In the second part of this three-part series, we address how to successfully interface ion exchange chromatography (IEX) with ESI mass spectrometry as a complementary orthogonal technique to monitor lysine variants.
Charge variants, such as C-terminal lysine variants in monoclonal antibodies, are known to be sensitive to manufacturing processes.1-3 Developing efficient methods for characterization and identification of charge variants in biotherapeutic proteins for monitoring and control of production processes is an area of continued interest in the pharmaceutical industry.
Orthogonal techniques such as ion exchange chromatography (IEX) and mass spectrometry (MS) are often employed to maximize the information gained in the characterization of biotherapeutics.4 While IEX separations are powerful in gathering information such as charge variant composition, the use of salts and buffer components prevents direct coupling to mass spectrometry (MS) to elucidate peak identity.5 Chromatographic fractions of interest are often manually collected, and desalted offline prior to MS analysis, which negatively impact overall analysis time and productivity.
Part 1 of this three-part application series demonstrated that the Waters ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology offers an efficient solution for increasing productivity in the fractionation and desalting of charge variants in complex biotherapeutic samples. When coupled to a mass spectrometer, the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology renders an efficient method for combining complementary orthogonal techniques employed in the monitoring of C-terminal lysine variants in therapeutic monoclonal antibodies without compromising productivity.
The objective of this application note is to demonstrate that the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology is a viable option for interfacing IEX to electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS. A therapeutic monoclonal antibody, infliximab, was used as a model protein to evaluate the functionality.
The Waters Protein-Pak Hi Res SP, 7 μm, 4.6 x 100 mm, strong cation exchange column (p/n 186004930) and ACQUITY UPLC Protein BEH C4, 300Å, 1.7 μm, 2.1 x 50 mm Column (p/n 186004495) were conditioned prior to use. Chemical reagents were purchased from Sigma Aldrich and used as received. The monoclonal antibody infliximab was received at a concentration of 20 mg/mL.
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio with 2D Technology 1st dimension pump: ACQUITY UPLC Quaternary Solvent Manager, ACQUITY UPLC Column manager 2nd dimension pump: ACQUITY UPLC Binary Solvent Manager, ACQUITY UPLC Autosampler with FTN, ACQUITY UPL Column Manager |
|
Detectors: |
(1st dimension) ACQUITY UPLC TUV (2nd dimension) ACQUITY UPLC PDA |
|
Absorption wavelength: |
280 nm |
|
Vials: |
Total recovery vial:12 x 32 mm glass, screw neck, cap, nonslit (p/n 600000750cv) |
|
Column: |
Protein-Pak Hi Res SP, 7 μm, 4.6 x 100 mm (p/n 186004930) ACQUITY UPLC BEH C4, 300Å, 1.7 μm, 2.1 x 50 mm (p/n 186004495) |
|
Column temp.: |
25 °C (IEX); 80 °C (C4) |
|
Sample temp.: |
4 °C |
|
Injection vol.: |
2 μL unless otherwise stated |
|
Quaternary solvent manager: |
|
|
Flow rate: |
0.500 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase A: |
100 mM MES monohydrate |
|
Mobile phase B: |
100 mM MES sodium salt |
|
Mobile phase C: |
1000 mM NaCl |
|
Mobile phase D: |
18 MΩ H2O |
|
Auto•Blend Plus setting: |
20 mM MES buffer, pH 6.5, 25–65 mM NaCl in 15 minutes |
|
Binary solvent manager: |
|
|
Flow rate: |
0.250 mL/min for heart-cut, otherwise 0.500 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase A: |
18MΩ H2O, 0.1% FA |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Acetonitrile, 0.1% FA |
|
Gradient: |
5–85% B in 10 minutes |
|
Capillary: |
3kV |
|
Sample cone: |
45 V |
|
Source temp.: |
150 °C |
|
Desolvation temp.: |
500 °C |
|
Desolvation gas: |
800 L/h |
MassLynx Software v4.1 (SCN 8.62)
As described in part 1 of this three part series, the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology featuring the heart-cut process is readily deployed with a two-column configuration as shown in Figure 1. With both valves in position 1 (Figure 1A), the flow from both the quaternary solvent manager and binary solvent manger are independent of each other, allowing for independent gradients to be performed on column 1 and 2.
