Analytical LC-MS Platform Methodologies to Support Upstream Bioprocess Optimization
Yun Alelyunas, Julie Wushensky, Jurgen Sanes, Mark Wrona, Rui Chen
Waters Corporation, United States
Published on October 10, 2025
Introduction
Effective process monitoring and product critical quality attribute analysis are critical components for a given upstream process optimization operation. It is desirable that these analyses can be carried out by multi-disciplined scientists who can easily perform the analysis in the absence of deep discipline-based understanding. For liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis, high throughput is expected to ensure quick turn-around time, such that the results can be fed back to the cell culture design of experiment (DOE) model for a fast design-make-test cycle.
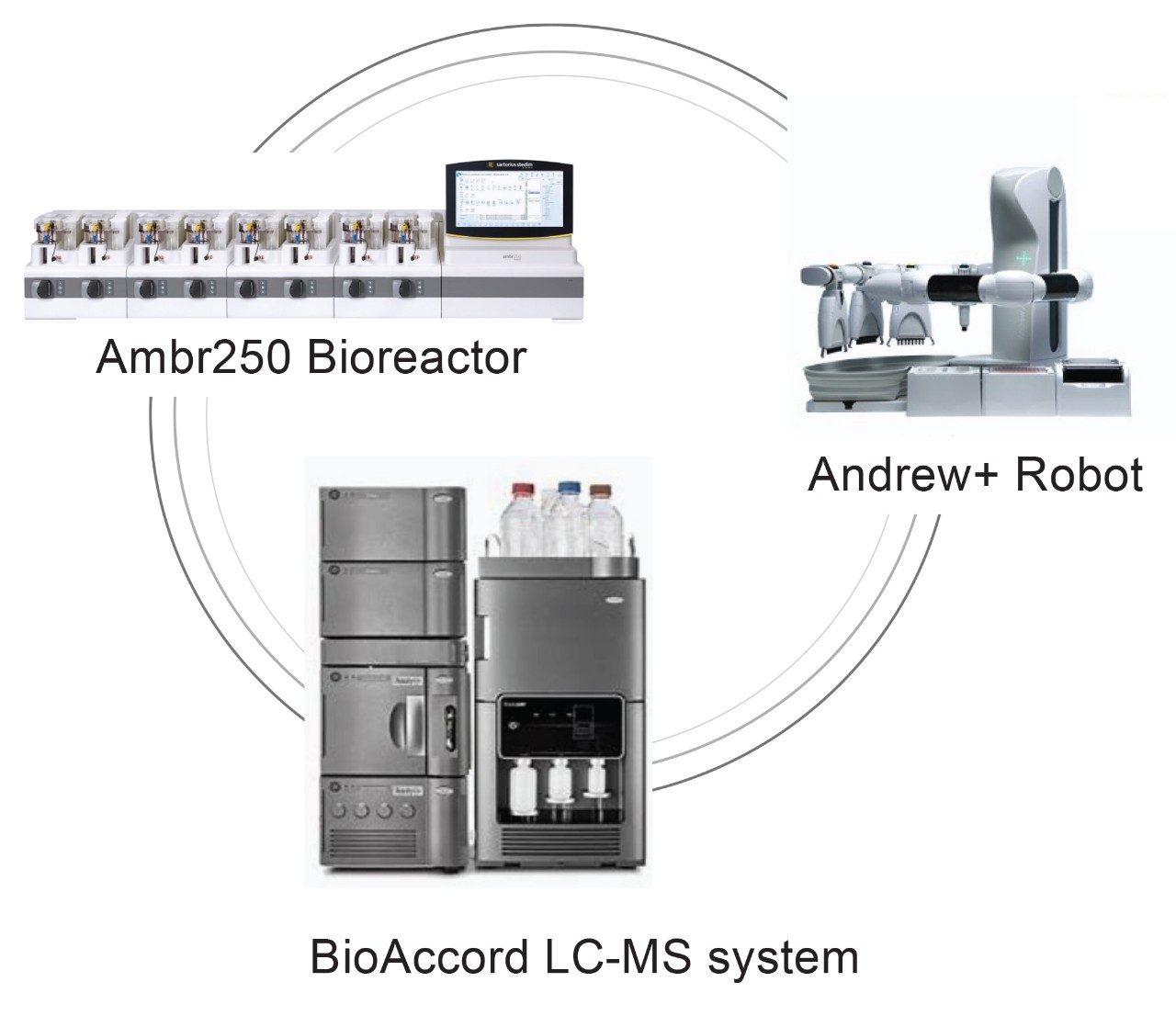
At Waters Immerse Delaware (WID) laboratory, cross-disciplinary scientists are assembled to include cell culture engineers and traditional LC-MS analytical scientists. In proof-of-concept studies, the team conducts upstream bioprocess optimization experiments for a monoclonal antibody (mAb) producing CHO cell line using an Ambr® 250 eight modular bioreactor system. The resulting harvested cell culture fluid (HCCF) samples are subject to LC and LC-MS analysis for process and product critical attribute measurements. These include titer, aggregation and impurities determination, cell culture media components and metabolite analysis, intact protein mass determination and major glycosylation profiling, reduced protein to heavy chain for major glycosylation profiling, and released glycan analysis, among others. All these analyses are carried out using ACQUITY™ LC and/or BioAccord™ LC-MS systems. BioAccord is a high-resolution mass spectrometer system with small footprints and user-friendly instrument control and operation. This allows the instrument to fit in bioprocess labs easily and enables