Oasis™ PRiME HLB Solid Phase Extraction for High Bioanalytical Plasma Analyte Recovery and Low Matrix Effects of Top-Selling Pharmaceuticals
Abstract
The following work demonstrates a simple, generic, and broadly applicable sample preparation method, requiring no method development, for the extraction of several top-selling pharmaceutical small molecule therapeutic drugs from plasma using Oasis PRiME HLB reversed-phase solid phase extraction (SPE) and subsequent LC-MS/MS quantification.
Benefits
- Simplified bioanalytical sample preparation strategy, requiring no method development for successful analyte extraction from plasma
- Simple 3-step SPE protocol, yielding high analyte recovery and low matrix effects, with no optimization required
- Removal of more than 90% phospholipids as compared to traditional SPE, resulting in cleaner extracts
- SPE extraction (<30 minutes) using the 96-well µElution SPE extraction plate format
- Fast, 3-minute UPLC-MS analysis using the ACQUITY™ I-Class Plus UPLC™, ACQUITY HSS T3 Column and Xevo™ TQ-XS Mass Spectrometer
- Excellent quantitative performance achieving accuracy and repeatability of ±15% from plasma
Introduction
With continued research and development of next generation therapies and generic pharmaceutical equivalents, there is continued need for their robust, sensitive, and selective bioanalytical sample preparation and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) methods for their accurate quantitation