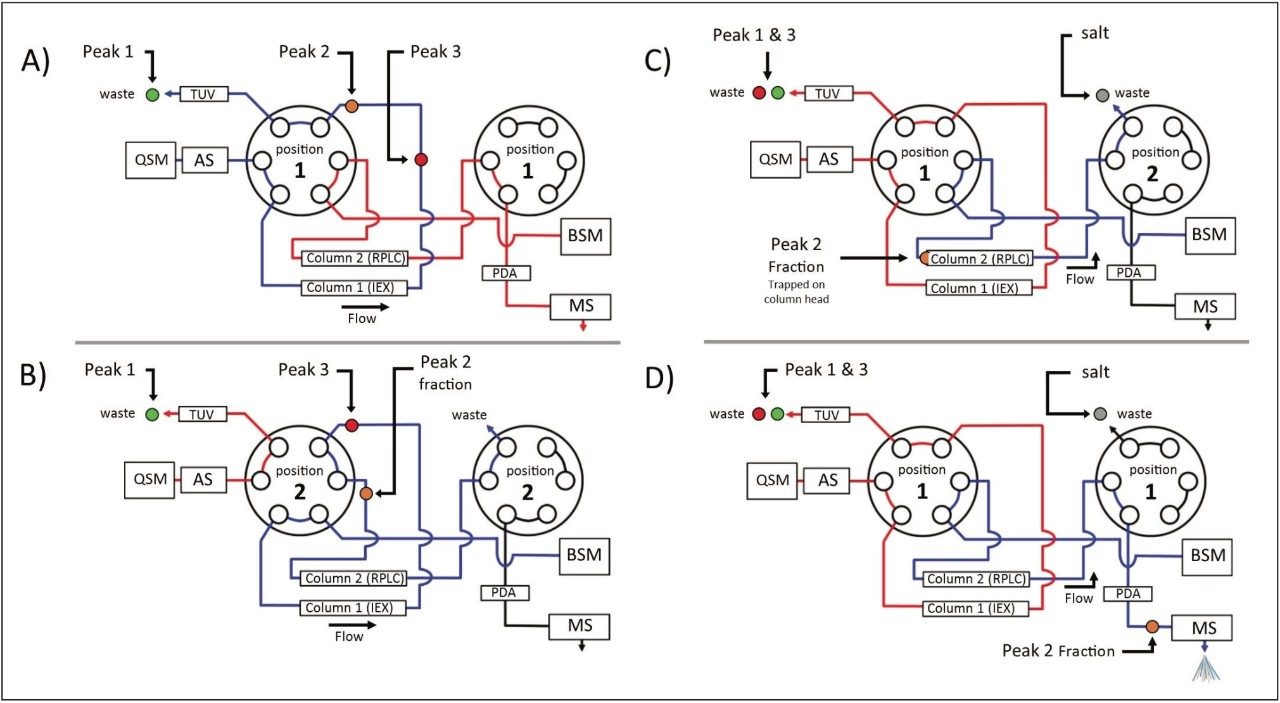
The heart cut is performed when the valve positions are temporarily switched to position 2 (Figure 1B), combining the flow paths (Figure 1B blue trace) where eluent from column 1 is redirected to column 2. The ACQUITY UPLC Column Manager supports independent valve control as shown in Figure 2C. With the left valve in position 1 and the right valve in position 2 the flow paths of each column are isolated again, with the 2nd dimension column being eluted to waste. This allows for unbound salts to be washed from the heart-cut fraction, which is trapped at the column head of the 2nd dimension column, using the aqueous phase of the 2nd dimension.
Once desalted, the heart-cut fraction can be readily eluted in a mobile phase amendable to MS analysis using the ACQUITY UPLC Binary Solvent Manager, demonstrating the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology facilitates a viable option for interfacing IEX to MS analysis.
One aspect of successful multidimensional chromatography relies on reproducible 1st dimension separations. Aqueous separations such as IEX can involve preparing multiple sets of buffers over the course of a project. This iterative process is time consuming and has an increased potential for error in buffer preparation resulting in irreproducible separations.