scientists who have minimal training in LC-MS technology to carry out analysis quickly. The WID lab is also equipped with an Andrew+™ Robot with intuitive OneLab™ software for writing automation protocols; this allows for the automation of both routine and complicated sample preparations, such as ProA purification or released glycan analysis. A summary of major instruments in WID laboratory that are involved in the present study are shown on the title page.
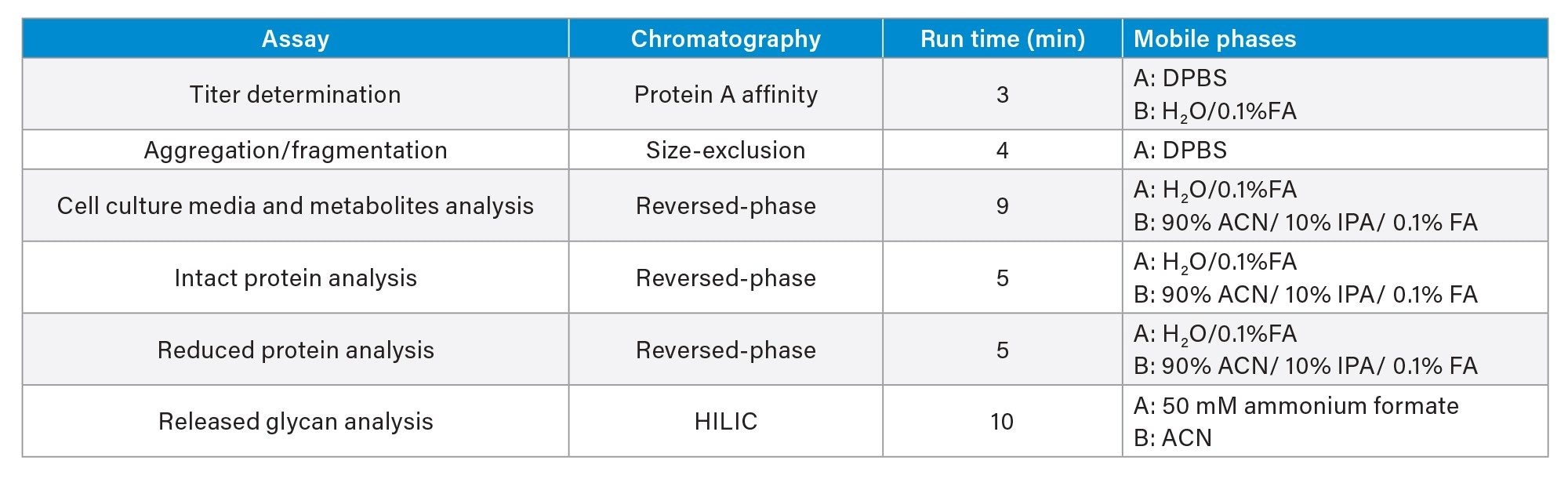
This application note is a compilation of optimized automation and analytical methods for ease of reference. Method optimization resulted in both reduced analysis time and enhanced operational efficiency. These include sharing mobile phases among multiple analyses and using commercially available mobile phases for minimizing preparations. Assays included are summarized in the table below:
Experimental
I. Sample Collection and Distribution
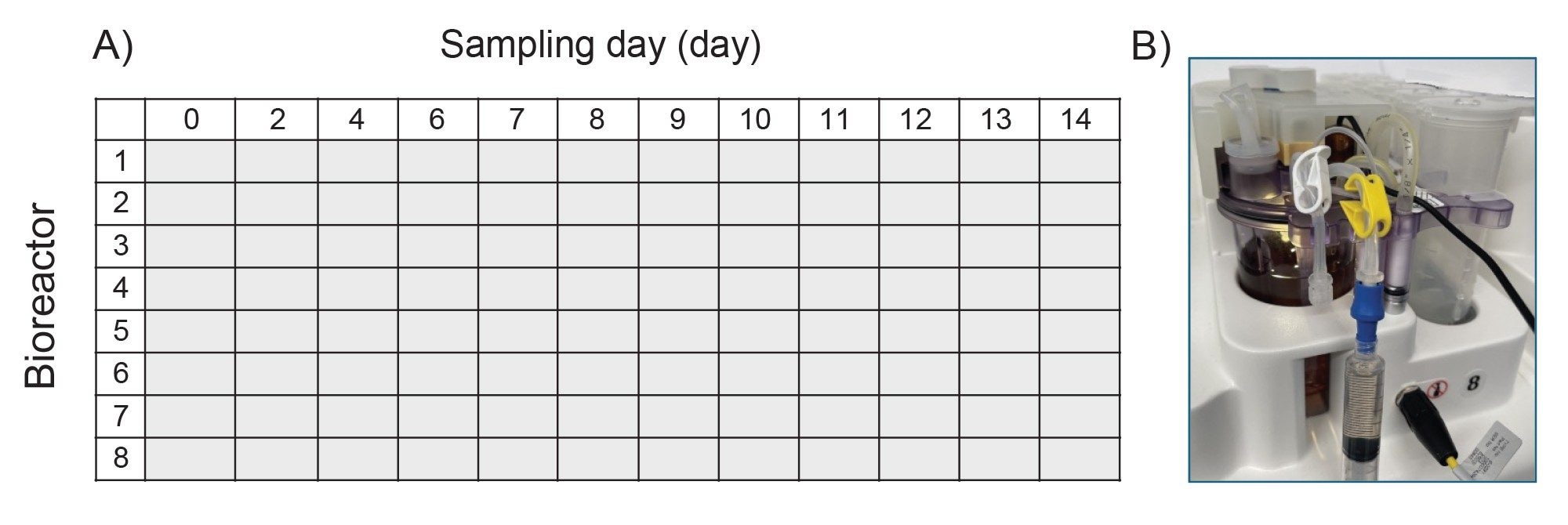
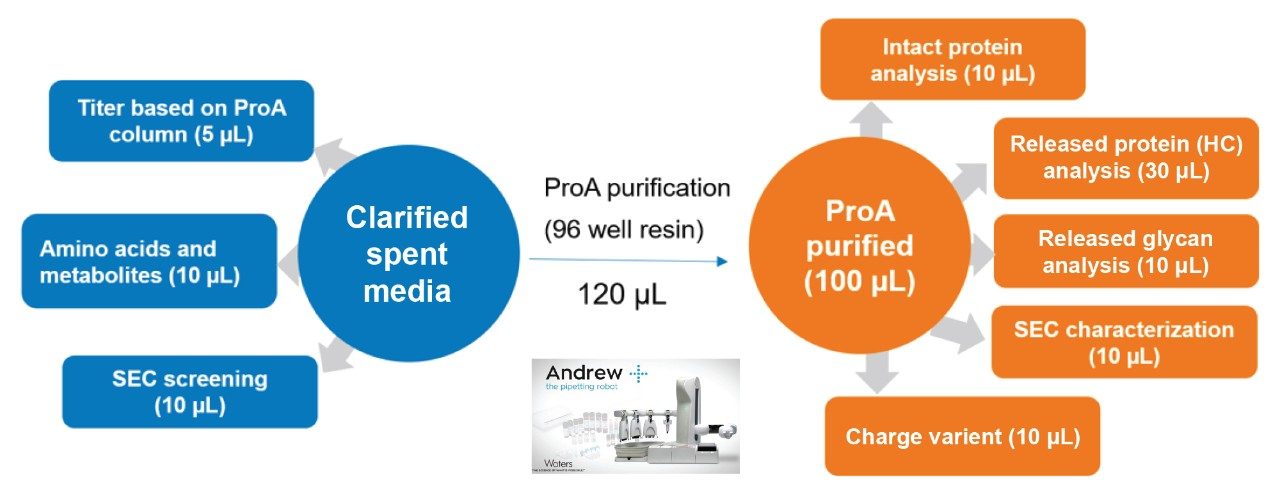
- In a typical DOE designed experiment in upstream process optimization, HCCF could be collected daily for a 14-day fed-batch experiment. After centrifugation and filtration, the clarified samples would then be stored in 1.4 mL tubes in 96 well format at -80 °C.
- These clarified samples are subject to analysis such as protein titer, amino acids and metabolites, and aggregation screening. For product critical attributes such as intact protein, reduced protein, released glycan and other assays, the product protein is purified based on Protein A affinity purification using Andrew+ Robots.
II. Titer Determination using Protein A Affinity Chromatography
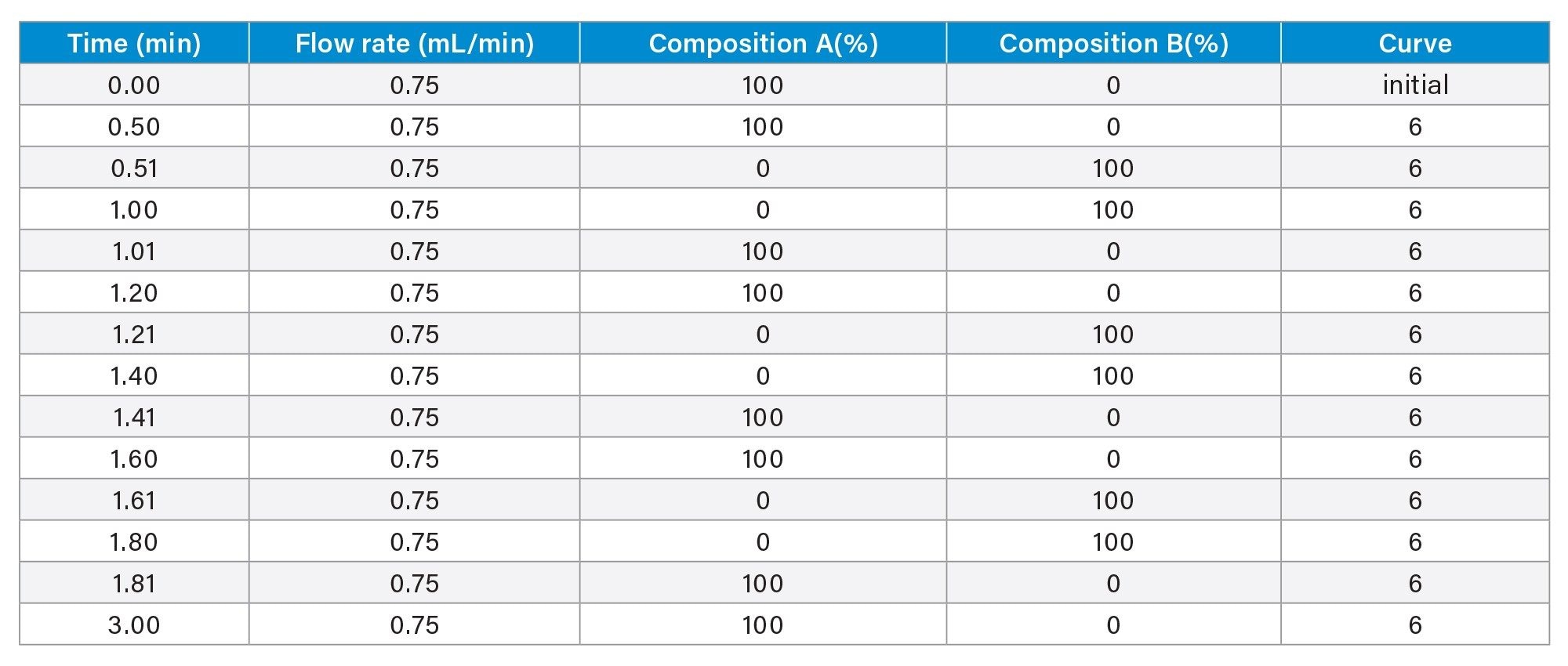
- Protein titer measurement is based on Protein A affinity chromatography on an ACQUITY Premier LC-UV System. The run time is 3 minutes. Samples are centrifuge- and filter-clarified HCCF solutions without further preparation.
