This application note focuses on the use and benefits of micro-elution extraction methods and also the use of the ACQUITY TQ Detector in obtaining a signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio of ~225 at the LLOQ level for docetaxel.
Docetaxel is a clinically well-established anti-mitotic chemotherapy medication used mainly for the treatment of breast, ovarian, and non-small cell lung cancer. It belongs to the chemotherapy drug class of “Taxane”, and is a semi-synthetic analogue of Paclitaxel (Taxol). Docetaxel binds to microtubules reversibly with high affinity and has a maximum stoichiometry of 1 mole docetaxel per mole tubulin in microtubules.
This molecule also has high protein binding nature, and it has been reported that protein disruption results in improper assay results. Hence, it is highly challenging to extract such types of molecules. Micro-elution offers the advantage of using less plasma volume, coupled with the fact that the sample cleanup can be done effectively. This application note focuses on the use and benefits of micro-elution extraction methods and also the use of the ACQUITY TQ Detector in obtaining a signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio of ~225 at the LLOQ level for docetaxel.
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY UPLC |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY UPLC BEH C8 1.7-μm, 2.1 x 100 mm |
|
LC column elution: |
70% aqueous buffer over 2.0 min followed by a 90% organic elution until 4.2 min; then change back to initial conditions. |
|
Column temp.: |
40 °C |
|
Flow rate: |
0.300 mL/min |
|
Injection volume: |
20 μL |
|
MS system: |
ACQUITY TQD |
|
MS mode: |
ESI positive MS/MS method |
|
MRM transition: |
808.7 → 226.3 and 808.7 → 282.3 |
The analyte from the spiked plasma samples was isolated using solid phase micro-elution extraction employing Waters Oasis HLB Micro-Elution Plates. A 300-µL aliquot of plasma was diluted with