
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
This application brief demonstrates to evaluate the Xevo TQ-GC as a fit for purpose electron ionization (EI) GC-MS/MS for the routine analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) extracted from sediment samples.
Xevo TQ-GC is a fit for purpose GC-MS/MS solution for routine analysis of PCBs in sediment samples.
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a class of man-made chemicals that, although were banned in the late 1970’s, are still persistent in the environment. Exposure to PCBs is well known to cause a variety of adverse health effects. There are 209 congeners varied by the number and substitution pattern of chlorines on the biphenyl backbone. Toxicity varies by congener and the World Health Organization hosts additional information about toxicity on their website. Therefore, environmental monitoring of these compounds is still necessary.
Various sediment sample extracts previously prepared on site at Environment and Climate Change Canada Quebec Laboratory for Environmental Testing (QLET) were used for this evaluation. A suite of 41 PCBs (Cl3 through Cl10) were chosen based on toxicity, abundance in Aroclor mixes, and persistence in the environment. This list of PCBs was evaluated on the Xevo TQ-GC for routine performance criteria such as sensitivity, accuracy, and robustness based on analysis of the extracted sediment samples.
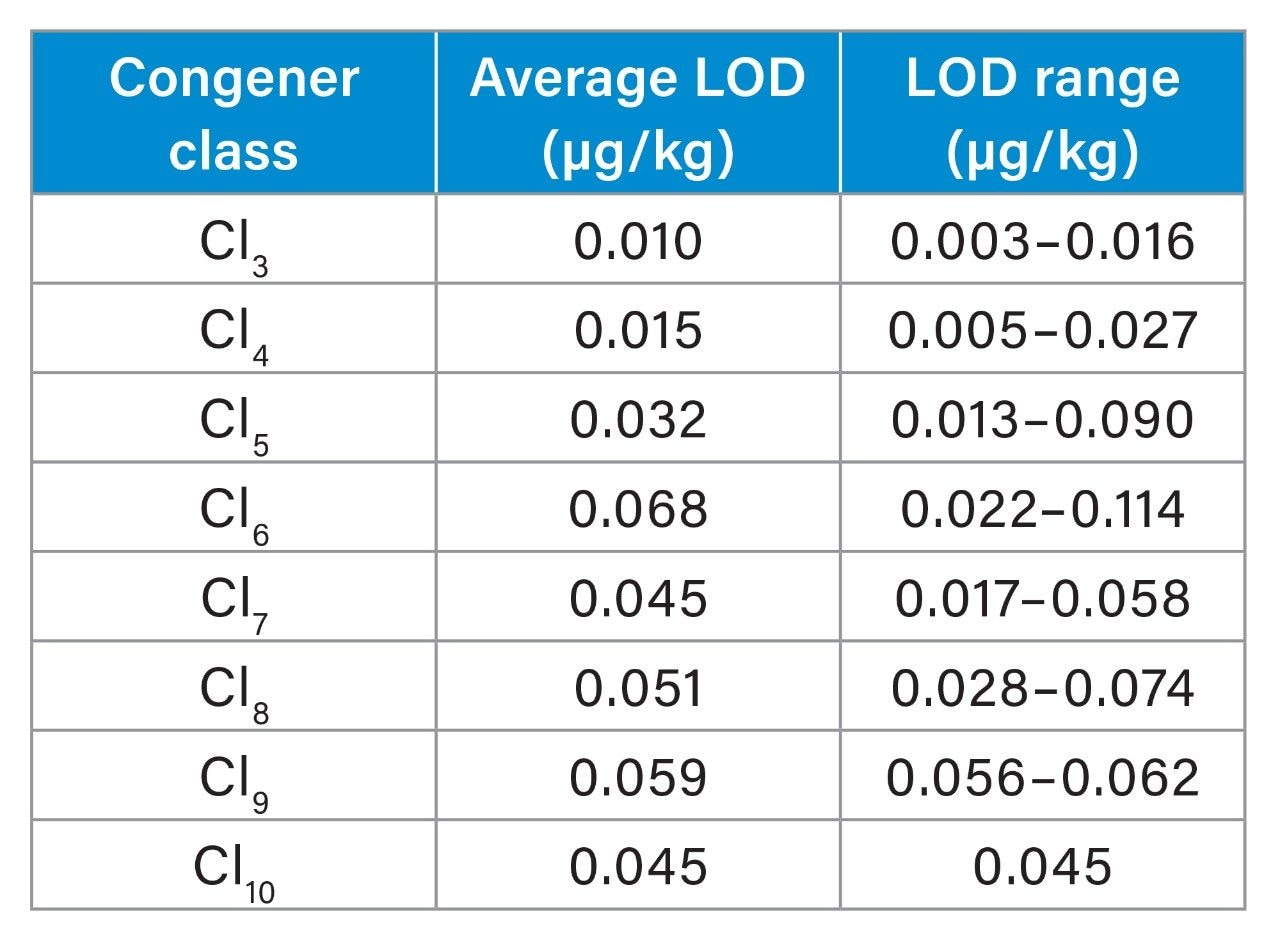
For analysis, a calibration range of 0.1–20 μg/kg was utilized and the Xevo TQ-GC demonstrated excellent linearity for all compounds with R² values ≥0.997. Sensitivity was evaluated by determining limit of detection (LOD) values using solvent standards for each PCB based on 5 replicate injections. Table 1 highlights the overall results of the