LC Method Conditions I
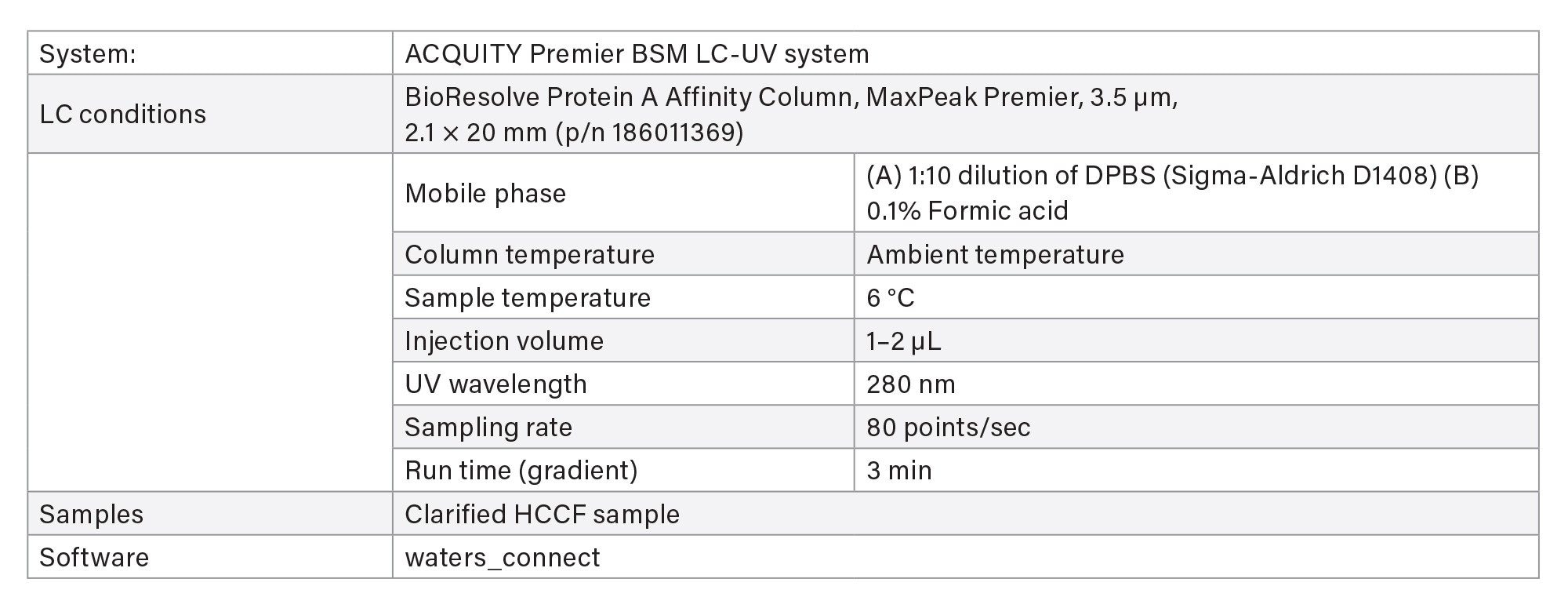
Gradient Table
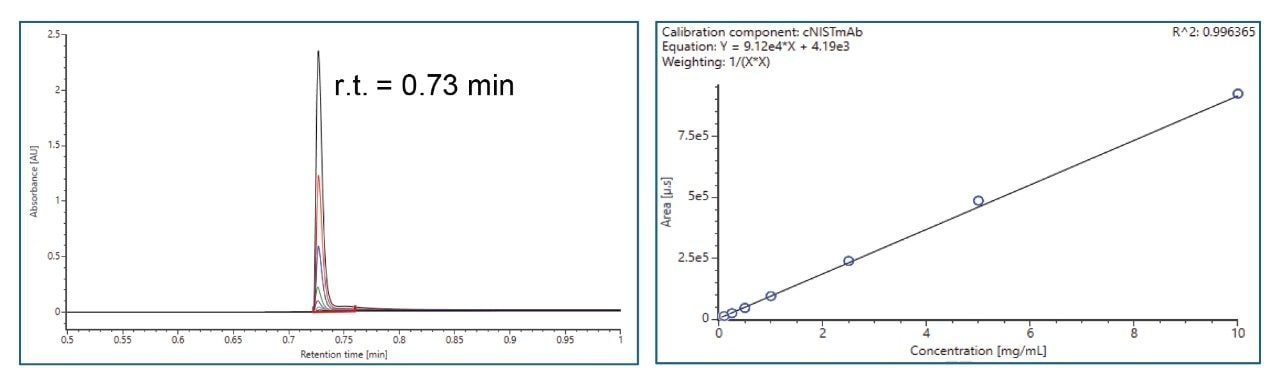
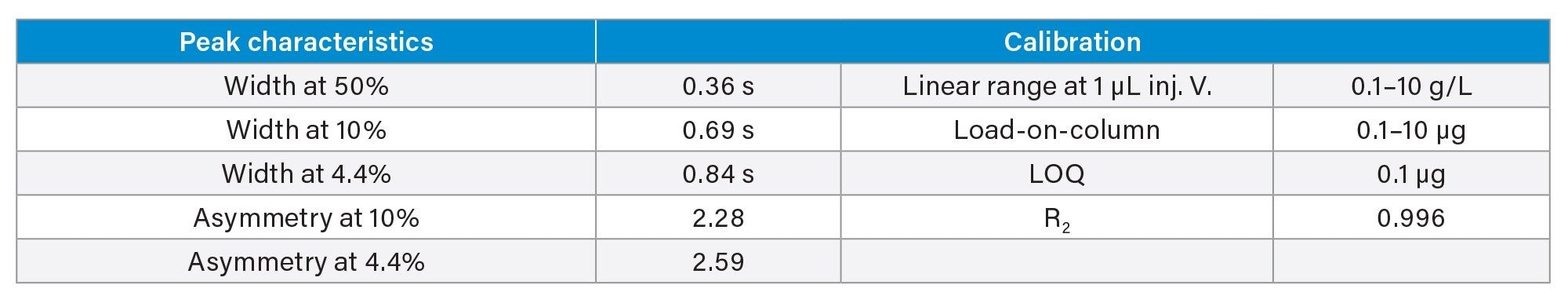
III. Cell Culture Media and Metabolites Analysis
- Spent culture media and metabolites analyses are based on reversed-phase chromatography using Waters ACQUITY Premier HSS T3 Column on BioAccord System. Samples are centrifuge- and filter-clarified HCCF solution, diluted 20 to greater than 400 times using 0.1% formic acid (FA). Run time is 9 minutes.
- The method includes 220+ compounds library and guided workflow for ease of data processing/reporting.