from biological matrices. However, developing robust bioanalytical methods can be quite challenging, with sample preparation often identified as the most challenging aspect of bioanalytical LC-MS method development in terms of complexity, time and assay performance.
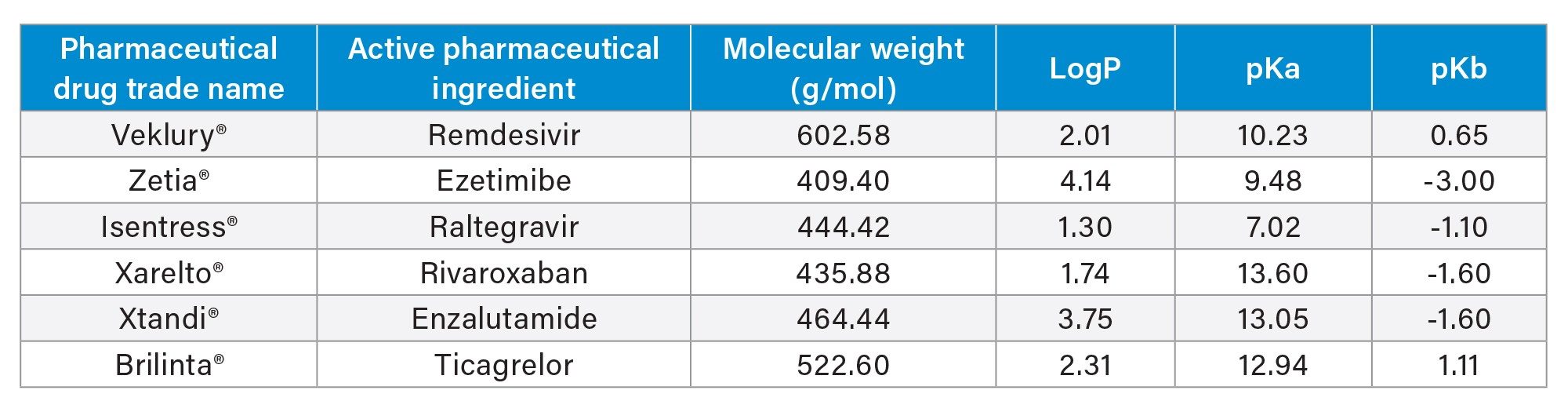
In this application, Oasis PRiME HLB, a reversed-phase solid phase extraction (SPE) sorbent with phospholipid removal was used for extraction of several top-selling pharmaceuticals in 2023 (Table 1) from plasma, employing a 3-step load-wash-elute SPE protocol. Excellent analyte recovery ≥80% were achieved with matrix effects ≤15%.1
Experimental
LC Conditions
|
UPLC: |
I-Class, FL with Column Manager (CMA) |
|
Mobile phase A: |
0.1% FA in Water |
|
Mobile Phase B: |
0.1% FA in ACN |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 100 Å, 1.8 µm 2.1 mm x 30 mm (p/n: 186003944) |
|
Col temperature: |
35 ˚C |
|
Sample temperature: |
10 ˚C |
|
Inj. volume: |
10 µl |
|
Analysis time: |
3.0 min |
|
WNW: |
90:10 Water:ACN + 0.1% FA |
|
SNW: |
25:25:25:25 Water:IPA:ACN:MeOH |
MS Condition
|
MS: |
Xevo TQ-XS |
|
Capillary (kV): |
2.0 |
|
Cone voltage: |
32 V |
|
Desolvation temp: |
500 °C |
|
Desolvation flow: |
1100 L/Hr |
|
Cone gas flow: |
150 L/Hr |
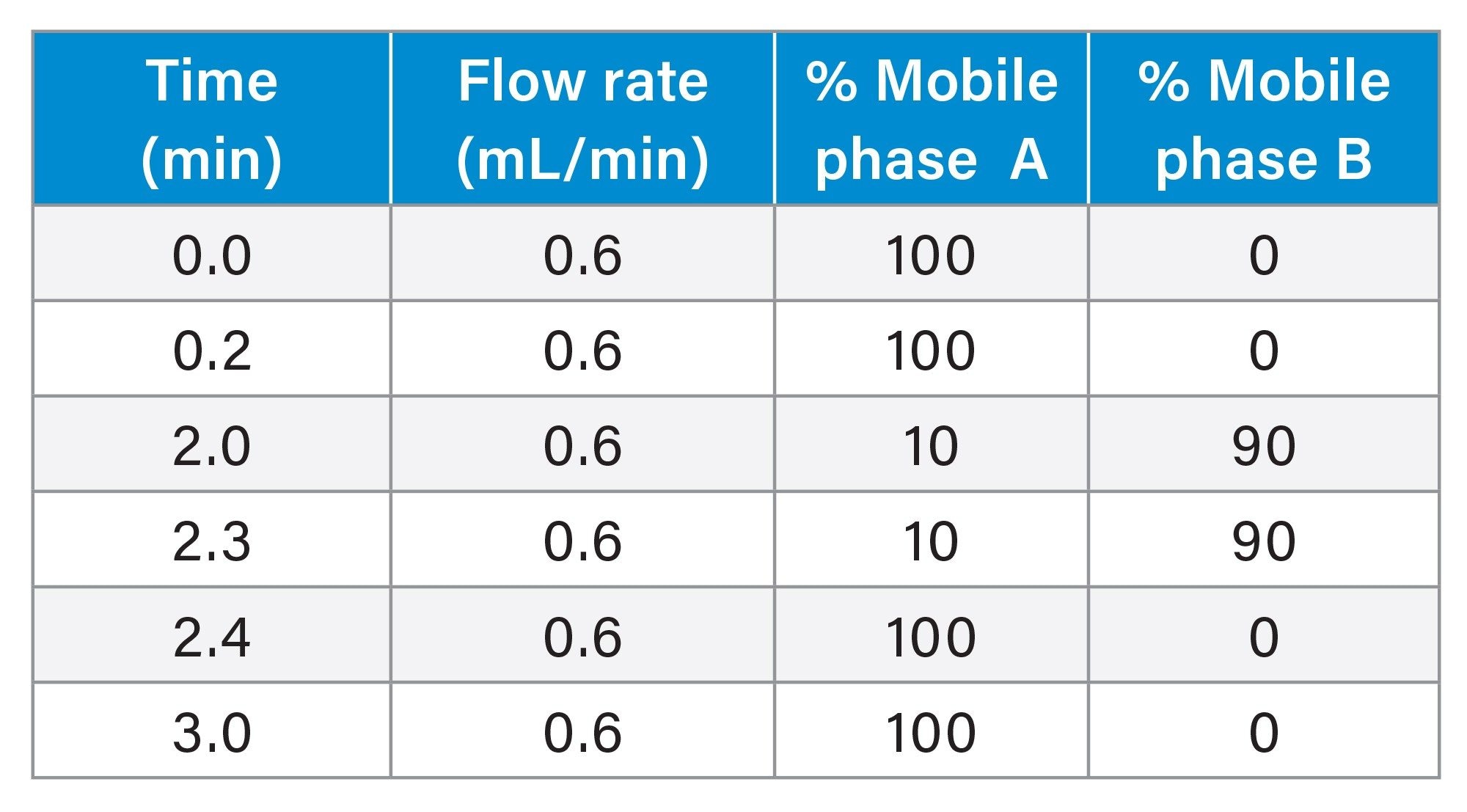
UPLC Gradient Table
Data Management: All data was acquired and analyzed using Waters MassLynx™ Software v. 4.1 and quantification performed using TargetLynx™ Software.
