaussian distribution. Higher percent RSD was observed for the early eluting peptides (>0.05%) and was not unexpected due to lower k’ values. While these results demonstrate excellent precision, optimization of column chemistry and mobile phase could further improve this result.
Area percent RSD is reported in Figure 1 for eight peptides selected throughout the gradient. These values ranged from 0.26–0.93% for each of the peptides selected. Larger discrepancies in area precision are sometimes seen for low abundance peaks as well as for those peaks that are not baseline resolved, but in this case, area precision is well within acceptable method and instrument parameters.
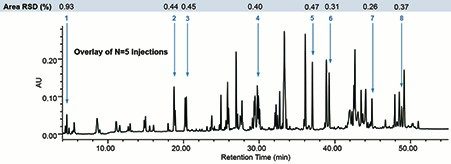
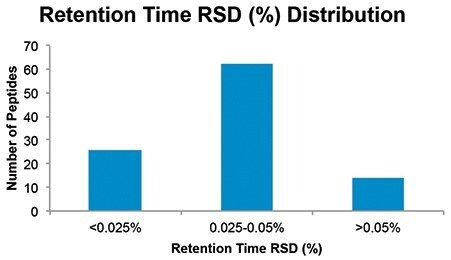
Retention time and peak area were used to assess repeatability of a peptide map of trastuzumab with the ACQUITY Arc Bio System. The retention time percent RSD for 102 peptides ranged from 0.025–0.05% for the majority of peptides. The percent RSD for the area of eight peptides selected throughout the gradient ranged from 0.26–0.93%. The percent RSD for both metrics demonstrated excellent instrument precision, which is important for generating reliable data and providing confidence in results.
720006224, March 2018