water, centrifuged at 12,000 rpm in a micro-centrifuge, and loaded onto SPE cartridges previously conditioned with organic solvent and water. The SPE cartridges were then washed with water twice followed by an organo-aqueous wash, and the samples were then eluted with the elution solvent. The eluted samples were injected on to the system directly.
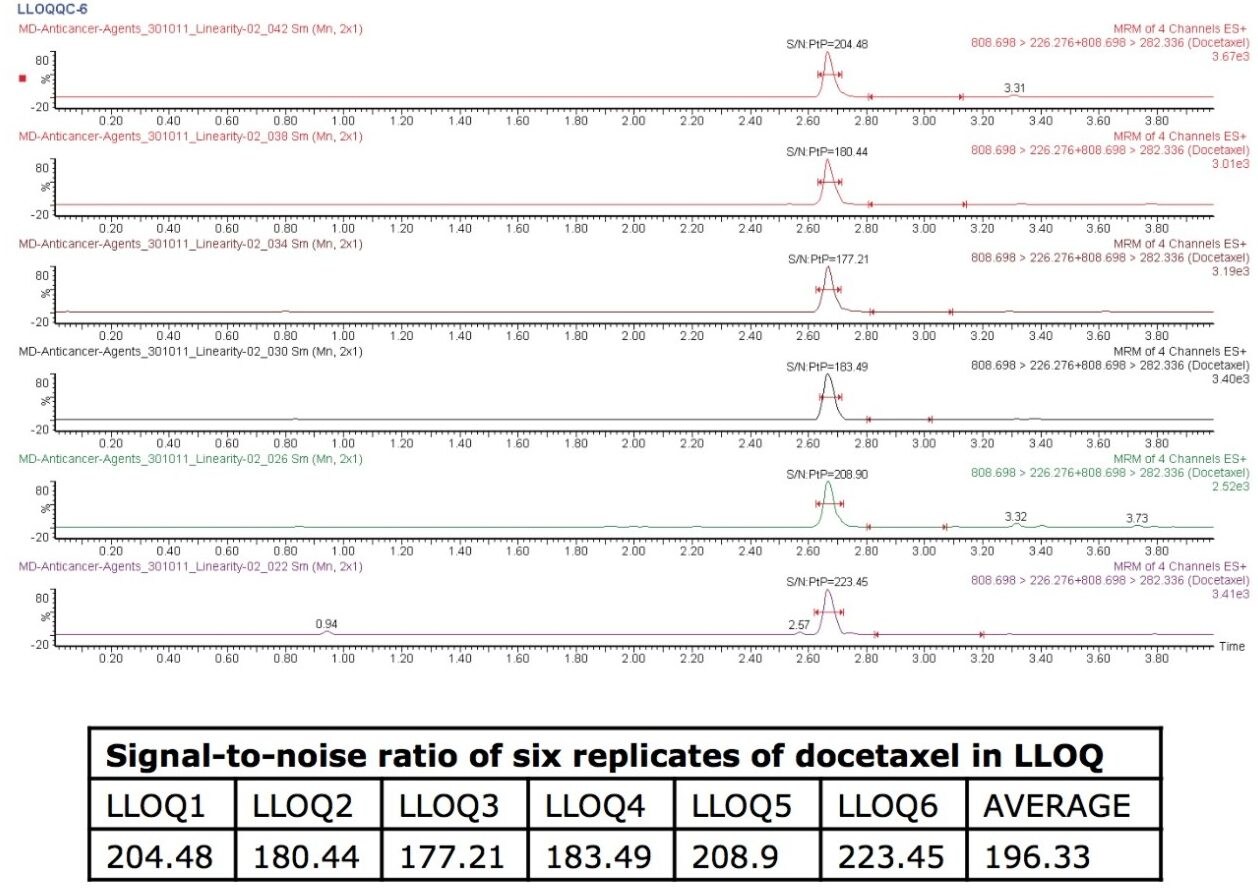
Docetaxel eluted with a retention time of 2.67 mins and with a peak width of 10 s at the base. The data shown below illustrates the blank signal, shown in Figure 3, as well as the signal obtained from the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of docetaxel in human plasma. It can be observed that the analyte was well resolved from co-eluting peaks coming from the endogenous plasma components, shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 also shows chromatograms of six LLOQ samples and their respective signal-to-noise (S/N) ratios. The average of the S/N ratios was found to be 196.33.