Materials: The small molecule pharmaceuticals were purchased from Selleckchem (https://www.selleckchem.com) and from Cayman Chemicals (www.caymanchem.com) LC-MS grade formic acid, and phosphoric acid, were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (www.sigmaaldrich.com). Methanol and Acetonitrile were purchased from Honeywell (lab.honeywell.com).
Sample preparation and extraction
Stock solutions of each individual pharmaceutical (1 mg/mL) were prepared in a 50:50 water: methanol solution. Aliquots of each 1 mg/mL pharmaceutical stock solution were combined to yield working stock solution mixtures of 50, 10, and 1 µg/mL, respectively. Initial recovery and matrix effects evaluations were conducted using 0.5–1.0 µg/mL prepared in rat plasma. Calibration curve samples were prepared between 0.9–1,000 ng/mL. The SPE extraction protocol, using the Oasis PRiME SPE 96-Well µElution Plate, is shown in Figure 1.

Pharmaceutical analyte recovery was calculated according to the following equation:
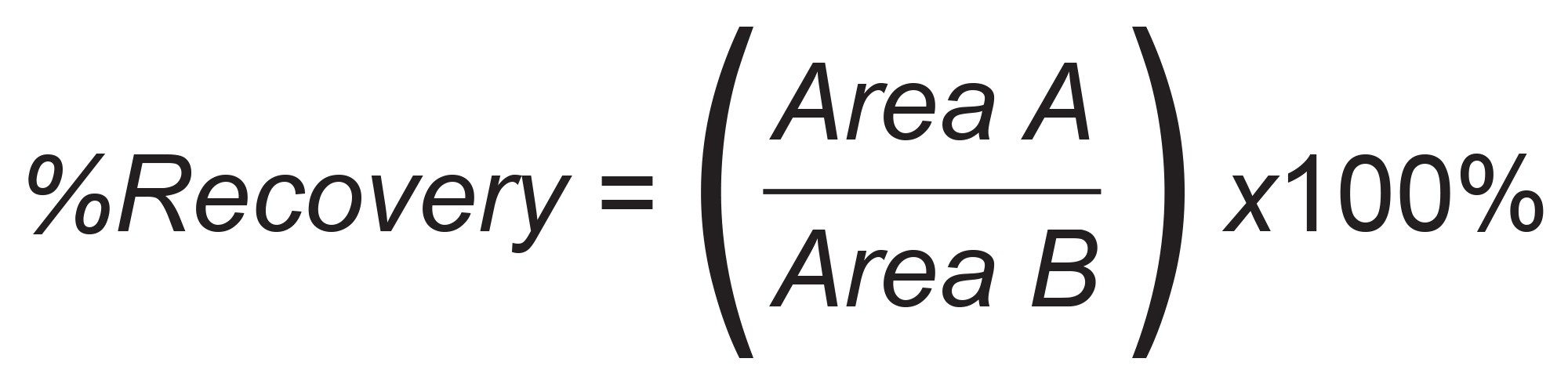
Where Area A = the peak area of an extracted sample and Area B = the peak area of an extracted matrix sample in which the compounds were added post-extraction.
