
This application note describes how to quantify aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, and G2 confidently and rapidly using the Xevo TQ-XS and VICAM affinity sample prep.
Mycotoxins are toxic secondary metabolites of fungi that grow on crops pre- and post-harvest. The presence of these toxins at certain levels in crops poses health risks for consumers1 leading regulators to set limits in order to minimize exposure to the public. Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCM) often consist of or contain cultivated products and therefore testing for toxic contaminants becomes necessary.
Coix seed, also known as Coix lacryma-jobi, semen coicis, Job’s tears, and Yi-Yi-Ren (薏苡仁), is the seed of a tall grass native to tropical Asia. It is commonly consumed in Asia as foods, and often as a tea or drink. It is also often prescribed for its therapeutic properties to restore balance by removing or clearing excess heat and dampness. Treatments are given to restore circulation in organs (spleen, kidneys, lungs) through the mild promotion of diuresis. Recently, it has been shown that coix seed also has synergistic effects on inhibiting tumor growth when its administration accompanies other chemotherapy agents2 and its extract is the subject of past and present clinical trials in the United States.
Due to their toxicities, aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, and G2 limits in TCM in China are regulated at 5 µg/kg for B1 and 10 µg/kg for B2, G1, and G2 combined, according to the 2015 edition of Chinese Pharmacopeia. UltraPerformance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) coupled with sensitive tandem mass spectrometry (MS) enables fast and confident analysis on small sample amounts. These platforms are key to ensuring the quality of consumed medicinal natural products used for treatment of various ailments. In this application note, we show how to quantify aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, and G2 confidently and rapidly using the Xevo TQ-XS and VICAM affinity sample prep.
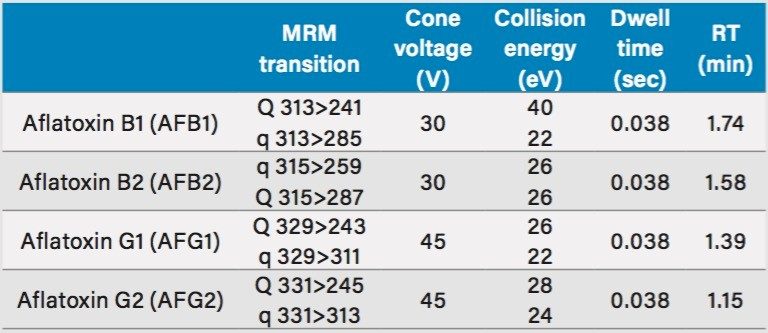
The traditional Chinese medicine, coix seed, was purchased from six sources A–F; one sample was pre-ground, the other five were dried, whole seeds. The seeds were mechanically ground to a very fine powder in a table-top grinder for processing. The extraction and purification method was used in accordance with the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Figure 1 shows the extraction workflow. Calibrators were prepared by serial dilution of analytes spiked into 50:50 MeOH/H2O. Five microliters of purified sample was injected onto the LC-MS system for analysis. Table 1 lists the MRM transitions, collision energies, and cone voltages for each analyte.
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY UPLC I-Class FTN System |
|
Column: |
CORTECS UPLC C18, 1.6 μm, 2.1 x 50 mm, |
|
Column temp.: |
25 °C |
|
Inj. volume: |
5 μL |
|
Flow rate: |
0.450 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase A: |
H2O with 10 mM ammonium acetate |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Methanol |
|
Gradient: |
35 to 85% B over 2 minutes, 85 to 100% B over 0.5 minutes 100 to 35% B over 1 minute |
|
MS system: |
Xevo TQ-XS MS |
|
Ionization mode: |
ESI+ |
|
Capillary voltage: |
1 kV |
|
Source temp.: |
150 °C |
|
Desolvation temp.: |
550 °C |
|
Cone gas flow: |
250 L/hr |
|
Desolvation gas: |
1000 L/hr |

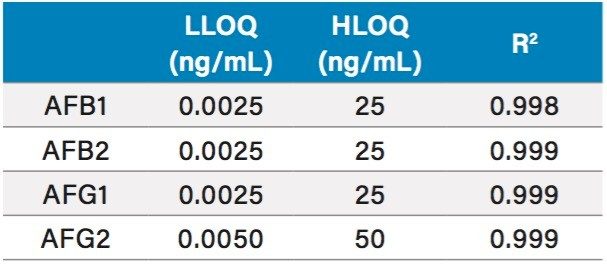
The method for aflatoxins in Traditional Chinese Medicines as written in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia uses immunoaffinity purification in the sample preparation.3 Extraction efficiency was tested by spiking 30 µL of 2.5 ng/µL into 15 g of ground coix seed to make 5 µg/kg, the regulatory limit. The measured concentration against the calibration curve for the final prepared sample was 3 ng/mL. The spiked sample was allowed to sit at room temperature in the dark for 60 minutes before extraction. Recovery was calculated against a sample spiked after extraction and matrix effects were calculated by comparing a spike after extraction sample to standard. Recovery and matrix factor are summarized in Table 2. Sensitivity and linearity were tested by preparing calibration curves of all four analytes in 50:50 MeOH/H2O. AFB1, B2, and G1 had an LOQ of 0.0025 ng/mL (12.5 fg on column) and AFG2 had 0.005 ng/mL (25 fg on column) (Table 3). Each analyte exhibited 4 orders of linearity.