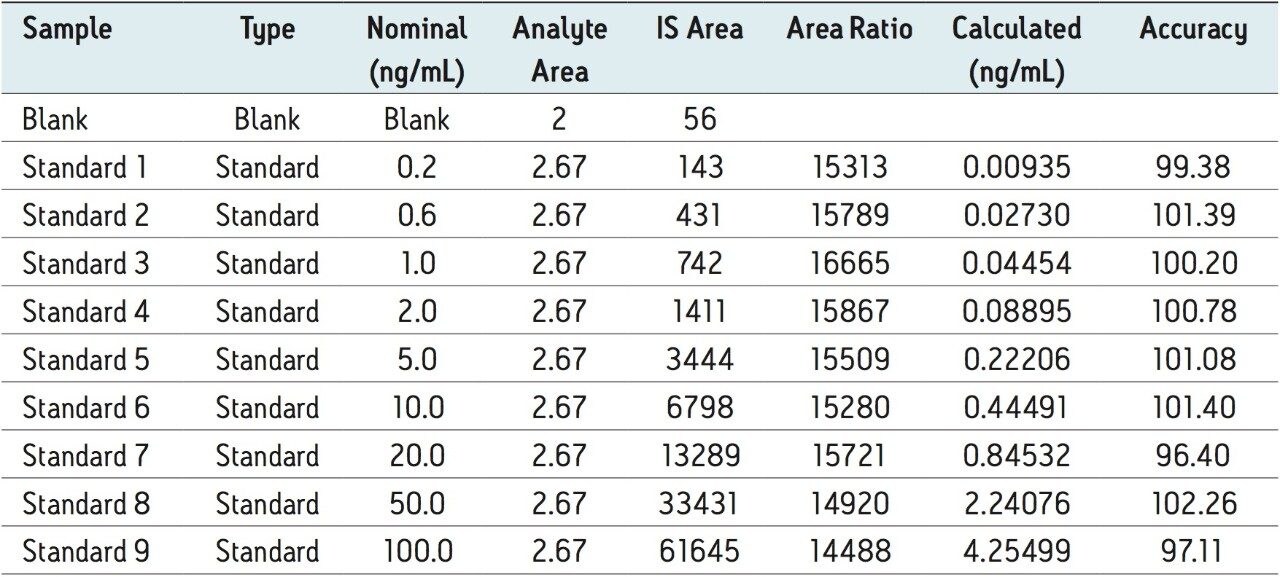
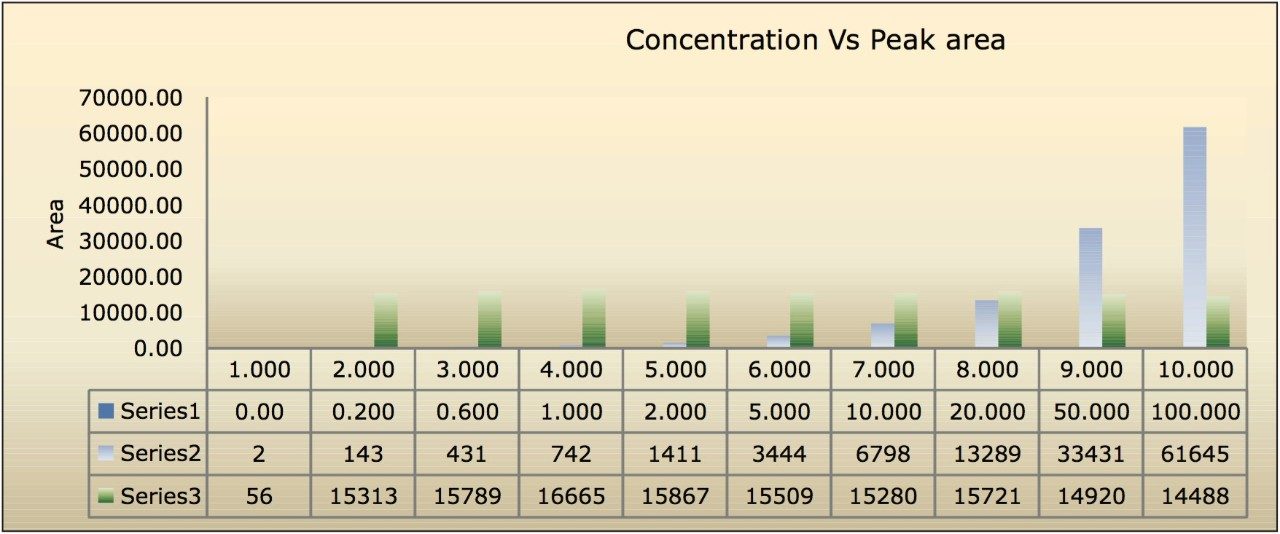
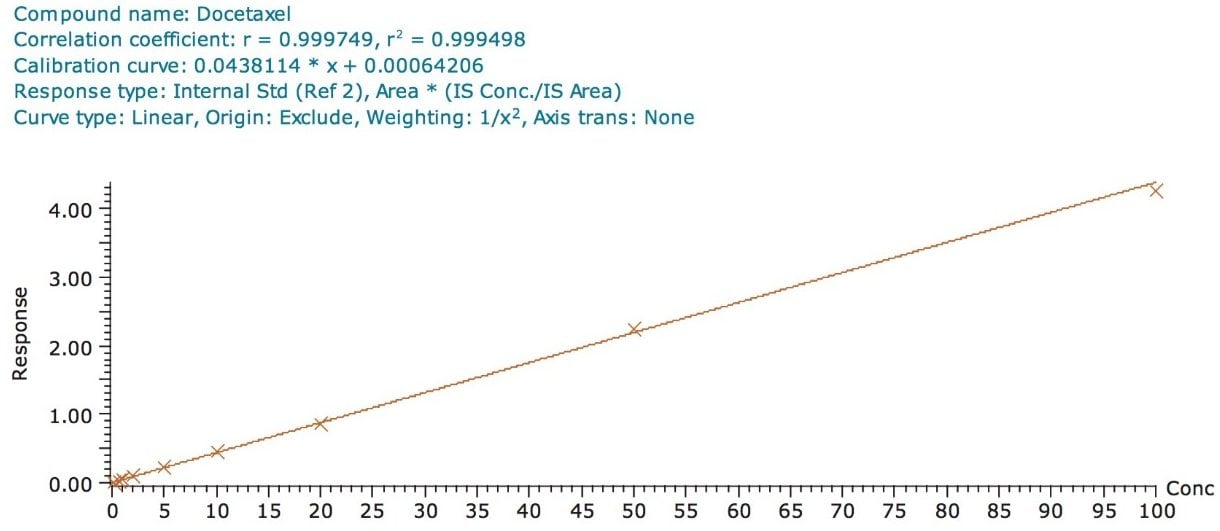
The assay in this report showed a linear calibration over the range of 200 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL with an excellent r2 value of 0.9994, shown in Table 1 and Figures 3.1 and 3.2. The back-calculated concentration of the standard was found to be within 12% of the nominal concentration, shown in Table 1.
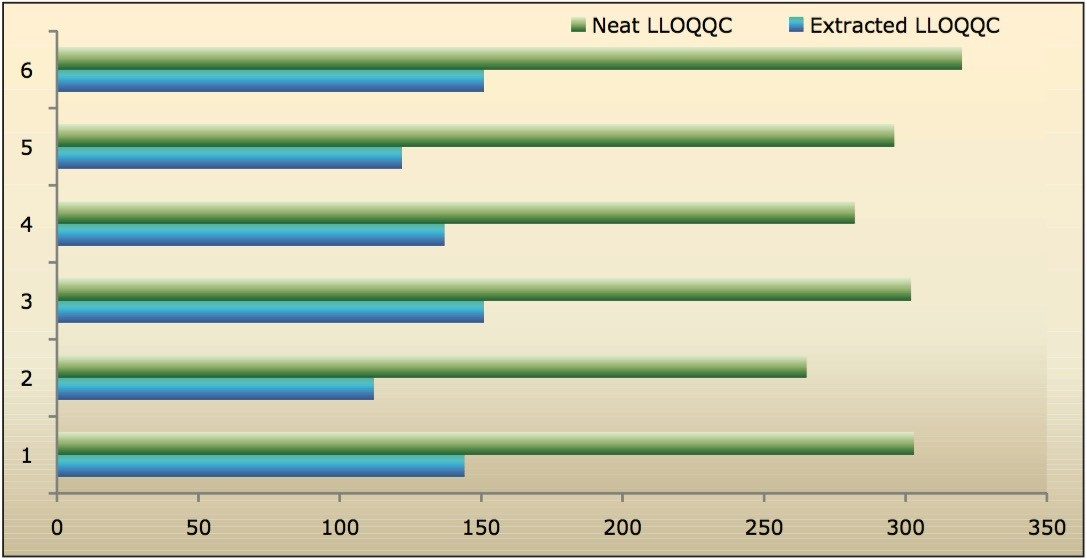
Recovery of the analyte and internal standard (IS) was performed by comparison of the extracted QC samples against six post-extracted samples, which was found to be approximately 48% at LLOQQC, LQC, MQC, and HQC levels for both analyte and the internal standard, as shown in Figures 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, and 4.4, and Table 2. The %CV for repeat batches was found to be within 10% of LLOQQC and varied between 1% to 3% for all QC levels.