Matrix effects were calculated according to the following equation:

The peak area in the presence of matrix refers to the peak area of an extracted blank matrix sample in which the compounds were added post-SPE extraction. The peak area in the absence of matrix refers to analytes in a neat solvent solution comprised of the final SPE eluate composition injected for analysis. In this case, 90:10 acetonitrile:methanol (elution solution) diluted 1:1 with water.
Results and Discussion
LC/MS Analysis
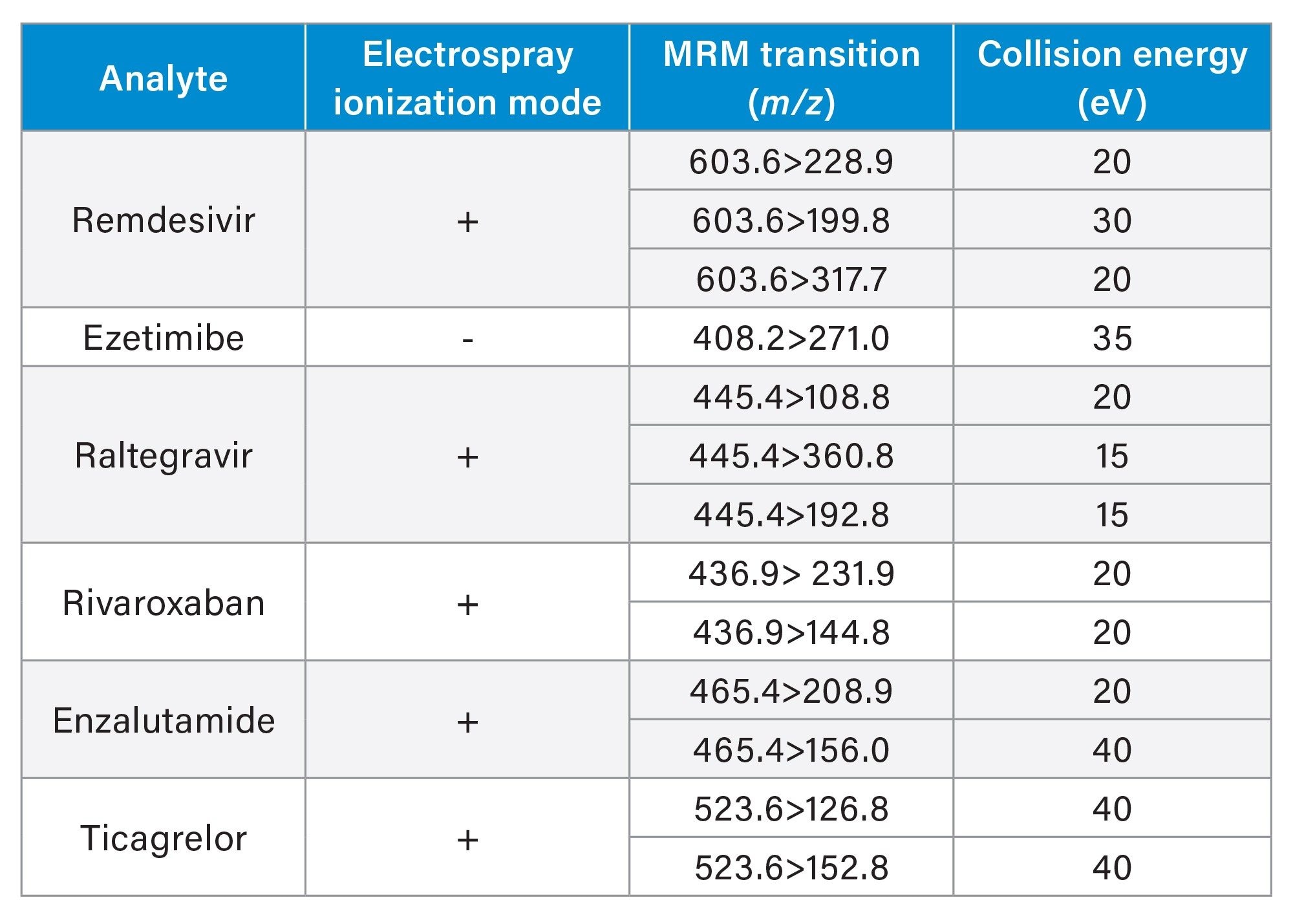
LC-MS/MS analysis was performed using a Waters Xevo TQ-XS tandem quadrupole MS using an electrospray ionization (ESI) source and Multi Reaction Monitoring (MRM). The MS MRM transitions for each pharmaceutical are listed in Table 2. Chromatographic separation of these analytes were performed using an ACQUITY I-Class PLUS UPLC system and ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 Column (p/n: 186003538). The column