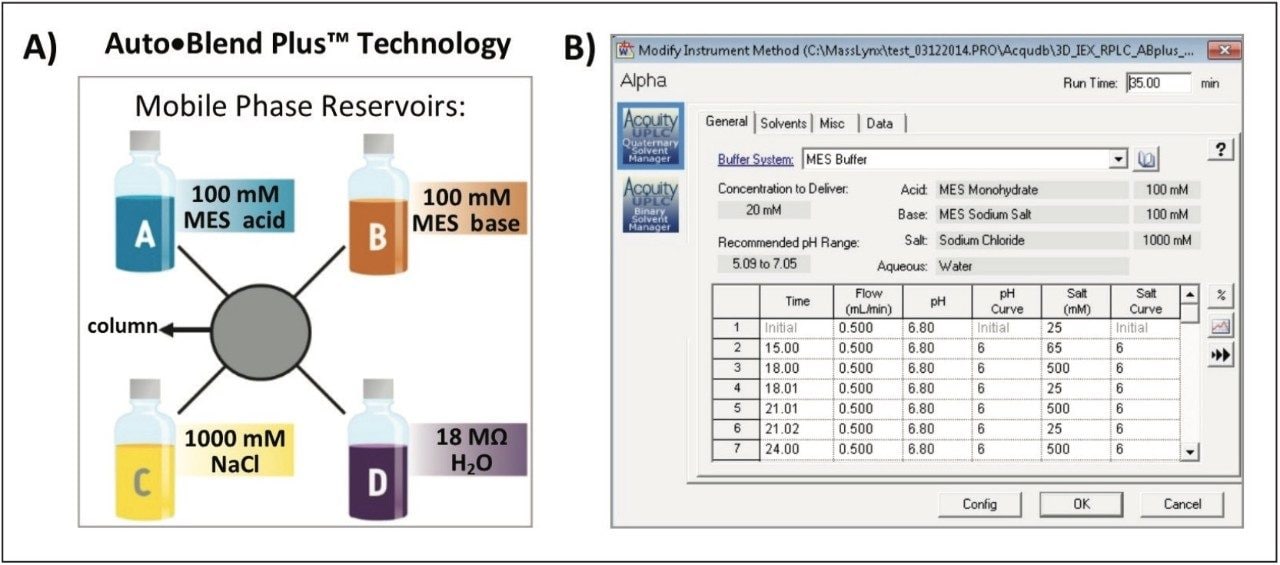
Auto•Blend Plus Technology is an integrated software solution designed to increase productivity and reproducibility of chromatographic separations. Auto•Blend Plus incorporates a solvent management system using pure solutions and concentrated stocks (Figure 2). The end user is presented with an easy-to-use gradient table interface, where the gradient is expressed directly in terms of pH and ionic strength. The software then automatically calculates the percentage of acid and base required for the specified pH using the known pKa value of the chosen buffer system or a small empirical calibration table. Auto•Blend Plus allows for multiple buffer compositions to be tested from a single set of pure components and can be easily automated to increase productivity.
Biotherapeutics undergo routine analysis throughout the manufacturing process to ensure regulatory guidelines are met with regards to product quality. Orthogonal techniques that can be employed to characterize the homogeneity (or lack thereof) in biotherapeutics drugs without compromising productivity are highly desirable.
The ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology is capable of combining complementary orthogonal detection techniques on-line for improved productivity. The heart-cut technology featured in the system is readily deployed with a two column configuration (IEX/RPLC) as shown in Figure 1 for on-line desalting of biotherapeutic samples, which was demonstrated in part I of this application series.
To demonstrate the MS amenability of this technology in comparability analyses, a Xevo G2 QTof Mass Spectrometer was interfaced with the 2D UPLC system after the ACQUITY UPLC Photodiode Array Detector as shown in Figure 1. Heart-cuts were performed on the individual lysine variants as outlined by the red box in Figure 3A–C. Using the same method and gradients as described in part 1, heart-cut fractions were desalted and eluted with the BSM pump to the source of the Xevo Mass Spectrometer (settings in MS conditions).
From the deconvoluted mass spectrums shown in Figure 3, the infliximab +0 Lys, +1 Lys, and +2 Lys peak mass were determined to be 148,511.0 Da, 148,640.0 Da, and 148,767.0 Da, respectively. The +1 Lys and +2 Lys peaks were determined to have a mass difference of Δ129 Da, and Δ256 Da, respectively, which correlates to the addition of one and two lysine residues (average mass 128 Da) while the glycosylation profile was confirmed to be identical between the major isoforms.
This application demonstrates that the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology is well-suited for desalting of biological samples and renders a viable option to interface IEX with ESI-MS analysis as an orthogonal detection technique.

Characterization methods of biotherapeutic proteins that provide increased informational content without compromising productivity require efficient solutions that are adaptable to the high-throughput environment of industry. The ACQUITY UPLC H-Class Bio System with 2D Technology offers an efficient method for the characterization of biotherapeutics with the ability to combine orthogonal detection techniques on-line for improved productivity.
The heart-cut feature offered with the system is well suited for fractionation and desalting of challenging biological samples. Compatibility with multiple column configurations and the ability to automate the process offers today’s analyst a flexible and efficient means to maximize the information obtained during characterization of biotherapeutics.
720005328, March 2015