LC-MS Method Conditions I
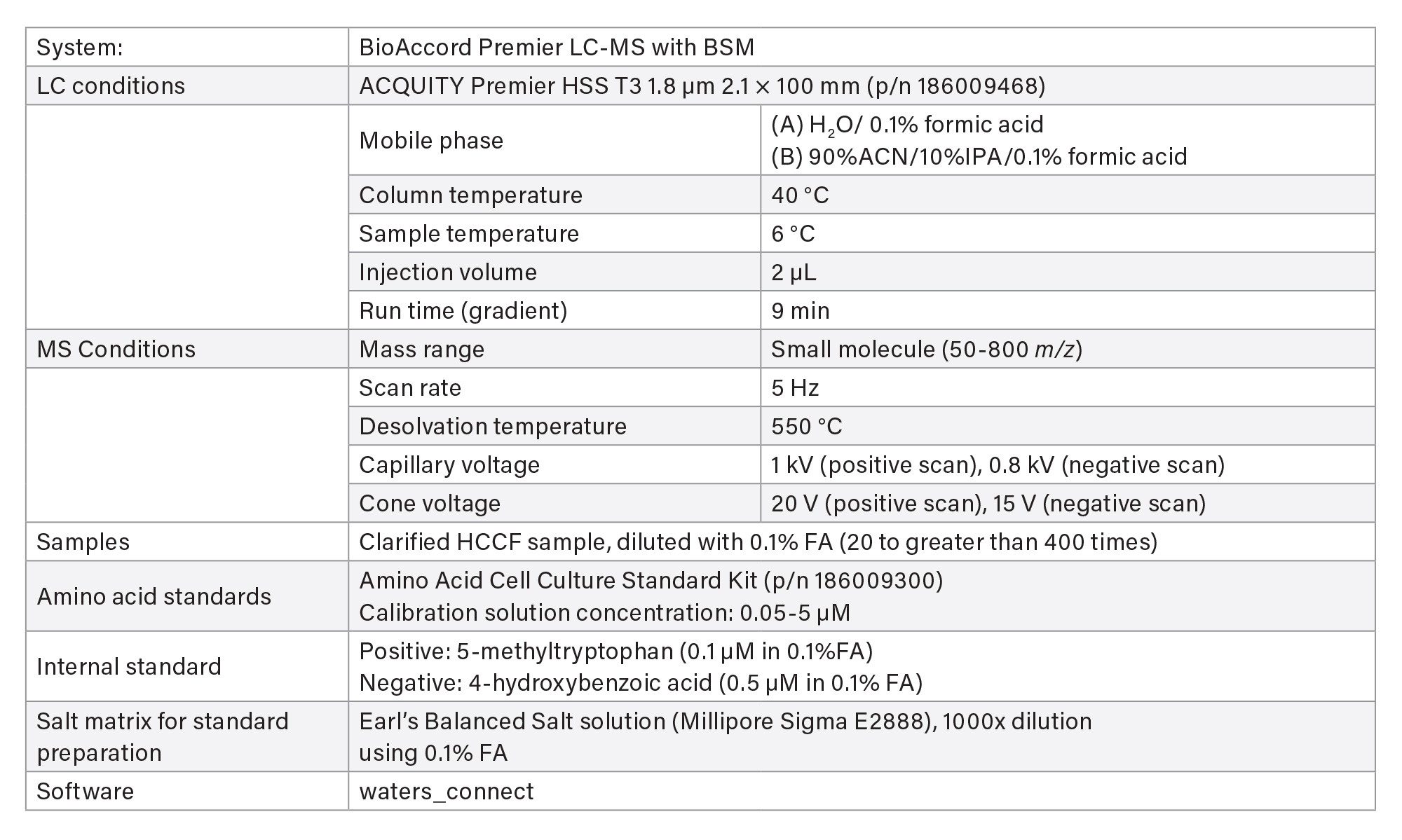
Gradient Table
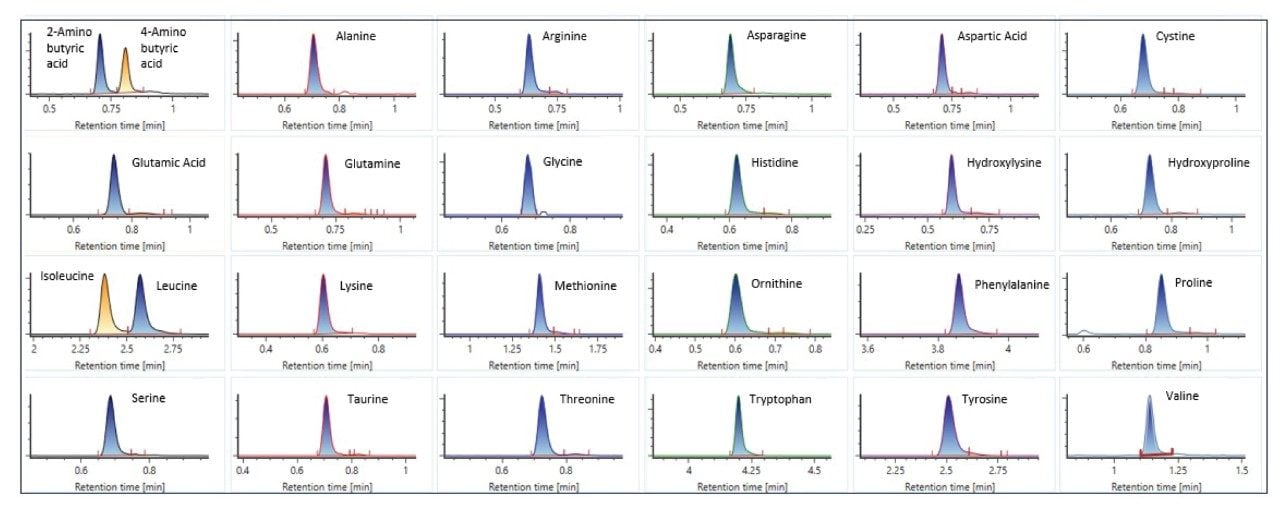
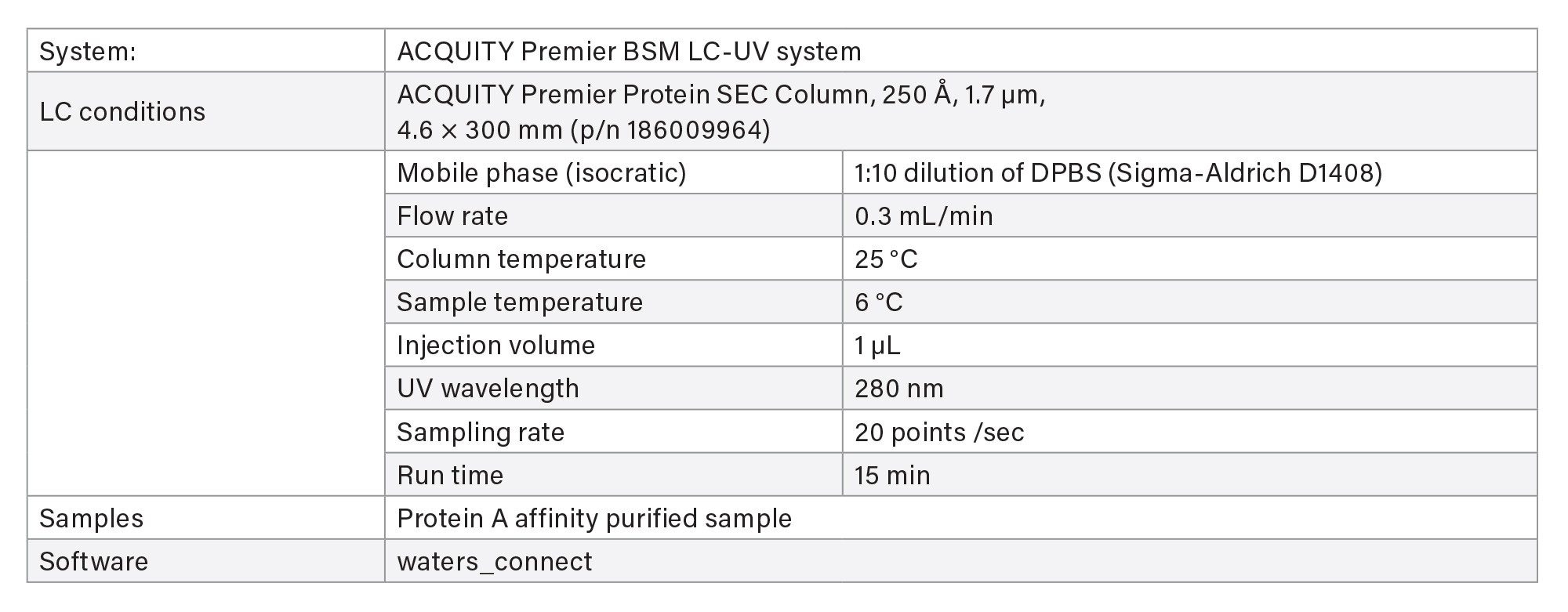
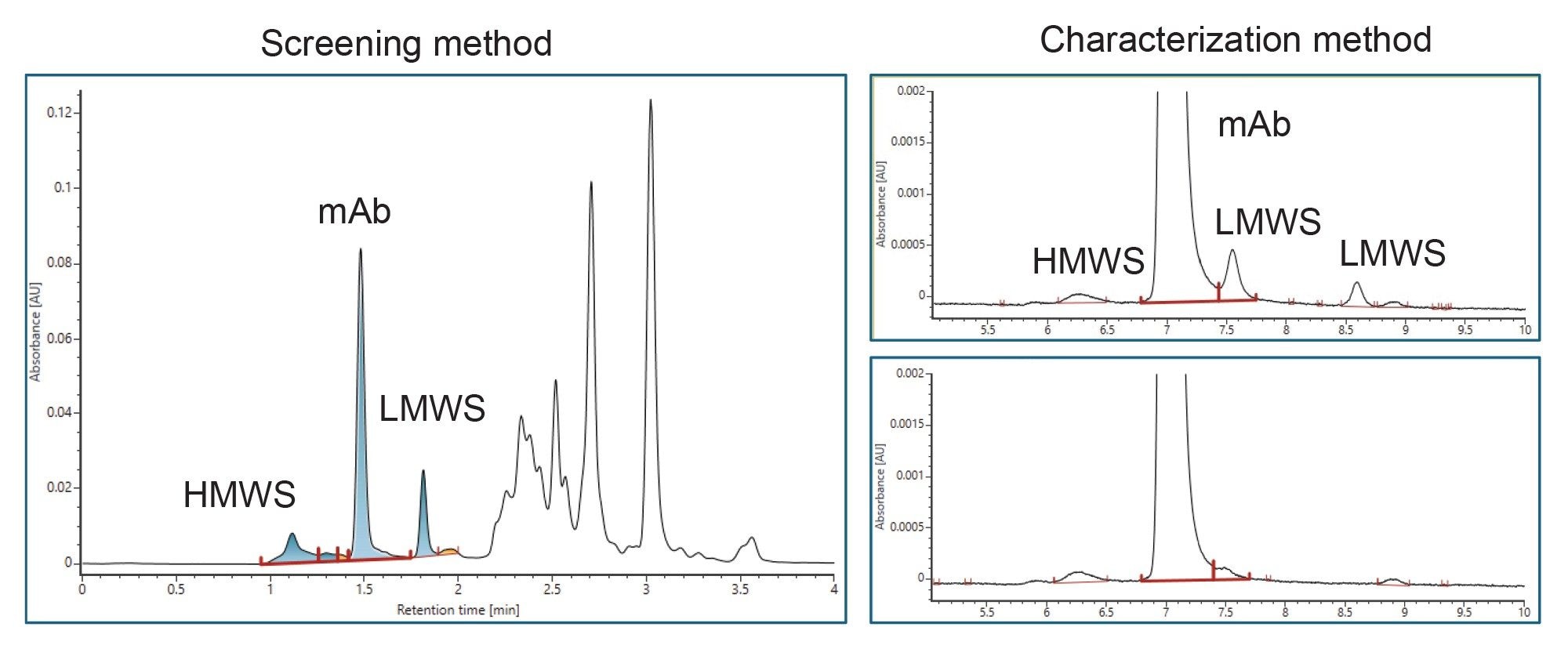
IV. Aggregation/Fragmentation Measurement Based on SEC Column
Two methods are available for aggregate and fragment measurement using size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) on ACQUITY Premier LC-UV System.
- The screening method is used for rapid throughput with 4 minutes run time.