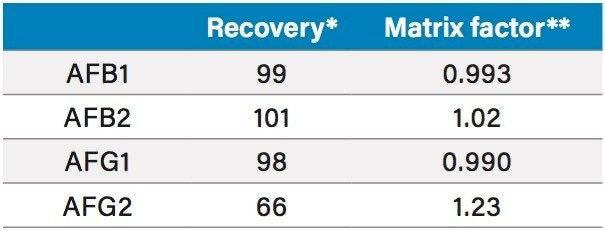
Table 2. Recoveries and matrix factor for the analytes in coix seed, n=5.
* Recovery = extracted ÷ spike after extraction
** Matrix factor = spike after extraction ÷ standard
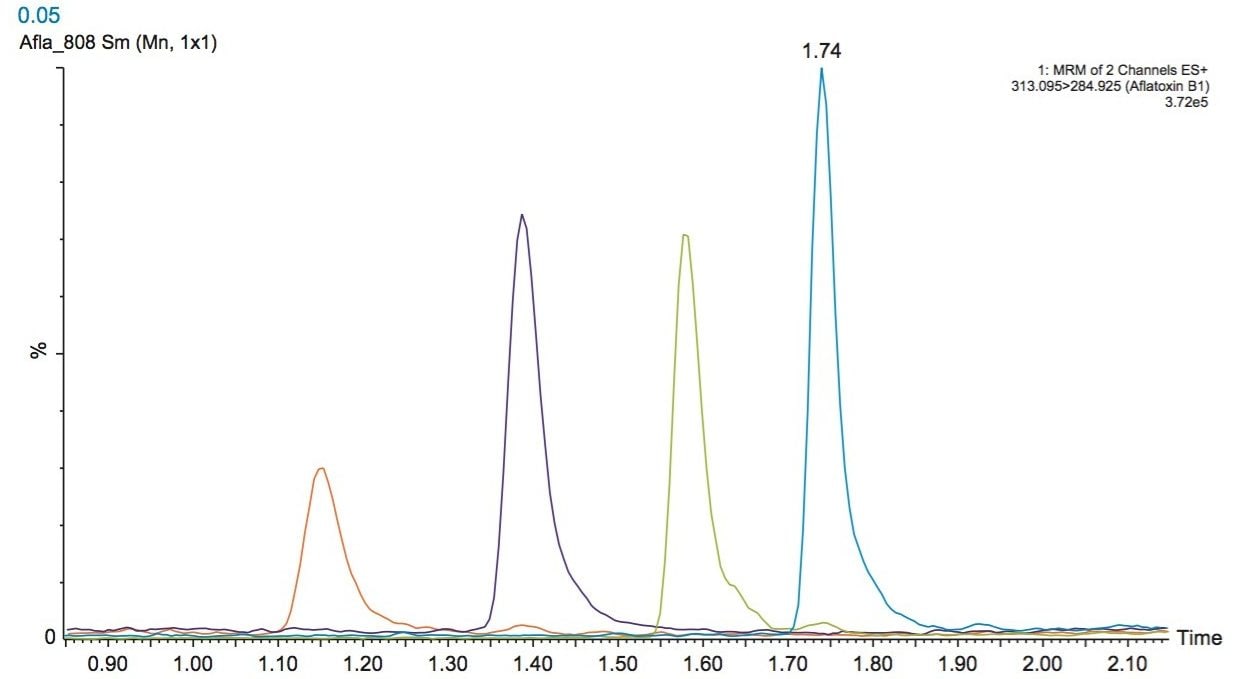
To test the robustness of the assay in matrix, a series of injections was performed at the Chinese Pharmacopoeia regulatory limit of 5 µg/kg for the aflatoxins. Figure 3 shows an example TrendPlot of AFB1 over 200 injections. The RSD areas were 0.85%, 0.79%, 0.76% and 0.89% for AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, and AFG2 respectively indicating solid method robustness.

Coix seed from 6 different suppliers was purchased and extracted as described above. A system suitability sample at 1 ng/mL was prepared by diluting an appropriate volume of 25 µg/mL stock solution of the four aflatoxins into 50:50 MeOH/H2O. The retention time and ion ratios were referenced from the system suitability injections. Concentrations in µg/kg were calculated from a solvent calibration curve using the following equation:
X = (A*2*50*75) ÷ (20*15*m) where X is µg/kg in coix seed, A is calculated concentration in ng/mL, and m is the mass weighed of the sample. The TargetLynx XS quantitation results are shown for AFB1 in figure 4 (TargetLynx Application Manager automates sample data acquisition, processing, and reporting for quantitative results.)