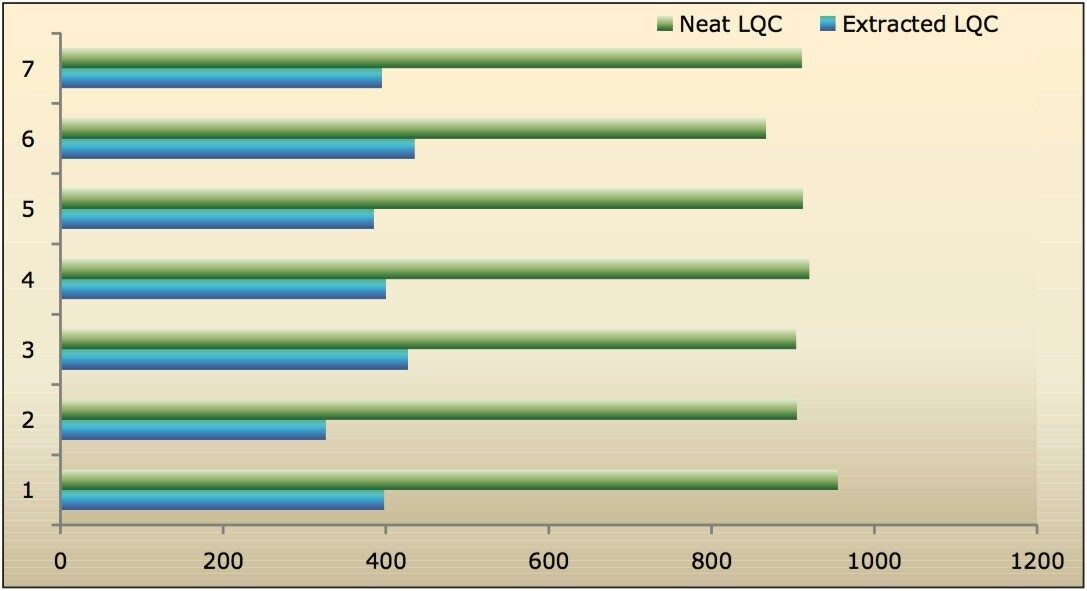
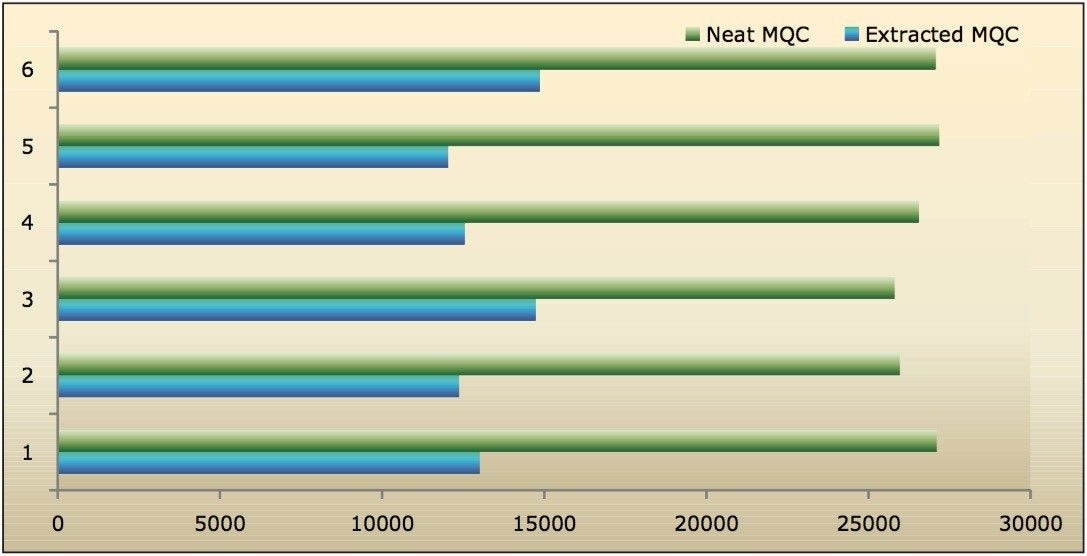
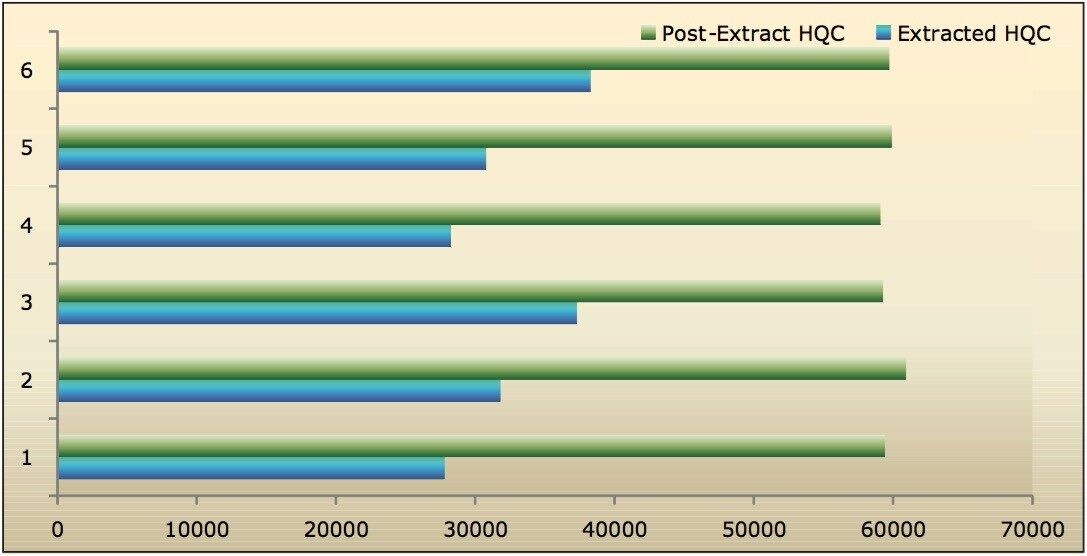
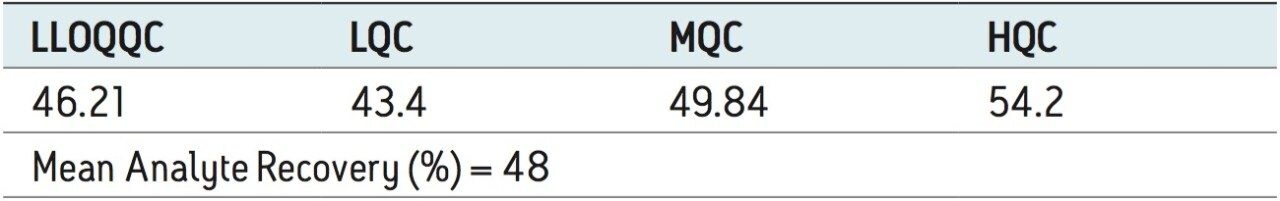
Data shown in Figures 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, and 4.4 shows that the analyte recovery values for the six samples did not vary significantly for any of the four concentration levels (LLOQQC, LQC, MQC, and HQC). In addition, as detailed in Table 2, the mean analyte recovery for the three concentration ranges was 48%.
For a comparison of samples within the global batches, three separate batches were prepared with six samples in each batch for LLOQQC, LQC, MQC, and HQC concentration levels. The data showed excellent agreement between the six samples for all three batches, as shown in Table 3. The mean accuracy obtained for all the samples levels was found to be > 93% for every concentration, shown in Table 3.