- The characterization method uses a longer column for purified final product when separation of fragment impurities is important.
LC-UV Conditions - Screening
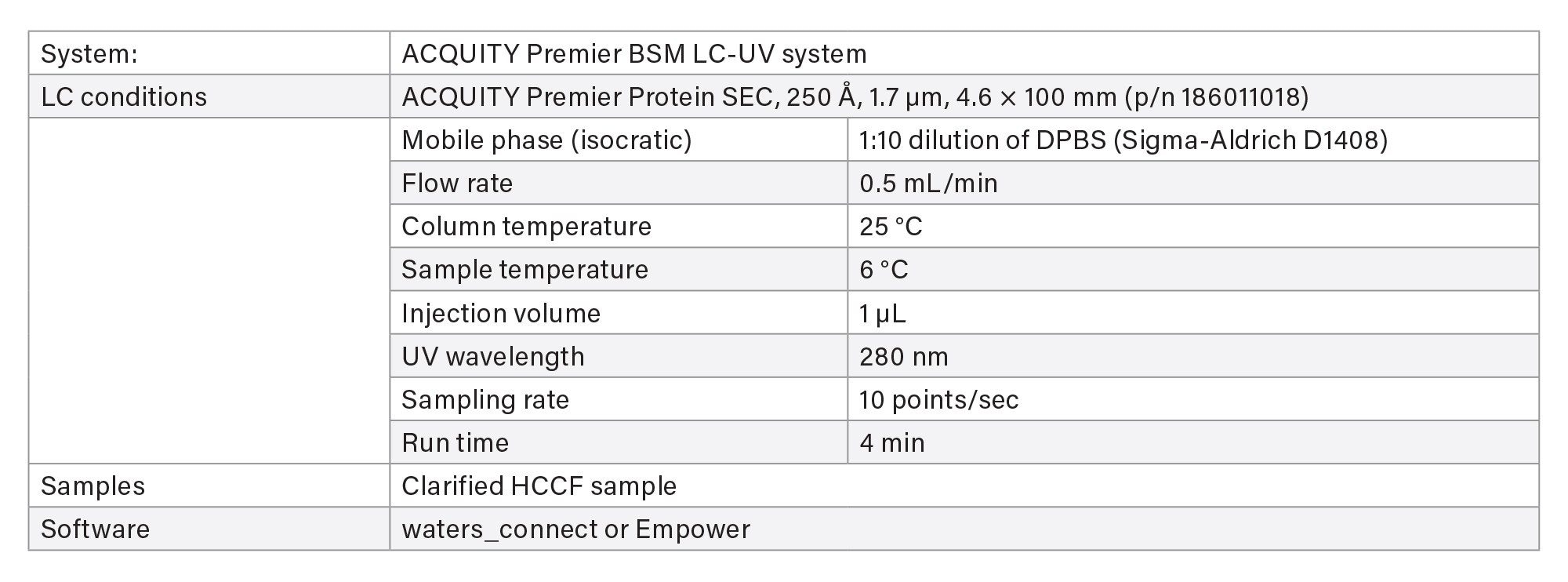
LC-UV Conditions - Characterization
V. Intact Protein Analysis
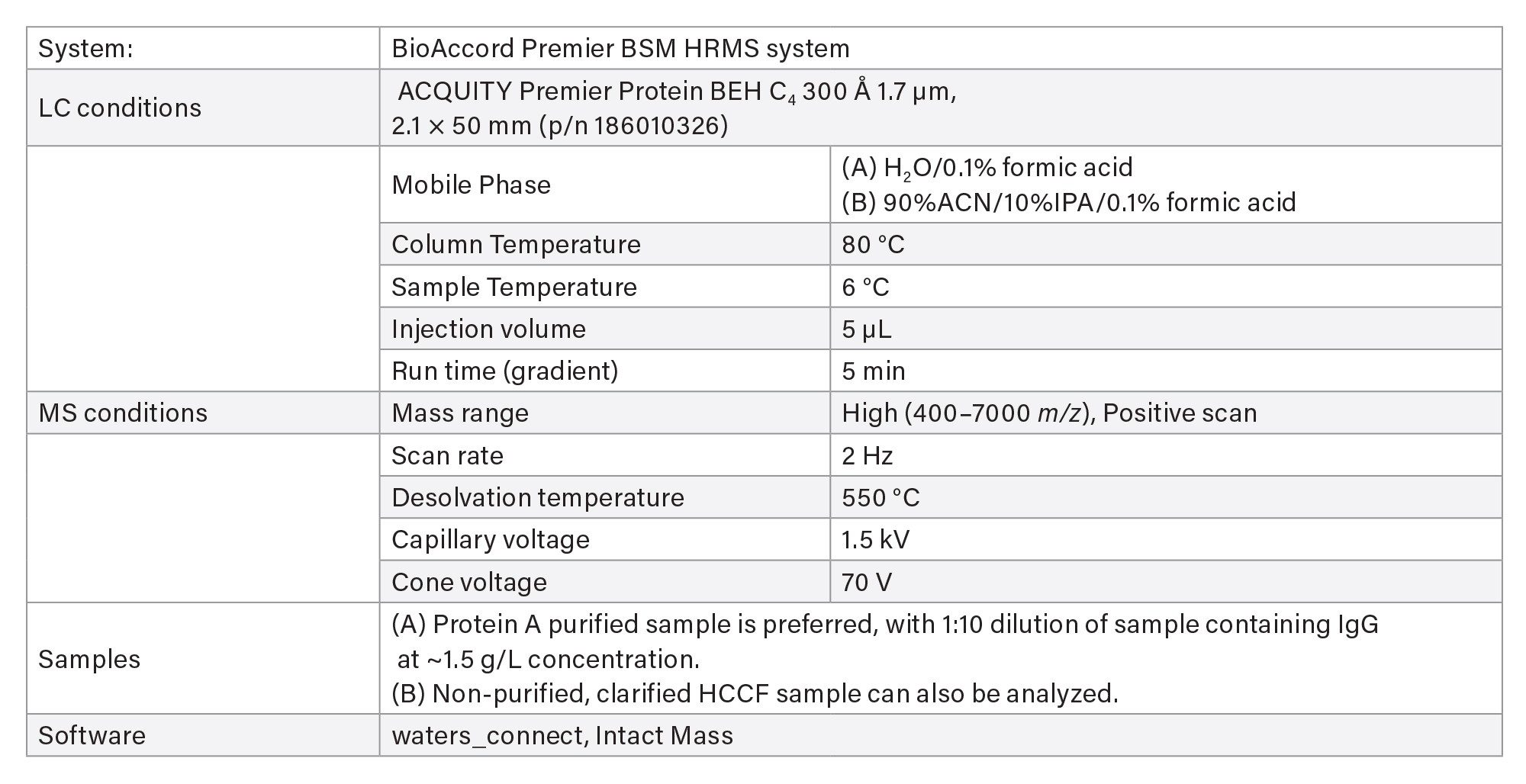
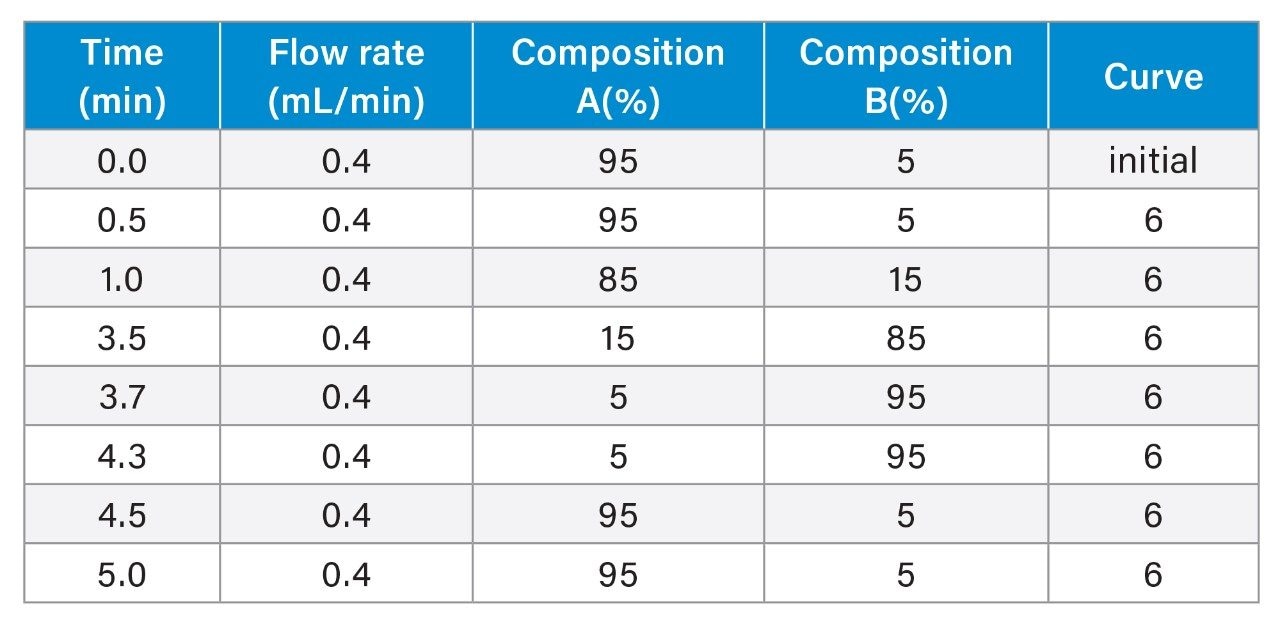
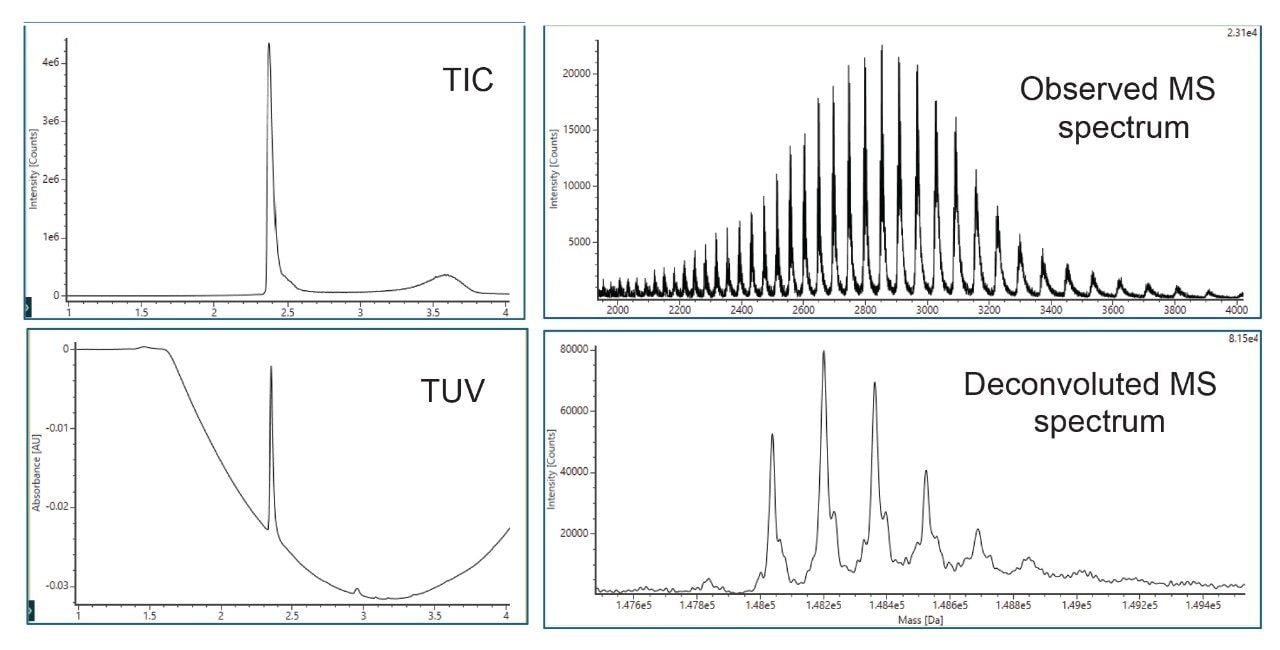
- Intact protein analysis uses ACQUITY Premier Protein BEH C4 Column on BioAccord HRMS System. Run time is 5 minutes.
- Clarified HCCF media samples or Protein A purified samples using Andrew+ Pipetting Robot.