LODs for each congener group. On average, the LODs were well below 0.100 μg/kg, demonstrating sensitivity into the parts per trillion (ppt) range.
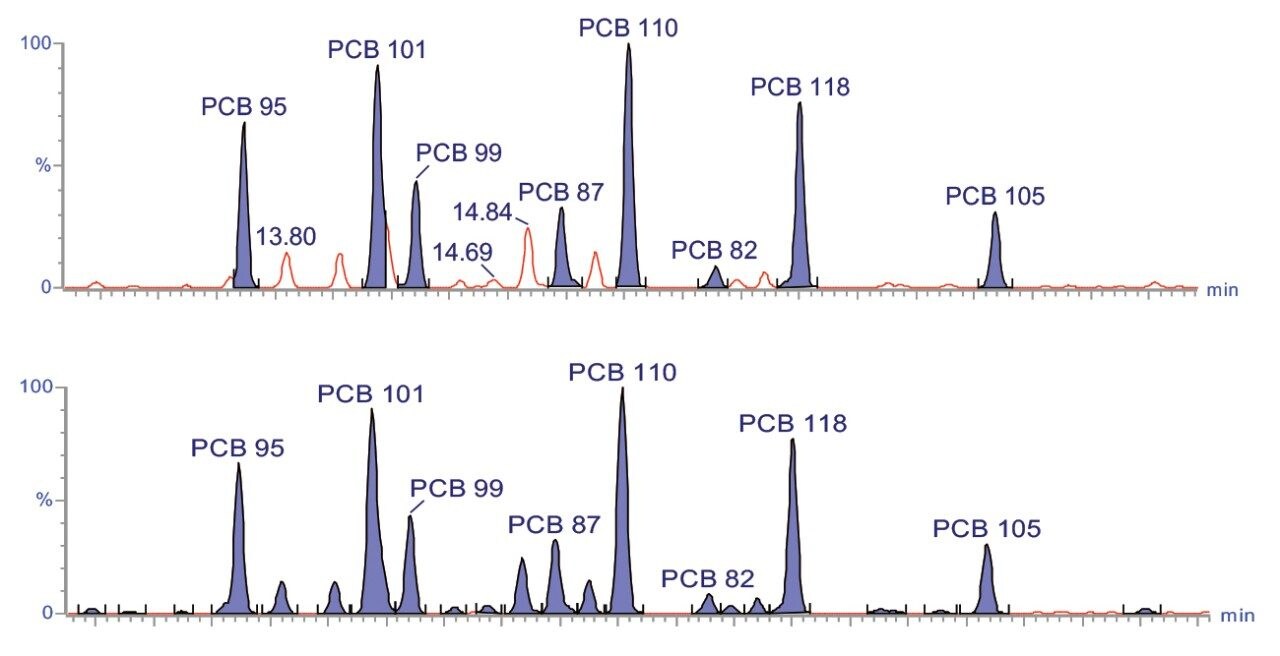
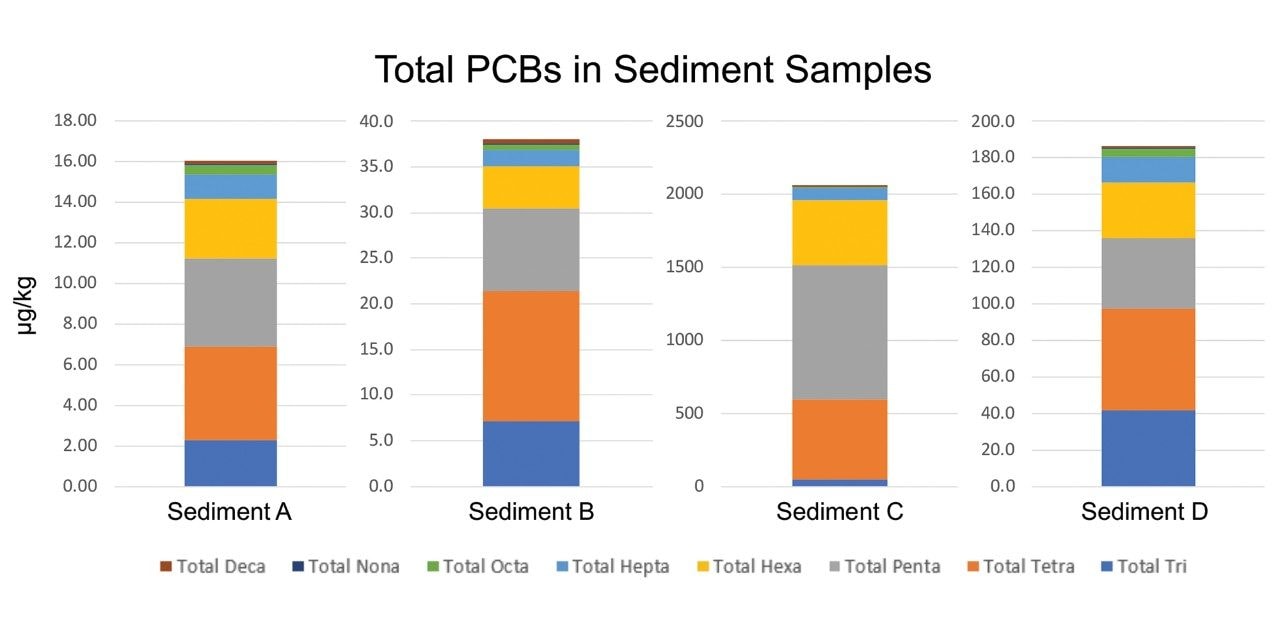
Quantitation of PCBs can be performed multiple ways depending on reporting requirements. Quantitative values can be determined for individual PCBs, by congener group, or by Aroclor mix. The totals functionality in TargetLynx allows for the latter two quantitative schemes as well as options for custom reports. Figure 1 demonstrates the pentachlorinated PCB MRM channel, with only the targeted penta PCBs summed on the top trace, and the entire congener group summed on the bottom trace. Four sediment samples were evaluated, and total PCB congener sums are shown for each sample in Figure 2. The total PCB concentration ranged widely between samples, ranging from 16–2000 μg/kg.