temperature was 35 ˚C. Gradient separation using 0.1% formic acid in water (MP A) and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (MP B) was employed. Initial LC conditions used a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min and 100% MP A, which was held for 0.2 minutes, followed by an increase to 90% MP B over 1.8 minutes and then held 90% MP B for 0.3 minutes to flush the column and returned to starting gradient conditions at 2.4 minutes. Total analysis time was 3 minutes. Injection volume of the extracted samples was 10 µL. An illustration of analyte chromatographic performance is illustrated in Figure 2.
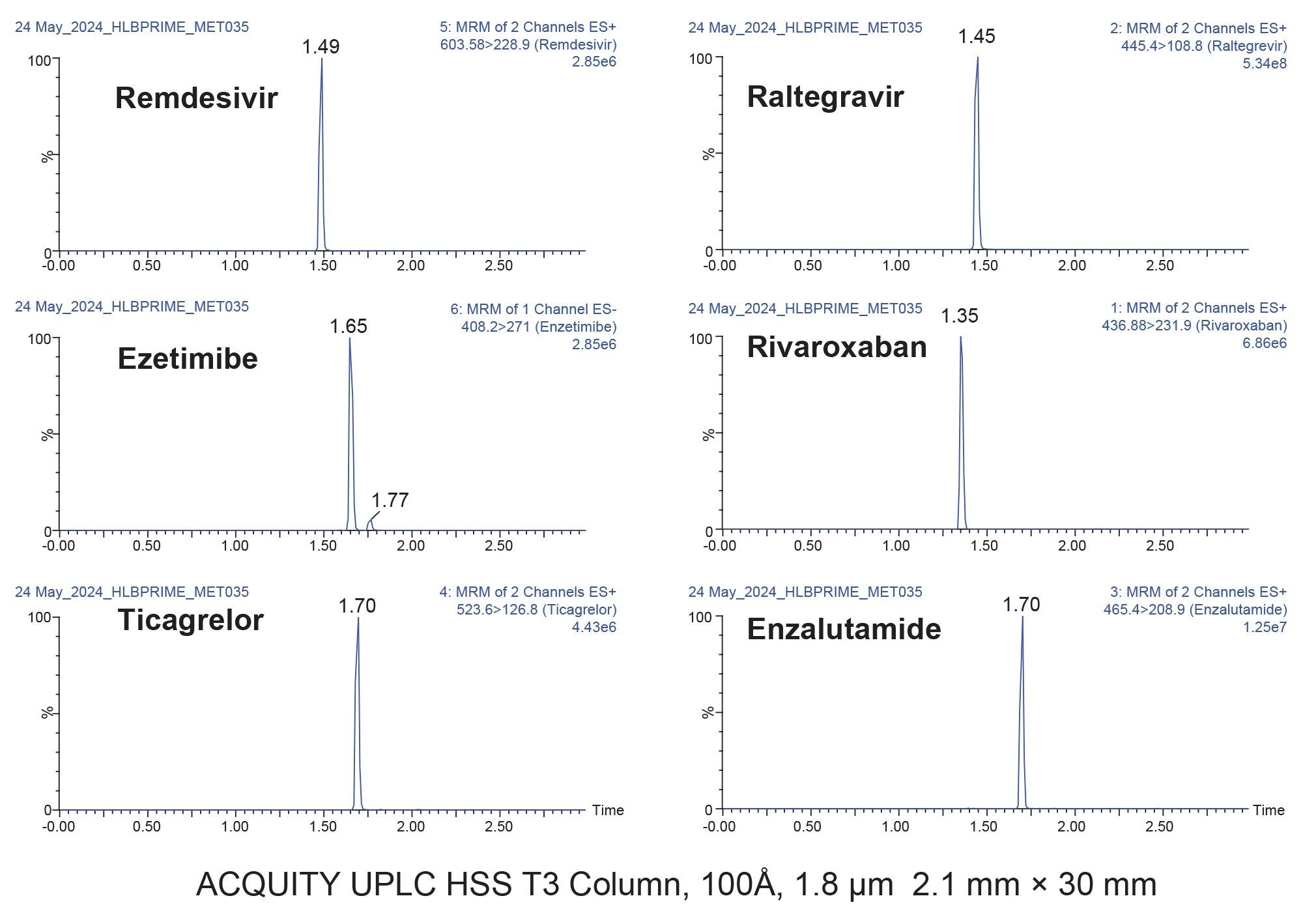
SPE Extraction
The pharmaceutical analytes in this application were neutral and basic analytes, with pKa ranges between 7-13. In addition, their hydrophilicity, LogP values ranged from 1.3-4.14. These physiochemical properties are provided in Table 1. Use of Oasis PRiME HLB reversed-phase sorbent enabled the simultaneous extraction of these diverse analytes, with >80% recovery from plasma (Figure 3).