LC-MS Method Conditions II (Protein Analysis)
Gradient Table
VI. Reduced Protein Analysis via LC and HC (DTT Reduction)
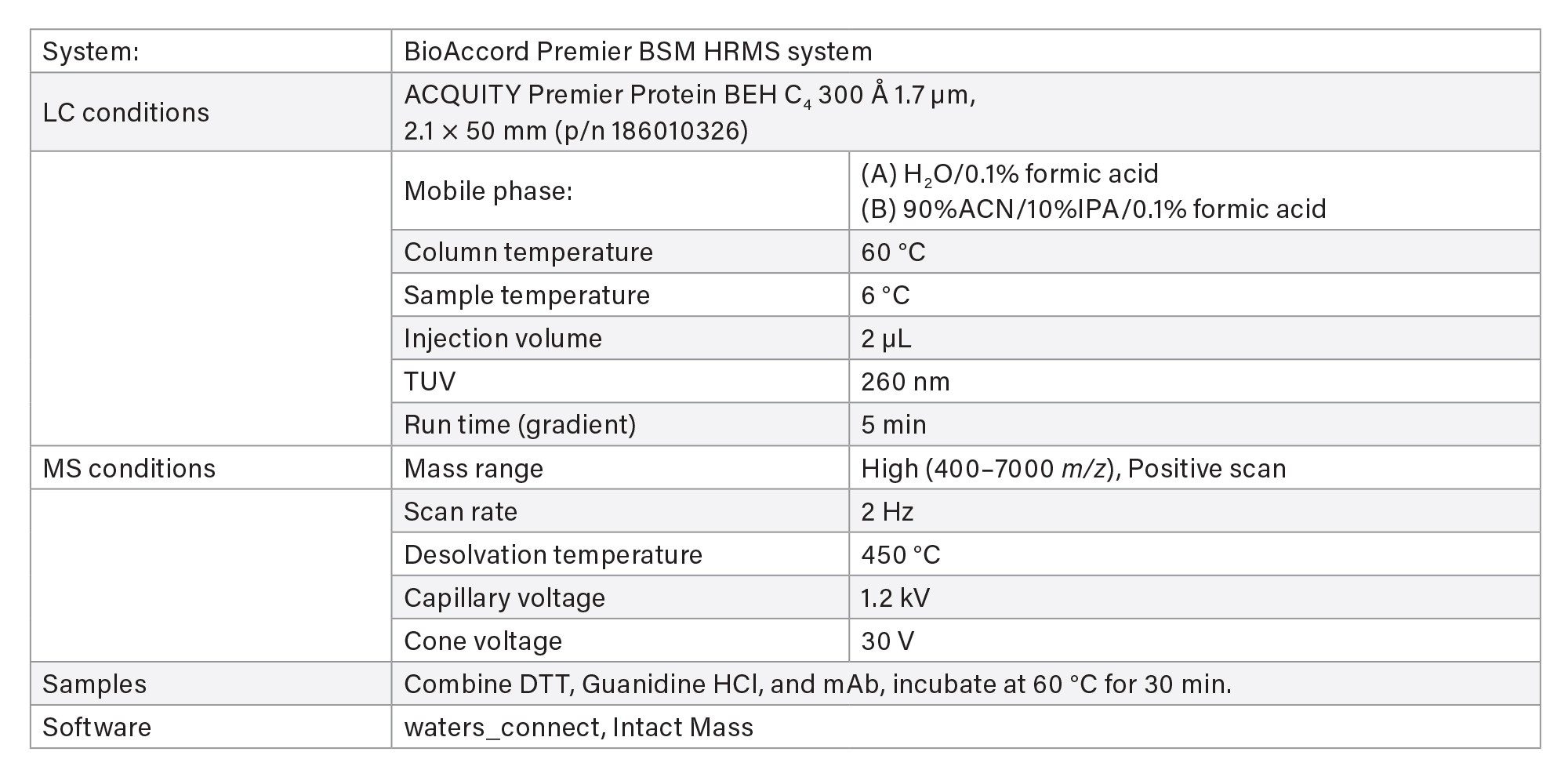
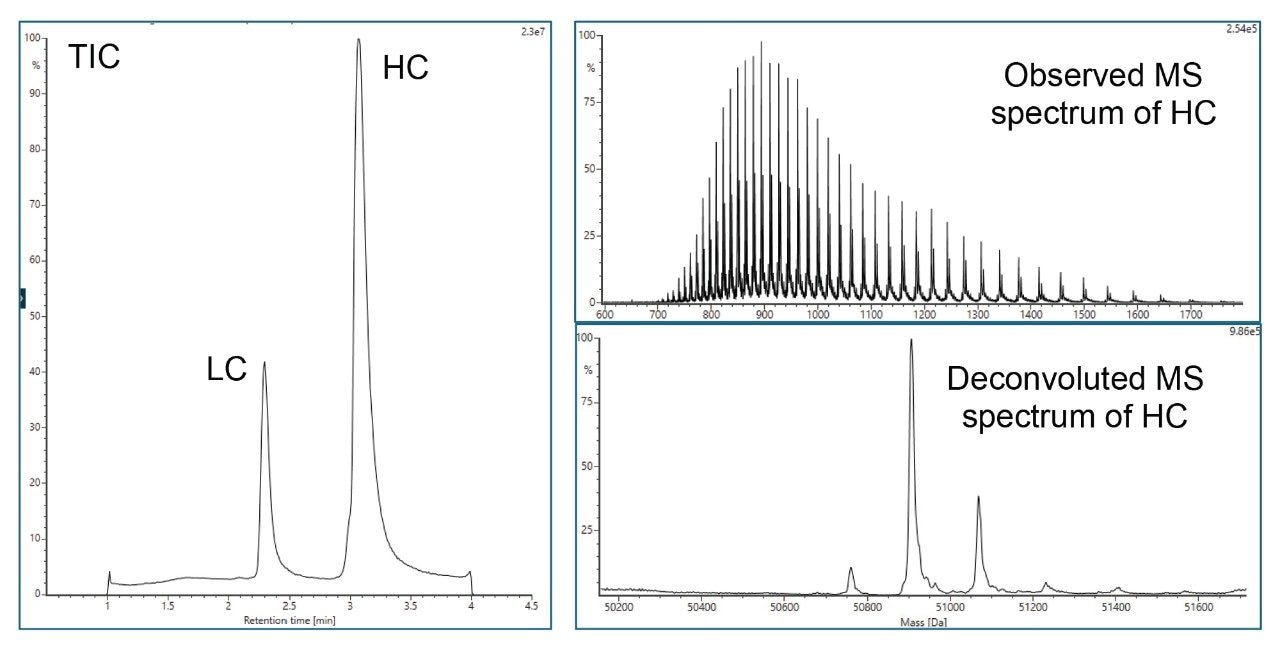
- Reduced protein analysis uses ACQUITY Premier Protein BEH C4 Column on BioAccord System. Run time is 5 minutes.
- Sample is prepared using guanidine denaturation and DTT reduction to produce light chain (LC) and heavy chain (HC).
LC-MS Method Conditions III (DTT Reduction)
Gradient Table
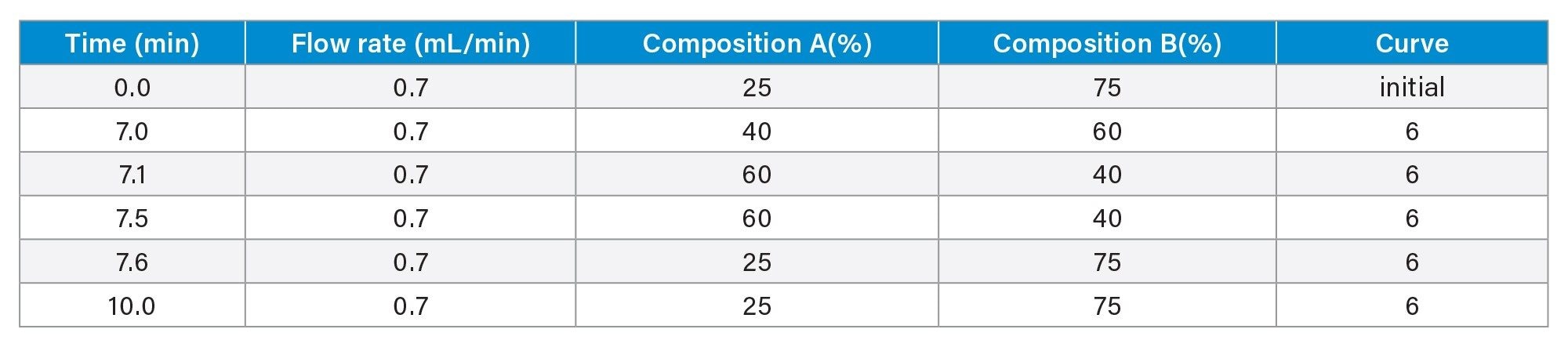
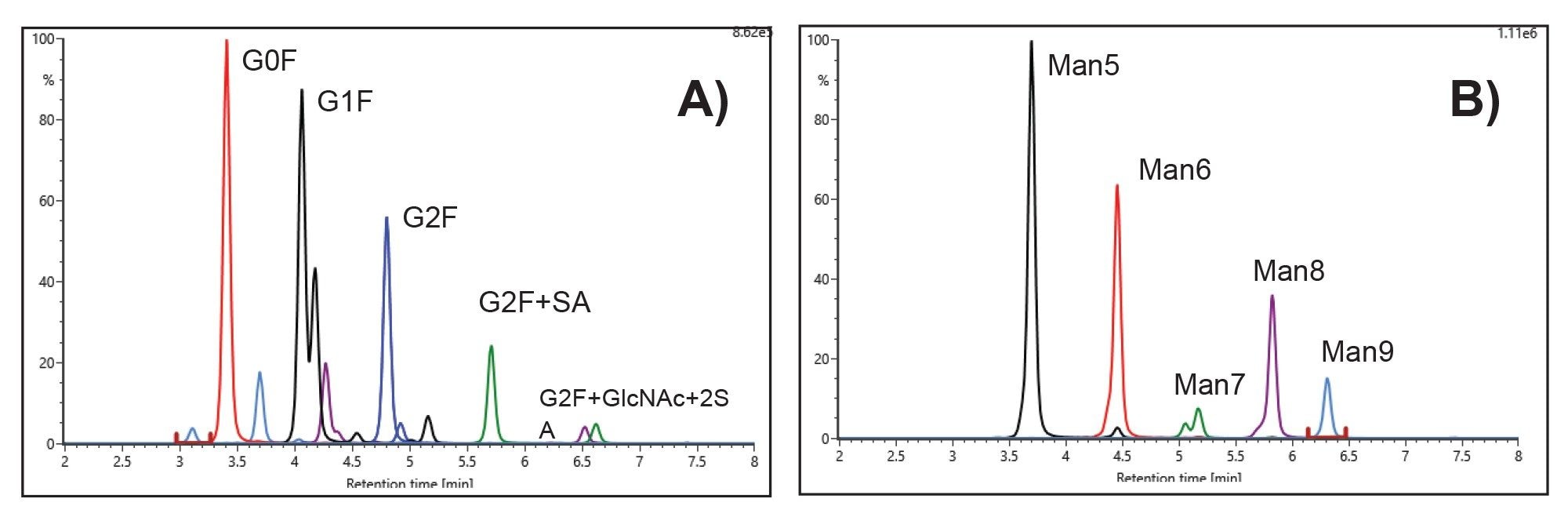
VII Released Glycan Analysis
- Released glycan analysis is based on HILIC chromatography using BioAccord System. Run time is 10 minutes. Samples are prepared using Waters GlycoWorks™ RapiFluor-MS™ released N-Glycan Kits using Andrew+ Pipetting Robots.