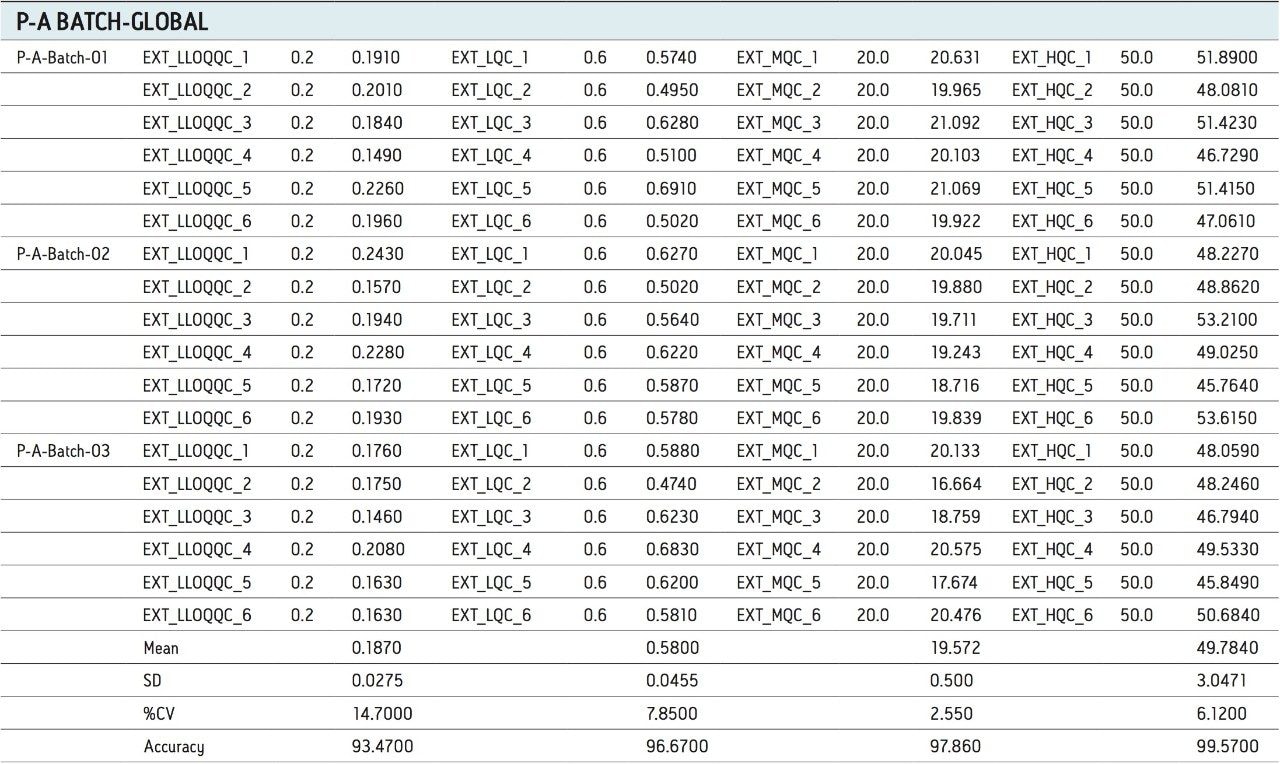
Micro-elution offered a better solution for extraction, which employed low plasma volumes, thereby reducing matrix effect, followed by enrichment of the samples for proper extraction. The sample cleanup was found to be very effective, which can be seen with the S/N ratio obtained for LLOQ (200 pg/mL). The analyte recovery varied very little through the entire range of the calibration including the LLOQ. Excellent reproducibility was observed after summing up of two traces. Thus the above method can be used for the estimation of docetaxel in human plasma with the ACQUITY UPLC System and ACQUITY TQD.
720004408, June 2012