As noted earlier, various equipment exists specifically to assist in the hydrolysis of samples. Regardless of the instrumentation, there are usually three different hydrolysis protocols: acid hydrolysis, used to determine the total protein composition; acid hydrolysis following performic acid oxidation, required to measure sulfur-containing amino acids such as cysteine and methionine; and alkaline hydrolysis, used to assess tryptophan recovery. While traditional equipment for sample hydrolysis often involves a time-consuming process, instrumentation for microwave hydrolysis can significantly speed up things. Implementation of microwave hydrolysis for all three protocols results in improved control of hydrolysis conditions with better accuracy, reproducibility, speed, and robustness.

Using microwave technology, the CEM Discover SP Microwave Reaction System (CEM Corporation 3100 Smith Farm Road Matthews, NC 28104) (Figure 7) can hydrolyze proteins and peptides in preparation for amino acid analysis in just 15 minutes. As illustrated in Figure 8, direct application of microwave energy and use of integrated IR temperature sensors allow for rapid heating and maintenance of the set temperature for each sample. In situ stirring ensures even heat distribution through the sample, and post-reaction quenching cools the sample in seconds.
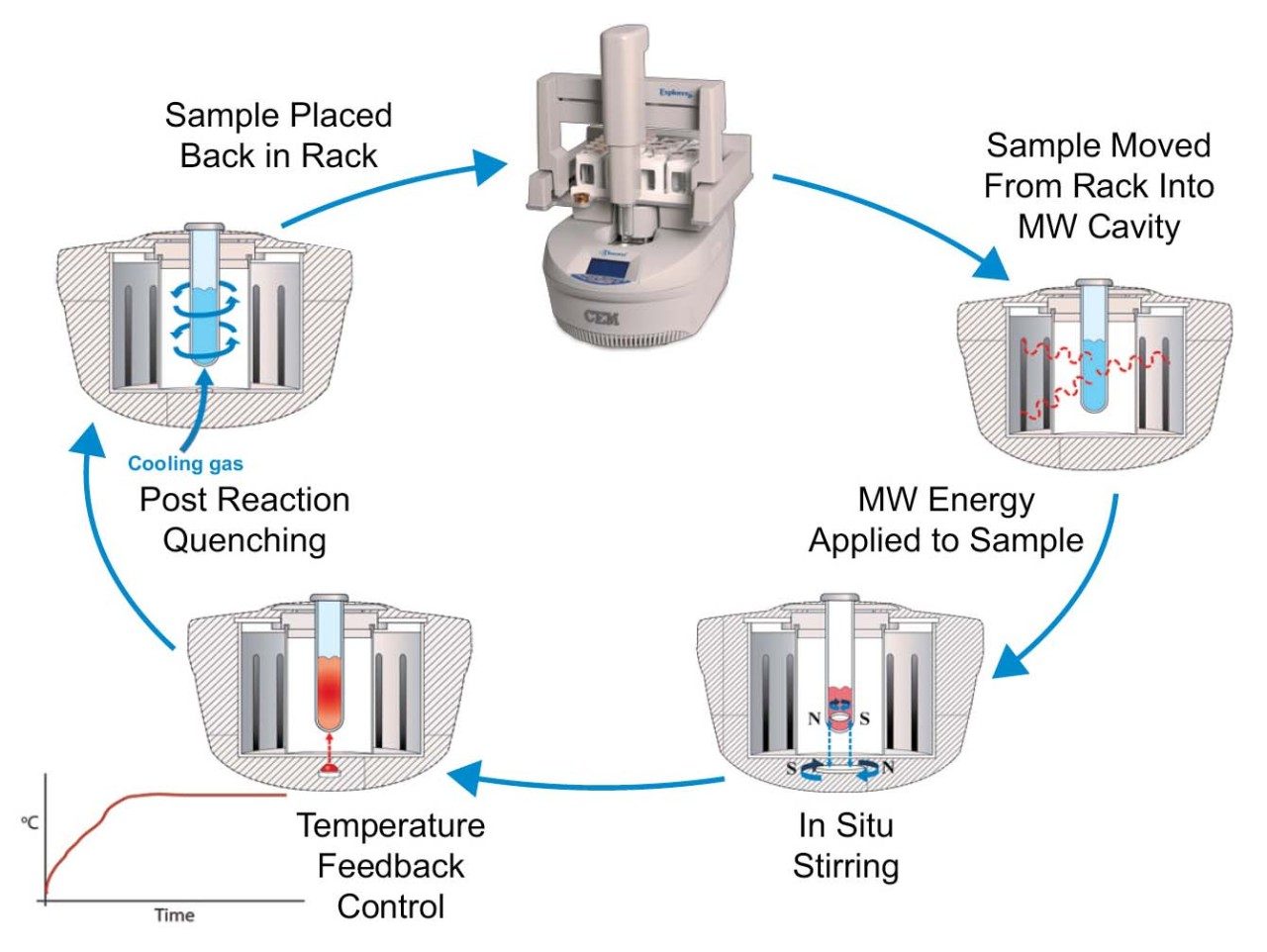
The following section outlines system setup and operation. For further information, contact CEM Corporation or refer to the system manual.