LC-MS Method Conditions IV (Glycan Analysis)
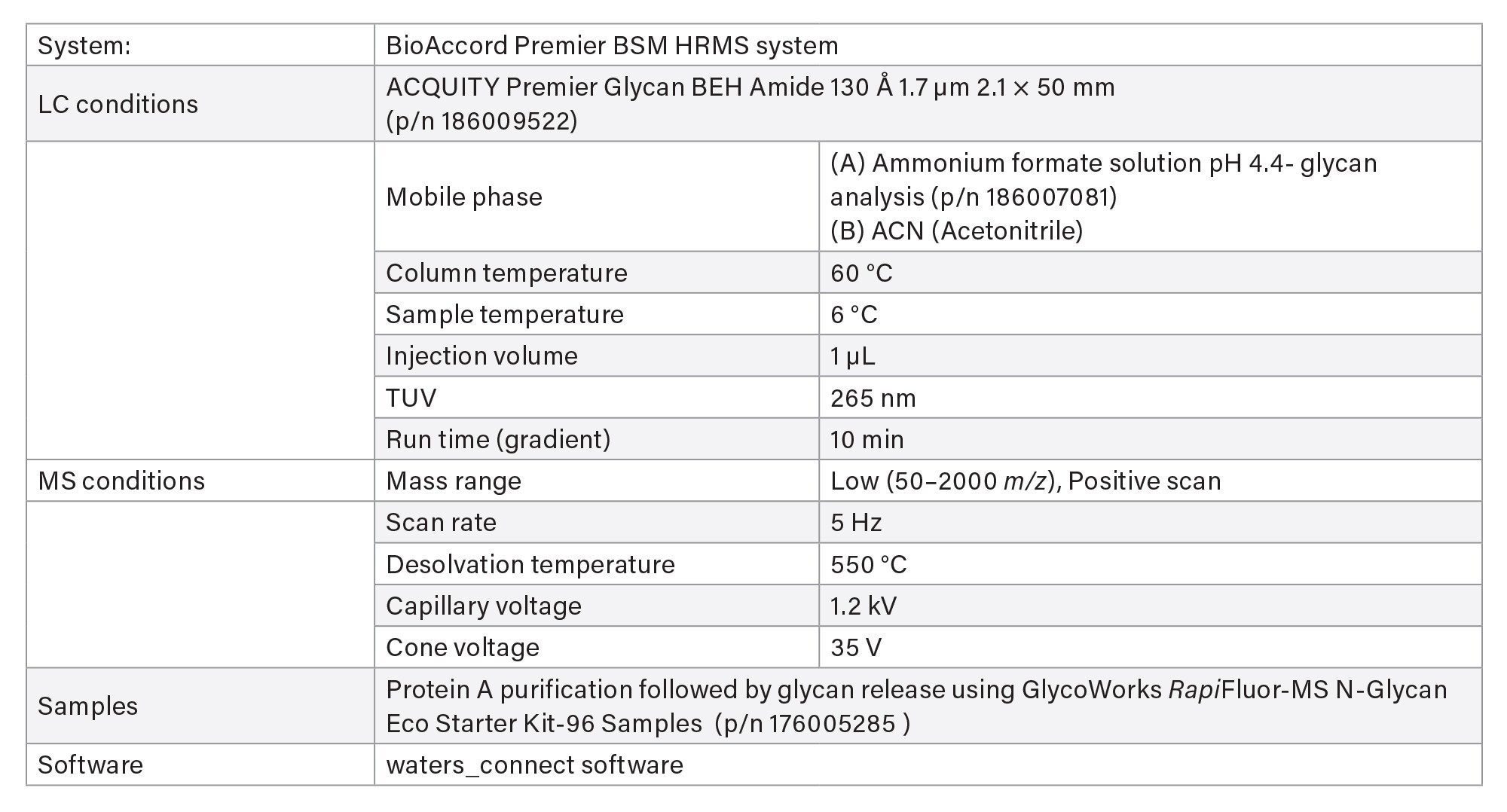
Gradient Table
VIII. Protein A Purification using Andrew+ Robot Supply Guide
- Dominos, supplies, and consumables used in Protein A purification on Andrew+ Robot is summarized in tables below. More detailed information on the purification can be found in Waters application note “Analytical Scale 96-well Protein A Affinity Resin-Based Purification using Andrew+ Automation Robot Supporting Upstream Bioprocessing”.
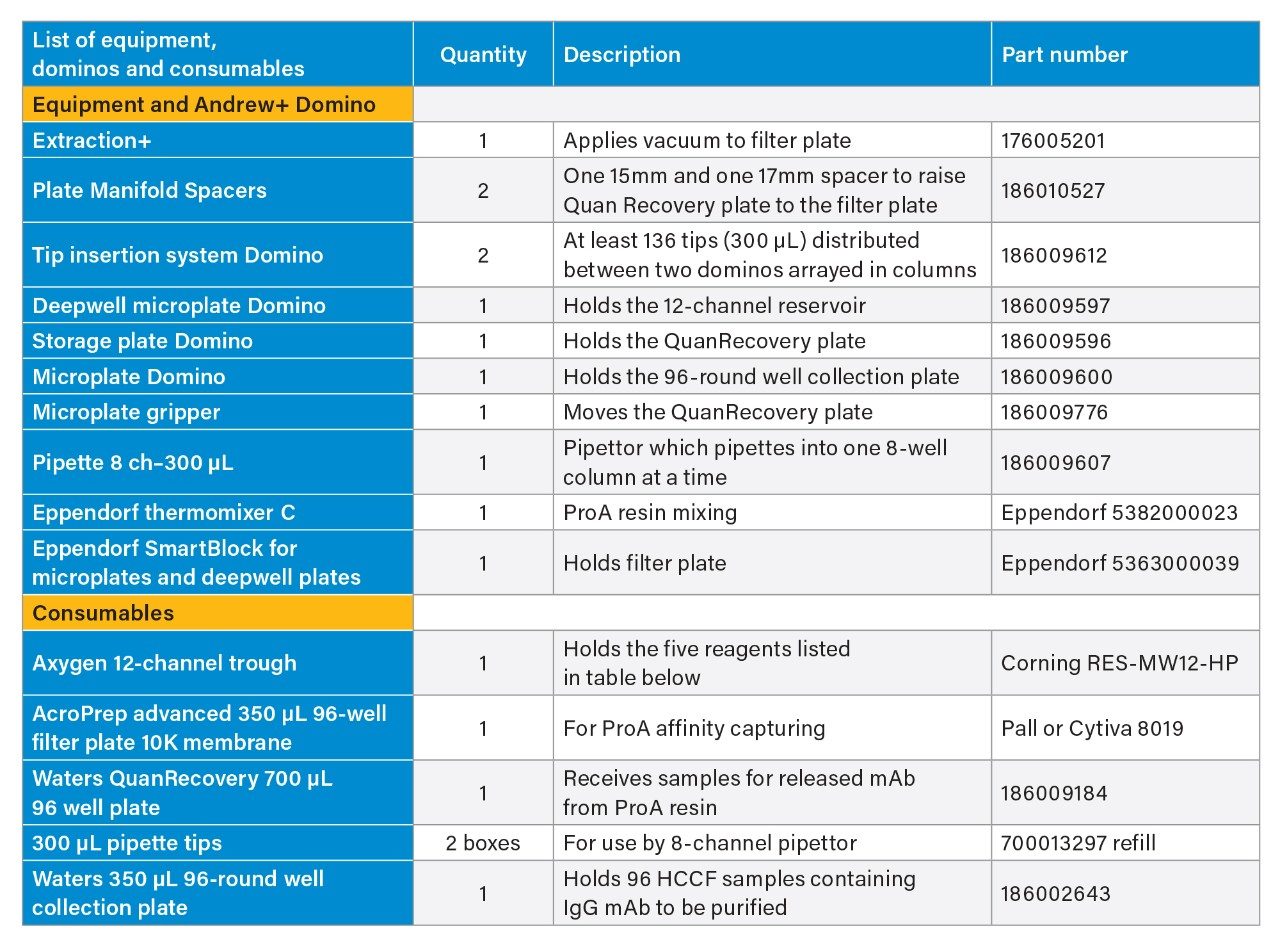
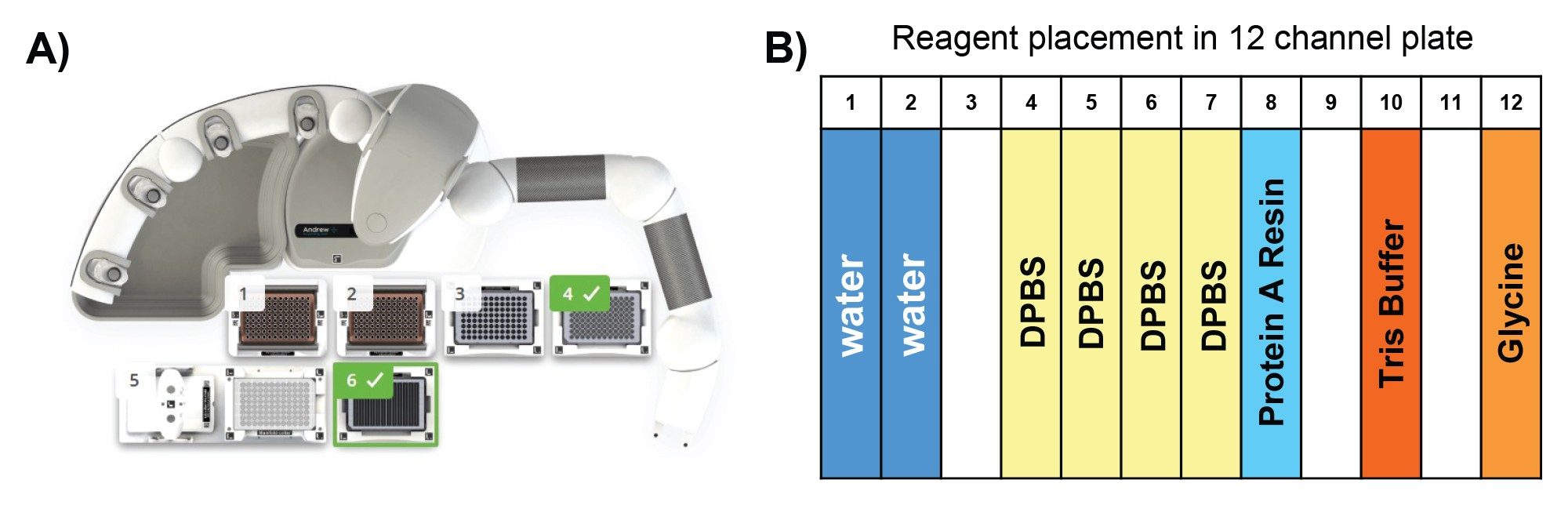
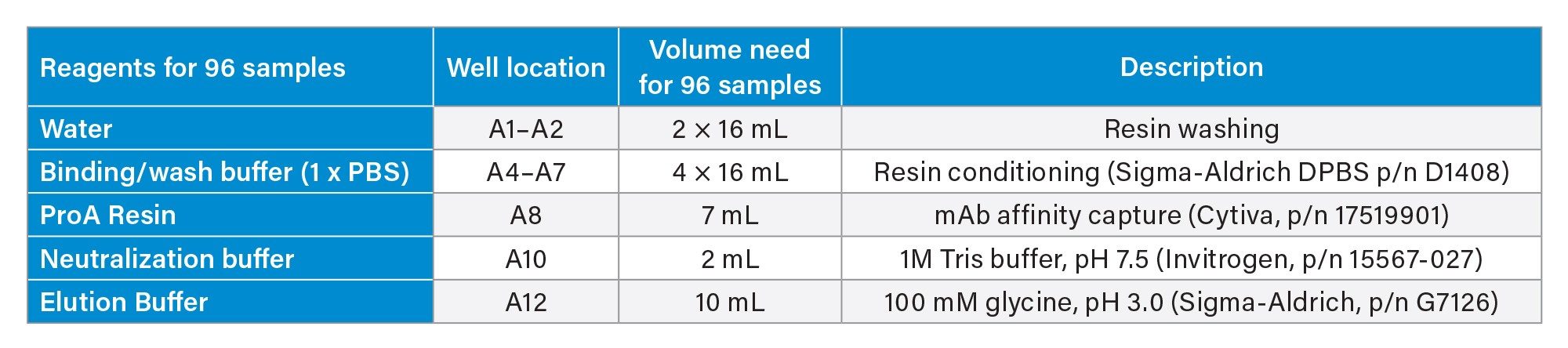
Reagents and their preparation for Protein A purification on Andrew+ Robot.
- Binding/wash buffer: Source Millipore Sigma 10x DPBS, dilute to 1x DPBS using H2O.
- ProA resin: The resin comes as 50% resin in 20% ethanol: Follow Cytiva’s instruction, centrifuge at 1000 g for 3 minutes, replace supernatant with 400 mM NaCl in 20% ethanol to 50% resin level. Further dilute with 1xDPBS to 25% resin as working solution. Thoroughly mix prior to transfer to reagent trough. After each use, mark the liquid level on the tube. In next use, if liquid level is reduced due to evaporation, fill to mark with 20% ethanol.
- Elution buffer: 100 mM glycine, pH adjusted to 3.0
- Neutralization buffer: 1M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5
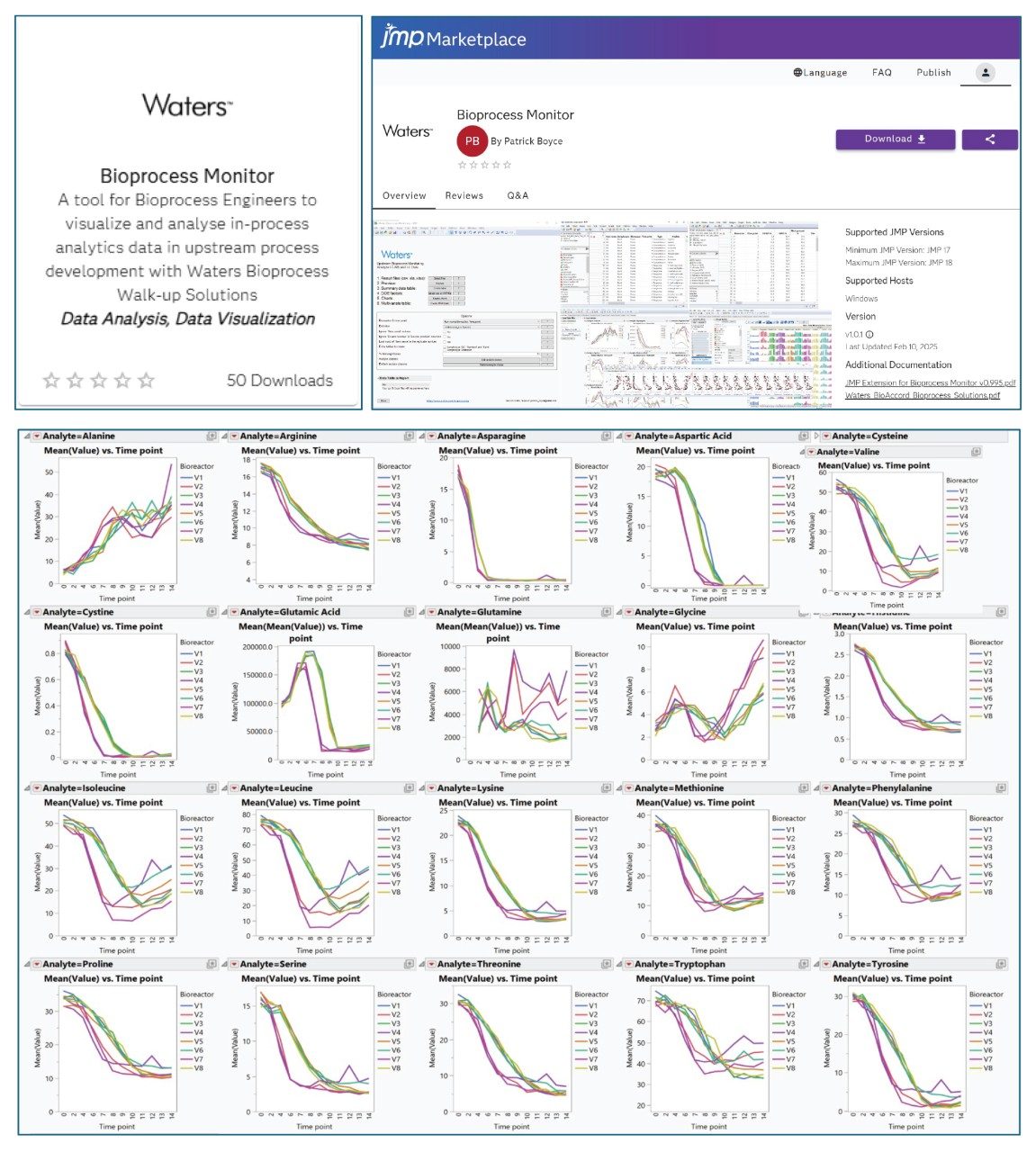
IX. JMP Add-in for Data Visualization and Analysis
- In JMP marketplace place, there is a Waters add-in available for download, free-of-charge. The add-in enables data import, organize and display based on analyte class or biotransformation pathways. One example is shown below displaying overlaid plot of amino acids in 8 bioreactors over 14 days of incubation.
References