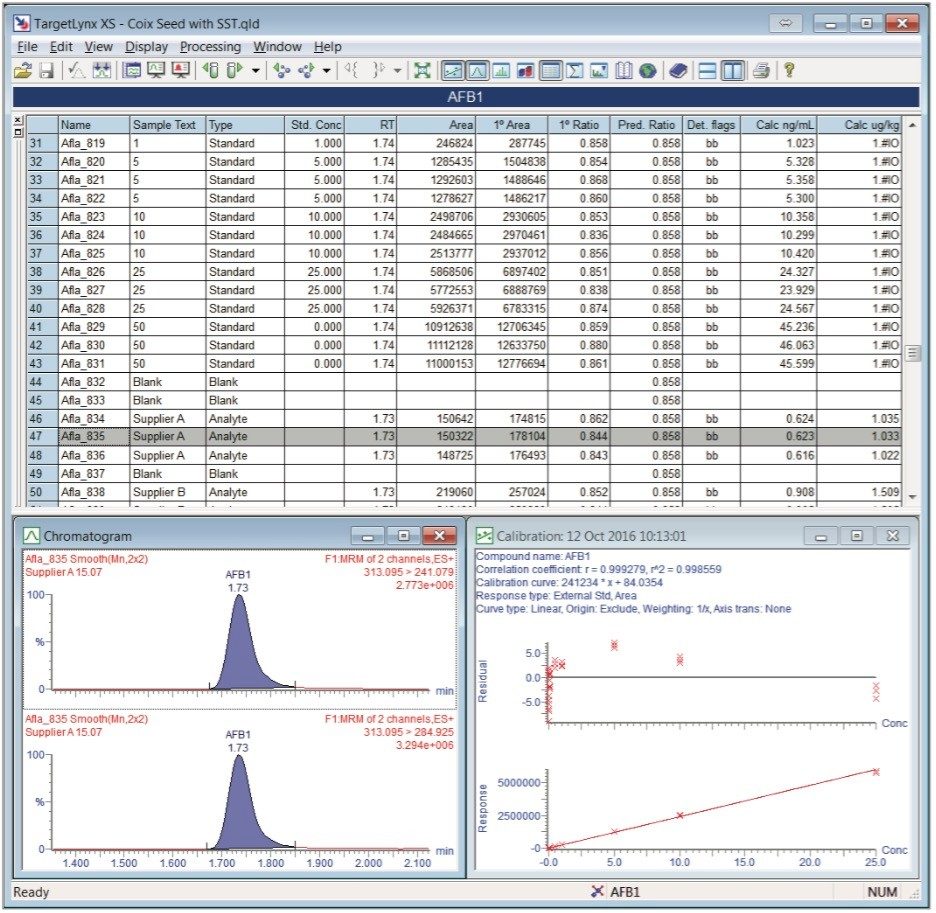
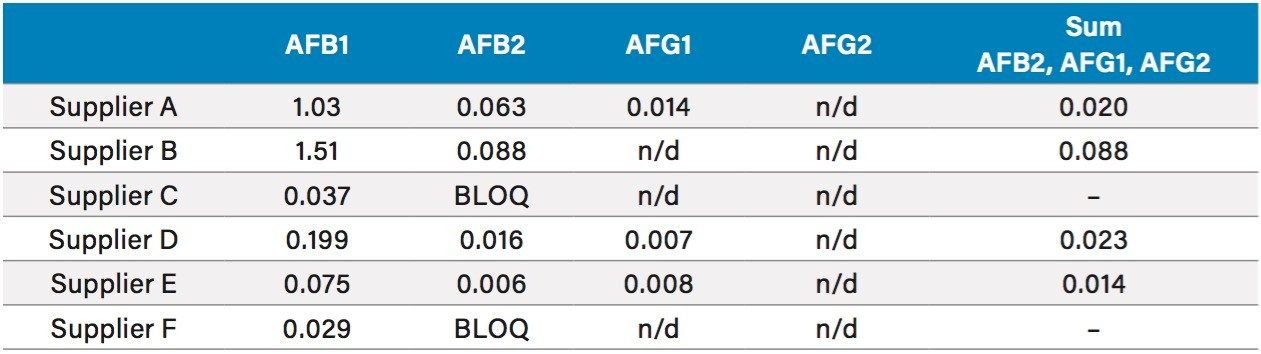
A summary of the concentrations of aflatoxins in coix seed are listed in table 4. As is listed, AFB1 is found in every sample at varying concentration levels with the other aflatoxins at much less concentration, all below the regulatory limits of 5 µg/kg for AFB1 and 10 µg/kg for AFB2, AFG1, and AFG2 combined.
720005898, January 2017