Oasis PRiME HLB is a novel reversed phase SPE sorbent developed to enable simpler and faster SPE protocols, while at the same time generating cleaner extracts than other traditional sample preparation methods.3 A key attribute of Oasis PRiME HLB, is the ability to remove > than 90% of endogenous phospholipids compared to traditional SPE and protein precipitation.3–5 Selectively removing phospholipids aids in the reduction of their co-elution with analytes of interest, which then reduces the associated MS ion enhancement or suppression, and often results in lower matrix effects. In this application, resulting matrix effects ranged from -15.2 to 5.4%.
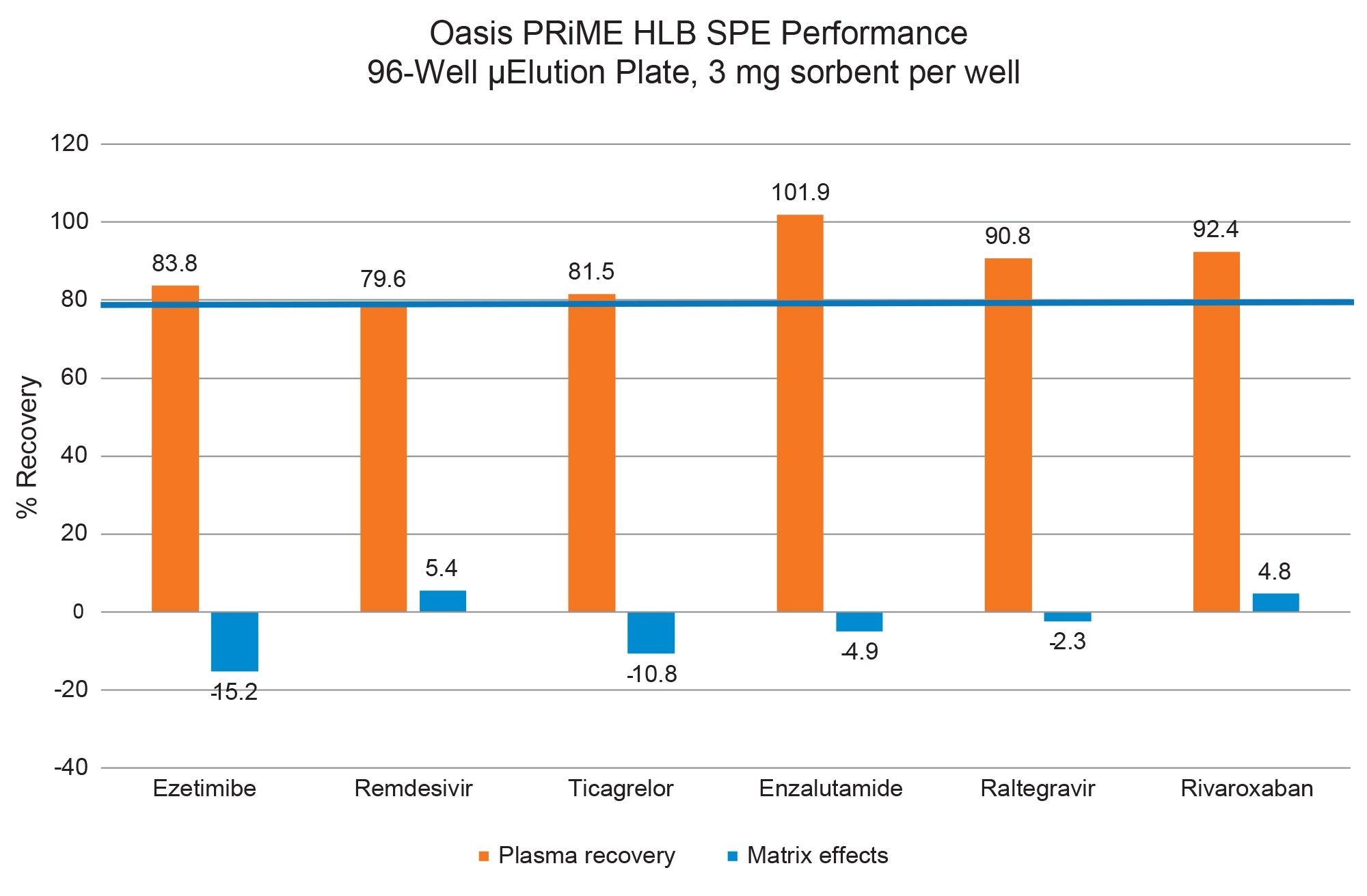
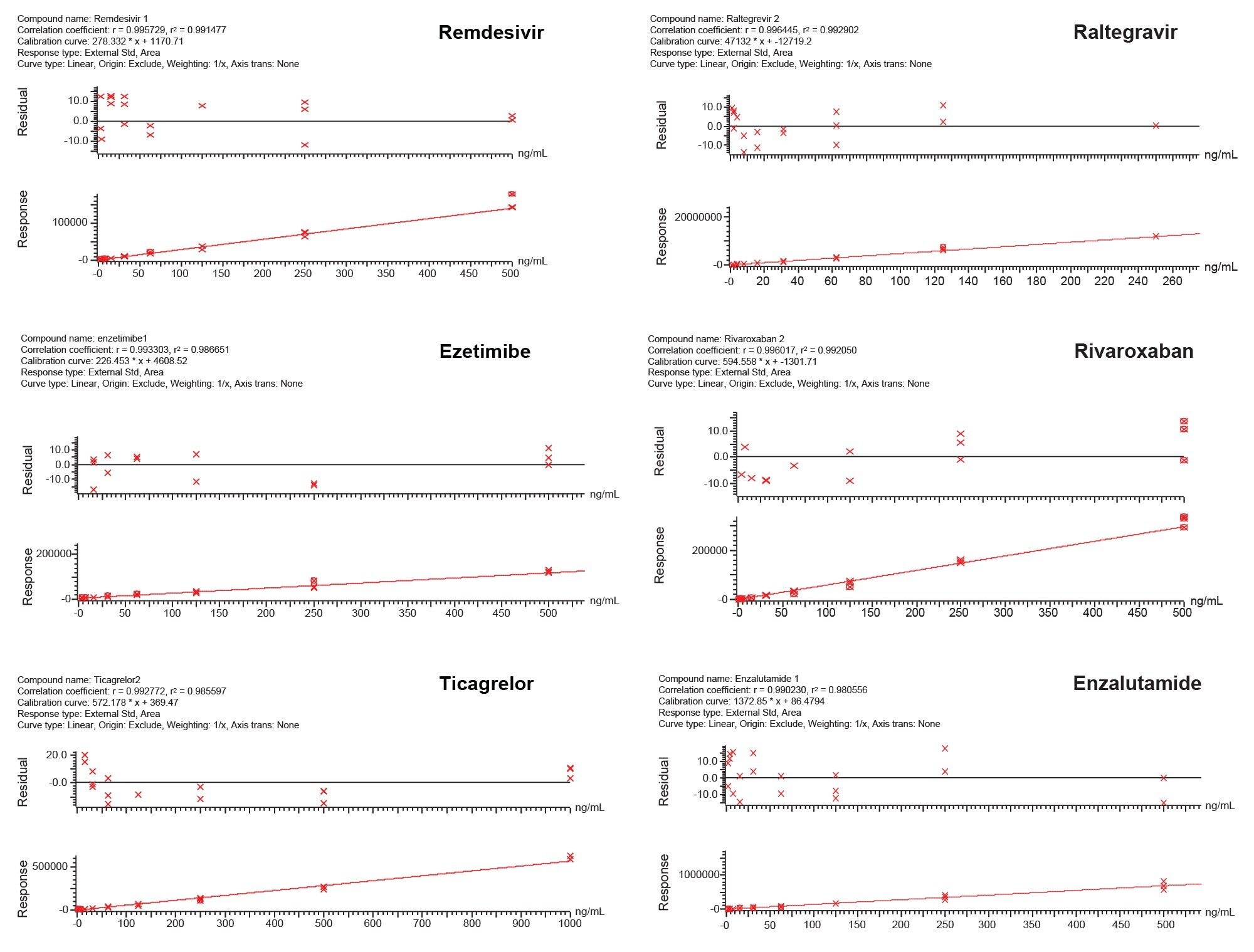
Bioanalytical Quantitation