Option 1
Option 1: 50–300 mg sample
Option 1: 50–300 mg sample
The temperature, time and power settings are dependent of the types of samples being hydrolyzed. It's important to maintain the microwave to be functioning all of the way through the procedure. This can require some experimentation by the user to best optimize their samples using this technique.
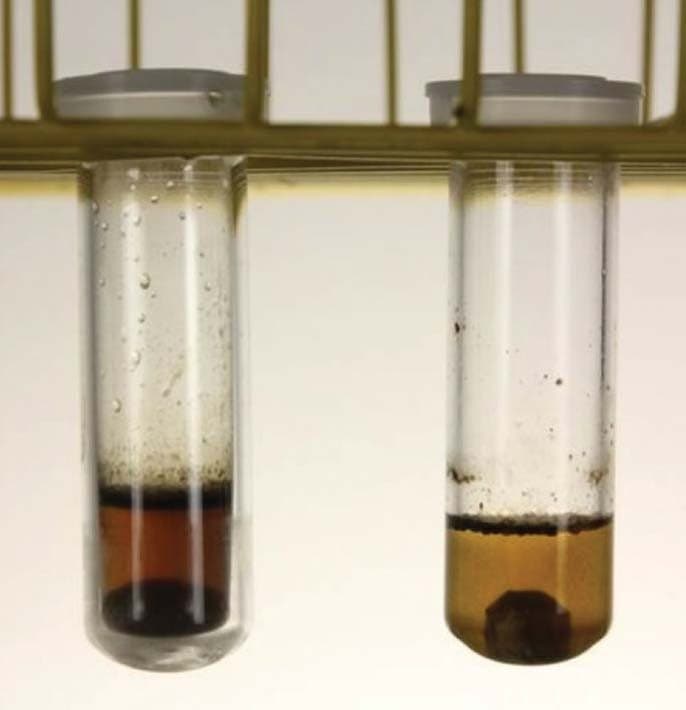
It is recommended that you use the correct sample size, volume, and vessels in the procedures described earlier. These factors are critical to the success of the hydrolysis. Some components of the sample will remain in the solid phase after hydrolysis, and they typically turn black during the process, as shown in Figure 9. This occurrence is normal; the amino acids will be in solution. Please direct all questions related to use of CEM equipment to CEM Corporation via molecular.support@cem.com or by calling 1-704-821-7015 and requesting the CEM Molecular Sample Preparation Team.

Comprehensive Guide to Hydrolysis and Analysis of Amino Acids
Hydrolysis of Purified Proteins and Peptides
Hydrolysis of Food and Feed Samples
Operation of the Eldex Hydrolysis/Derivatization Workstation for Liquid- and Vapor-Phase Hydrolysis
Operation of the CEM Discover SP Microwave Reaction System for Amino Acid Hydrolysis
Derivatization of Amino Acids Using Waters AccQ•Tag Chemistry