- Titer determination based on Protein A affinity chromatography
—BioResolve Protein A Affinity Columns Care & Use Manual (p/n: 720008817)
—Lowering Quantitation Limits for mAb Titer Measurements Using Small Volume 3.5 µm Particle-Size Protein-A Affinity Columns (p/n: 720008775) - Aggregation/fragmentation analysis
—ACQUITY Premier Protein SEC 250 A, 1.7 uM columns Use and Care Manual (p/n: 720007477) - Cell culture and metabolites analysis
—Monitoring Nutrients and Metabolites in Spent Cell Culture Media for Bioprocess Development Using the BioAccord LC-MS System with ACQUITY Premier (p/n: 720007359)
—Introducing a Rapid Throughput LC-MS Method for Cell Culture Media Nutrient and Metabolite Analysis Supporting Upstream Bioprocessing (p/n: 720008170) - Intact protein analysis
—ACQUITY UPLC and ACQUITY Premier Protein BEH C4, 300 Å Columns Care and Use Manual (p/n: 715001870) - Released glycan analysis
—GlycoWorks RapiFluo-MS N-Glycan Kit—24 Sample Care and Use Manual (p/n: 715004903)
—Rapid Preparation of Released N Glycans for HILIC Analysis Using a Labeling Reagent that Facilitates Sensitive Fluorescence and ESI-MS Detection, Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5401−5409 DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00758 - Protein A purification
—Analytical Scale 96-well Protein A Affinity Resin-Based Purification using Andrew+ Automation Robot Supporting Upstream Bioprocessing, Waters application note 720009002
—Automated High-Throughput Analytical-Scale Monoclonal Antibody Purification Using Production-Scale Protein A Affinity Chromatography Resin, Waters application note 720007861. - JMP data visualization, MVA analysis
—Transforming BioAccord LC-MS Quality Attribute & Cell Culture Analysis with JMP Workflows (in layout)
720008953, August 2025