Proof-of-concept bioanalytical quantification of the pharmaceutical analytes extracted from plasma using the Oasis PRiME HLB SPE is highlighted in Figure 4. Linear fit of calibration curves was >0.99. Lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all pharmaceutics was 0.91 ng/mL, while upper limit of quantification (ULOQ) was 500 ng/mL for remdesivir, ezetimibe, rivaroxaban, and enzalutamide. Raltegravir ULOQ was 250 ng/mL and 1000 ng/mL for ticagrelor. Accuracy of all calibration points was ±15%.
Conclusion
This application highlights the successful SPE extraction and LC-MS/MS quantification of several key small molecule pharmaceuticals from plasma using Oasis PRiME HLB SPE. Use of generic protocols greatly simplified sample preparation method development while also providing excellent extraction performance, achieving high analyte recovery (80%), low matrix effects (≤15%), and removal of 90% of residual phospholipids in the extracted sample.
References
- Williams, RE and Leatherwood HM Top 200 Small Molecule Drugs by Retail Sales in 2023 https://bpb-us-e2.wpmucdn.com/sites.arizona.edu/dist/9/130/files/2024/05/2023Top200SmallMoleculePosterV5.pdf (accessed 21 June 2024).
- Drugbank Online https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00480 (accessed 21 June 2024).
- Zhang X., Danaceau, JP., Chambers, EE. Improvements in Recovery, Reproducibility, and Matrix Effects with Oasis PRiME HLB, a Novel Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbent, Waters Application Note, 720005495, September, 2015.
- Danaceau, JP., Trudeau ME.,A Simple, Broadly Applicable Automated Bioanalytical Sample Preparation Strategy for LC-MS Quantification of Apixaban: Evaluation of Common Bioanalytical Extraction Techniques, Waters Application Note, 720007946, July 2023.
- Rahim F., VanTran, K., Trudeau ME., Simple, Fast and Selective, Bioanalytical Sample Extraction for the Therapeutic Drug, Lenalidomide From Plasma Using Oasis MCX SPE, Waters Application Note, 720008140, December 2023.
720008426, July 2024