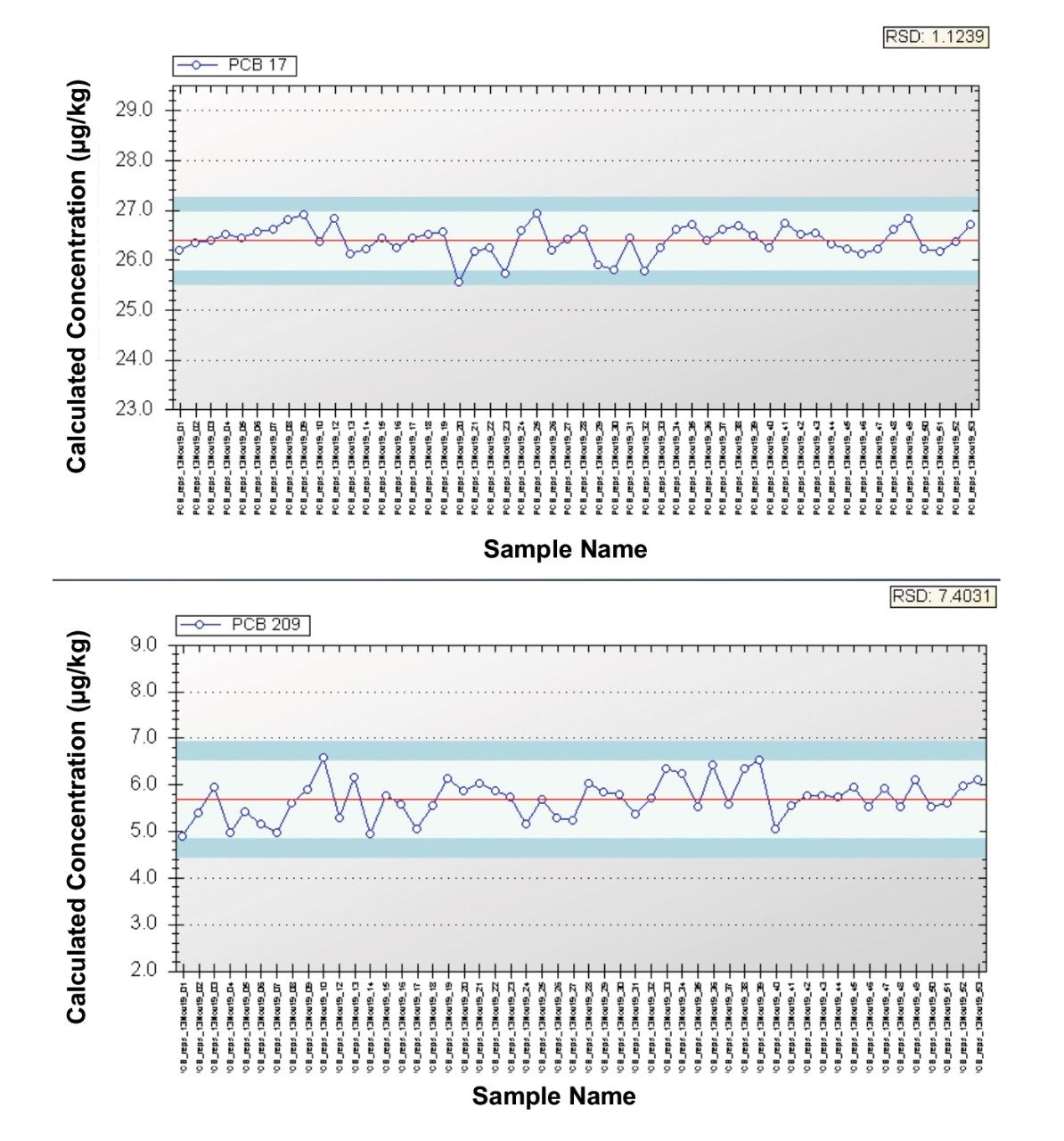
Finally, robustness of the quantitative method was evaluated using 50 replicate injections of one of the sediment samples. Percent RSD was monitored for the reported calculated concentration of all detected PCBs in the sample. Figure 3 demonstrates the Trendplot of PCB 17 (Cl3) and PCB 209 (Cl10) over the 50 injections with % RSD values of 1.1 and 7.4, respectively. All detected PCBs demonstrated % RSDs <10%, with a majority <5%. This establishes that the analysis of PCBs on the Xevo TQ-GC is robust and suitable for routine use.
The Xevo TQ-GC is demonstrated to be suitable for the routine, accurate, and robust analysis and quantitation of PCBs in sediment samples. Average limits of detection for each congener group ranged from 0.010 to 0.068 μg/kg, indicating the Xevo TQ-GC can detect trace levels of PCBs in sediment samples, allowing the instrument to meet and exceed global regulatory requirements. Analytical laboratories could extend this application for PCB analysis to other types of environmental and food matrices and analyses with proper sample preparation consideration.
720006885, July 2020